
You see electronic tags transforming asset tracking in 2025 with real-time, automated monitoring powered by technology like RFID, Bluetooth, and IoT. Businesses in Esl Retail, manufacturing, and healthcare now rely on Electronic Shelf Labels and electronic shelf price tags for rapid updates and data-driven decisions. The ESL Gateway AP connects ESL Price Tag systems to cloud platforms, enabling instant pricing and inventory control.
| Metric/Aspect | Data/Insight |
|---|---|
| Global Asset Tag Market Value | $2.5 billion (2025) |
| Asset Tracking Market Size | $28.93 billion (2025) |
The Rise of Electronic Tags in Asset Tracking
Key Drivers of Change in 2025
Demand for Real-Time Data
You now operate in a world where instant information is essential. Real-time data drives your decisions, especially when you manage valuable assets across multiple locations. Electronic tags provide you with immediate visibility, allowing you to track assets as they move and monitor their condition without delay. This shift to real-time monitoring helps you prevent losses, respond quickly to issues, and optimize your operations.
- Real-time visibility and efficiency have become critical drivers for adopting RFID and similar technology in 2025.
- Enhanced security features let you monitor sensitive assets and prevent unauthorized access.
- Integration with emerging technology, such as IoT and AI, supports smarter automation and predictive analytics.
- Improved durability and energy efficiency make electronic tags reliable, even in harsh environments.
- Cost-effectiveness compared to other tracking methods encourages you to choose electronic tags for your business.
Growth of IoT and Smart Devices
You see the rapid expansion of IoT and smart devices transforming asset tracking. These devices connect seamlessly with electronic tags, creating a network that delivers continuous updates and insights. As technology advances, you benefit from scalable and customizable solutions that adapt to your specific industry needs. The integration of electronic tags with cloud-based platforms and lifecycle management tools gives you comprehensive control over your assets.
Shifting from Manual to Automated Tracking
Limitations of Traditional Methods
Manual asset tracking often relies on spreadsheets or handwritten logs. You face challenges such as errors, lost records, and slow updates. These limitations can lead to costly mistakes and inefficient processes. The following table highlights the differences between manual and automated tracking:
| Challenge with Manual Tracking | Improvement with Automated Asset Tracking |
|---|---|
| Reliance on manual logs and spreadsheets, prone to errors | Automated asset tracking system with real-time updates |
| Difficulty monitoring shelf-life and expiration dates | Automated alerts for low stock and expiration monitoring |
| Slow and inaccurate check-in/out processes | Streamlined, user-friendly check-in/out interface |
| Lack of centralized asset visibility | Full control and real-time location tracking of assets |
Benefits of Automation
When you switch to automated asset tracking, you gain several advantages. Automated systems use technology like RFID, BLE, and IoT sensors to replace manual processes. You reduce human error, save time, and ensure your asset information stays current. Automated tracking also supports scalability, allowing you to expand your operations without losing control. You experience improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and the ability to manage assets across multiple locations with ease.
Note: Organizations that adopted automated asset tracking reported significant savings and near elimination of time-consuming inventory audits. You can expect similar results as you embrace new technology in your asset management strategy.
What Are Electronic Tags and Their Core Technologies?
Definition and Core Functions
Electronic tags serve as the backbone of modern asset tracking. You use these devices to identify, monitor, and manage assets automatically. The core functions of electronic tags include unique identification and wireless communication. These features allow you to track items without manual intervention, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
Unique Identification
You rely on electronic tags to assign a permanent, tamper-proof identity to each asset. RFID tags, for example, use radio frequency signals to store and transmit unique codes. This technology ensures that every item in your inventory has a distinct digital fingerprint. You can attach tags using methods such as ear tags, injectable glass-encapsulated tags, or oral bolus, depending on the asset type.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Automatic, permanent, and tamper-proof identification using radio frequency signals. |
| Tag Types | Passive (powered by reader), Active (battery-powered), Semi-passive (battery-assisted). |
| Attachment Methods | Ear tags, injectable glass-encapsulated tags, oral bolus. |
| Applications | Inventory control, product recall management, animal identification, food traceability. |
Wireless Communication
Wireless communication is essential for real-time asset tracking. RFID tags transmit data to readers using radio waves. You can collect information from multiple tags simultaneously, even without direct line of sight. This capability supports automated workflows and alerts, making your asset management process faster and more reliable.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| RFID System Components | Identifier (tag), reader (activating/reading device), software for data management. |
| Tag Power Types | Active, Passive, Semi-passive. |
| Operational Challenges | Electromagnetic interference, signal direction, protocol standardization. |
| Technical Considerations | Antenna orientation, read range, reader size limitations. |
Types of Electronic Tags
You have access to several types of electronic tags, each designed for specific asset tracking needs. Understanding their features helps you choose the right solution for your business.
RFID Tags
RFID tags dominate asset tracking due to their durability and automation capabilities. You can select passive RFID tags for low-cost, long-life applications or active RFID tags for extended range and real-time data transmission. RFID technology supports encrypted communication and simultaneous reading of multiple tags.
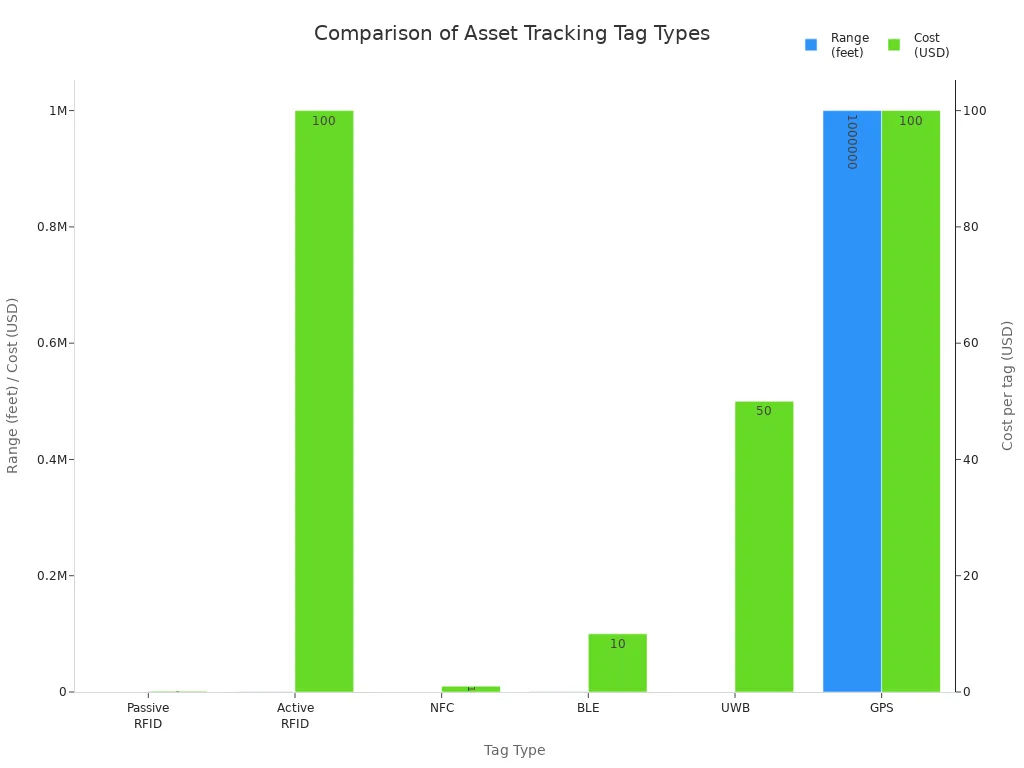
| Tag Type | Power Source | Range | Data Capacity | Cost | Key Features | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive RFID | Powered by reader | Short (up to a few feet) | Limited (several KB) | Very low | Multiple tag reading, durable, no line of sight | Inventory management, industrial |
| Active RFID | Battery-powered | Long (hundreds of feet) | Moderate | Higher | Real-time transmission, longer range | Outdoor asset tracking |
NFC Tags
NFC tags offer secure, short-range communication. You use them for contactless payments and limited asset tracking. NFC technology works well with smartphones, providing two-way data exchange.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Tags
BLE tags provide medium-range tracking with low power consumption. You benefit from location tracking and theft prevention alerts. BLE technology is ideal for indoor environments and construction sites.
| Feature | RFID | BLE |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Powered by reader | Battery-powered |
| Range | Shorter | Up to 300 feet |
| Data Storage | Limited | Larger (several MB) |
| Security | Encrypted | Secure protocols |
| Cost | Lower tag cost | Moderate |
GPS-Enabled Tags
GPS tags track assets globally. You use them for vehicle tracking and outdoor asset management. GPS technology consumes more power and costs more but provides unmatched location accuracy.
Electronic Shelf Price Tags
Electronic shelf price tags have transformed retail and logistics. You update prices and inventory instantly across multiple locations. This technology integrates with ESL Gateway AP systems, enabling cloud-based management and automated stock replenishment. You enhance customer experience and streamline operations with electronic shelf price tags.
Tip: Choose electronic shelf price tags for rapid price updates and real-time inventory control in retail environments.
How Electronic Tag Systems Work in Asset Tracking
Understanding how electronic tag systems operate gives you a clear advantage in asset management. These systems combine advanced technology, robust hardware, and powerful software to deliver real-time tracking and automation. You can break down the process into three main areas: system components, data flow and communication, and integration with digital platforms.
System Components
Tags and Transponders
You start with the core of any asset tracking system: the tags and transponders. These devices attach directly to your assets. In rfid systems, you use passive or active tags. Passive tags draw power from the reader’s radio waves, while active tags use a built-in battery for longer range. NFC tags and labels also play a role, especially for short-range identification. You can attach these tags to equipment, inventory, or even vehicles.
- NFC tags and labels: Passive devices that store asset data.
- rfid tags: Available in passive, active, and semi-passive forms for different use cases.
- Wearables and POS terminals: Devices that interact with tags for tracking and management.
These tags store unique identification codes. When you scan them, they transmit data to the next component in the system.
Readers and Gateways
Readers and gateways form the bridge between your assets and your management platform. rfid readers emit radio frequency signals to activate tags and collect their data. You can use handheld readers, fixed readers at entry points, or even mobile devices with NFC capability. Gateways aggregate data from multiple readers and send it to your central system.
- rfid readers: Devices that power and read tags.
- NFC-enabled smartphones and tablets: Useful for quick scans and updates.
- Gateways: Collect data from readers and transmit it to cloud platforms.
You benefit from real-time data collection and the ability to monitor assets across large facilities.
Cloud Platforms and Software
Cloud platforms and software solutions process and store the data collected by readers. You access dashboards, analytics, and alerts through web or mobile interfaces. These platforms use advanced technology to automate workflows, generate reports, and support decision-making.
| Component | Function | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Platform | Centralizes and analyzes asset data | Inventory management |
| Management Software | Provides dashboards and reporting tools | Real-time asset tracking |
| Mobile App | Enables remote monitoring and notifications | Field equipment tracking |
You gain centralized control and visibility over your entire asset inventory.
Data Flow and Communication
Tag Activation and Data Transmission
The data flow in an electronic tag system begins when a reader activates a tag. In rfid and NFC systems, the reader emits a radiofrequency field. This field powers passive tags, which then transmit their stored information back to the reader. Active tags use their own battery to send data over greater distances. This two-way communication ensures you receive accurate, up-to-date information about each asset.
You see this process in action when you scan a pallet with an rfid reader. The tags respond instantly, sending asset details to your system. This seamless exchange supports real-time tracking and rapid updates.
Data Collection and Processing
Once the reader collects data from the tags, the information moves to your software platform. Data flow diagrams (DFDs) help you visualize this process. You can see how data travels from the tag, through the reader, and into your cloud database. The system processes this data, updating asset locations, statuses, and conditions.
A Technical Design Document (TDD) often outlines these processes in detail. It describes how each component communicates, the protocols used, and the steps for data validation. You rely on these documents to ensure your system operates efficiently and securely.
Note: Data flow diagrams and technical documentation help you understand and optimize the movement of information within your asset tracking system.
Integration with Digital Platforms
ERP and Inventory Systems
You maximize the value of your asset tracking by integrating rfid and other tagging systems with your ERP and inventory management platforms. Middleware or APIs connect your hardware to your software, enabling real-time data exchange. When you scan an asset, the system updates your inventory records instantly. This integration eliminates data silos and provides unified access across departments.
- Middleware bridges legacy ERP systems and modern rfid technology.
- APIs enable seamless synchronization and data sharing.
- Automated updates improve accuracy and reduce manual entry.
You support workflows in procurement, sales, and inventory management, enhancing operational efficiency.
Mobile and Web Dashboards
Mobile and web dashboards give you instant access to asset data from anywhere. You monitor inventory, receive alerts, and generate reports using intuitive interfaces. These dashboards display real-time updates from your rfid and NFC systems, helping you make informed decisions quickly.
- Mobile apps allow field staff to scan and update assets on the go.
- Web dashboards provide centralized control and analytics.
- Automated alerts notify you of low stock, asset movement, or maintenance needs.
You benefit from improved visibility, faster response times, and better planning.
Tip: Integrating your electronic tag system with digital platforms ensures you always have accurate, up-to-date information at your fingertips.
Technologies Powering Electronic Tags and RFID
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
Radio-frequency identification stands at the core of modern asset tracking. You rely on this technology to automate identification, monitor assets, and streamline operations. RFID systems consist of tags, readers, and software that work together to deliver real-time visibility and control.
Passive vs. Active RFID
You choose between passive and active RFID tags based on your asset tracking needs. Passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source. They draw energy from the reader’s radio waves, making them compact and cost-effective. You use passive tags for item-level tracking, inventory management, and access control. Active RFID tags contain a battery, allowing them to transmit signals over longer distances. You deploy active tags for real-time tracking of large assets, vehicles, and personnel in dynamic environments.
Tip: Select passive RFID tags for high-volume, low-cost applications. Use active RFID tags when you need extended range and continuous monitoring.
Here is a comparison of RFID tag types:
| RFID Tag Type | Power Source | Read Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active RFID | Battery-powered | Long (up to 100 m) | Real-time tracking of large assets, vehicle tracking, personnel monitoring |
| Passive RFID | Powered by reader signal | Short (up to ~50 m) | Item-level tracking, inventory management, access control |
| Battery-Assisted Passive (BAP) | Battery-assisted, no transmitter | Medium (improved over passive) | Enhanced read range and data transfer without active transmission |
RFID tags include an antenna and an integrated circuit. Active tags use their battery to send signals, which enables longer read ranges and real-time tracking. Passive tags reflect signals back to the reader, resulting in shorter ranges but lower costs and smaller size.
Frequency Ranges and Use Cases
You select the frequency range of RFID tags to match your environment and application. Each frequency offers unique benefits:
- Low-Frequency (LF) RFID (30 KHz to 300 KHz): You use LF RFID for short-range applications. It works well in environments with metal or liquid interference, such as access control and livestock tracking.
- High-Frequency (HF) RFID (3 to 30 MHz): HF RFID provides medium read range and higher memory capacity. You deploy it for electronic ticketing, payment systems, and library media tracking. NFC is a subset of HF RFID, designed for very short-range communication.
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID (300 MHz to 3 GHz): UHF RFID delivers long read ranges and fast data transfer. You use it for retail inventory tracking, pharmaceuticals, and large-scale asset management.
RFID asset tracking solutions combine hardware and software. You benefit from real-time maps, asset status updates, and customizable reporting. RFID systems automate asset identification, reduce operational costs, and improve control. You see applications in logistics, transportation, agriculture, healthcare, IT, manufacturing, education, and energy.
- RFID readers scan multiple tags simultaneously without line-of-sight.
- Software modules provide live maps, analytics, and integration with ERP or WMS systems.
- Alerts and notifications help you respond to unusual events quickly.
Near Field Communication (NFC)
NFC technology enhances asset tracking with secure, short-range communication. You use NFC tags to improve accuracy and efficiency, eliminating manual data entry errors and enabling precise location tracking.
Short-Range Applications
You attach NFC tags to assets for instant visibility into their status and location. NFC works well in secured areas, allowing you to scan tagged items with NFC-enabled devices. You support inventory management and prevent theft or misplacement. NFC tags are flexible and can be attached to various asset types, meeting diverse asset management needs.
- Real-time monitoring with NFC provides instant updates.
- You benefit from higher accuracy compared to manual methods.
- NFC tags support quick scanning with smartphones and tablets.
NFC offers higher security and convenience than QR codes. You take advantage of widespread smartphone adoption and multi-purpose use, although NFC tags are more costly and harder to embed.
Security Features
You rely on NFC for secure and reliable transactions. Its short-range communication and encrypted data transmission restrict access to authorized personnel only. You protect sensitive asset information and ensure only approved users can interact with tagged items.
Note: NFC’s security features make it ideal for environments where data protection and access control are critical.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy technology brings energy-efficient, scalable asset tracking to your operations. You attach BLE tags to assets for accurate, low-cost monitoring in real time.
Beacon Technology
BLE tags act as beacons, continuously transmitting signals detected by BLE gateways. You relay these signals to cloud platforms for real-time location tracking, especially indoors where GPS is unreliable. BLE’s adaptive range suits both short and medium distances, and its interoperability with standard profiles allows easy integration with existing systems.
- BLE tags are small and battery-powered, lasting years on a single coin battery.
- You deploy BLE systems quickly without complex wiring.
- Real-time location updates on dashboards enable faster asset retrieval and reduced downtime.
BLE technology supports integration with other tracking technologies. You receive customizable alerts and analytics, improving productivity and operational efficiency.
Power Efficiency
You benefit from BLE’s energy efficiency. Devices operate for months or years on small batteries. You configure beacon transmission intervals to balance battery life and detection speed. For example, a beacon transmitting every second at five meters requires about seven seconds of scanning. Shorter intervals reduce scanning time but increase power consumption.
Tip: Adjust BLE beacon settings to optimize battery life and detection speed for your asset tracking needs.
BLE technology reduces loss and theft through real-time geolocation. You improve stock and equipment management, facilitate predictive maintenance, and enhance operational efficiency. BLE is widely applied in Industry 4.0, smart buildings, healthcare, transport, construction, and smart agriculture.
GPS and Satellite Tracking
Outdoor Asset Tracking
You rely on GPS and satellite tracking when you need precise, real-time location data for outdoor assets. This technology gives you global coverage, making it ideal for monitoring vehicles, shipping containers, and heavy equipment across vast distances. You can track assets as they move through remote areas, construction sites, or international shipping routes. GPS receivers in asset tracking devices communicate with satellites orbiting thousands of miles above Earth, providing you with accurate coordinates and movement history.
You use GPS tracking to improve operational efficiency and prevent theft. When you manage a fleet of vehicles or oversee heavy machinery, you receive instant updates on asset location. This capability supports data-driven decision-making and helps you optimize routes, reduce downtime, and respond quickly to incidents. You can combine GPS with rfid tags to enhance asset visibility, especially when assets transition between indoor and outdoor environments.
Tip: Use GPS tracking for high-value assets that require constant monitoring and global reach. Pair GPS with rfid for seamless asset management across different locations.
Limitations and Solutions
You face several challenges when using GPS and satellite tracking. Physical obstacles such as tall buildings, tunnels, and dense forests can block or degrade GPS signals. In urban environments, signals bounce off structures, causing multipath distortion and reducing accuracy. You notice that GPS tracking becomes unreliable indoors or in enclosed spaces, making it less effective for certain asset types.
Continuous GPS operation drains device batteries quickly. You must consider battery life when deploying GPS trackers on mobile or remote assets. The initial setup and operational costs, including hardware purchase and network fees, can be significant. GPS tracking hardware is best suited for expensive outdoor assets, while other technologies may offer better value for smaller items.
To overcome these limitations, you often combine GPS with rfid, Bluetooth, or real-time location systems (RTLS). This hybrid approach allows you to maintain accurate tracking indoors and outdoors. You use rfid for inventory management and indoor asset tracking, switching to GPS when assets move outside. By integrating multiple technologies, you reduce power consumption, improve accuracy, and lower costs.
| Limitation | Impact on Asset Tracking | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Signal obstruction | Reduced accuracy in urban/indoor | Combine GPS with rfid or RTLS |
| High power consumption | Short battery life | Use low-power modes, hybrid tracking systems |
| Setup and operational cost | Expensive for small assets | Deploy GPS for high-value assets only |
Note: You achieve the best results by leveraging GPS for outdoor tracking and rfid for indoor environments, ensuring continuous asset visibility and control.
IoT Connectivity and Cloud Integration
Real-Time Analytics
You transform asset tracking with IoT connectivity and cloud integration. IoT asset tracking systems use sensors and communication modules embedded in assets to collect data on location, condition, and usage. You transmit this data over networks such as cellular, satellite, or Wi-Fi to centralized cloud platforms. These platforms process and analyze the information, turning raw data into actionable insights.
You benefit from real-time analytics that support preventive maintenance, immediate location tracking, and operational efficiency. When you manage assets with rfid tags and IoT sensors, you receive instant alerts about asset movement, environmental changes, or potential issues. Cloud-based analytics help you detect patterns, optimize asset utilization, and make faster decisions. You can integrate rfid data with cloud platforms to automate workflows and generate predictive maintenance alerts.
Callout: Real-time analytics powered by IoT and cloud integration enable you to respond quickly to asset events, reduce downtime, and improve overall productivity.
Scalability
You scale your asset tracking system effortlessly with IoT connectivity and cloud integration. As your business grows, you add new assets, sensors, and tracking devices without major infrastructure changes. Cloud platforms support seamless integration with existing enterprise networks, reducing deployment costs and ensuring operational continuity.
You use rfid and IoT technology to maintain visibility and control over assets in real time. Cloud integration allows you to expand your tracking capabilities across multiple locations and business units. You adapt to changing needs, whether you manage a small warehouse or a global supply chain. IoT asset tracking systems provide flexible connectivity options, including cellular, Bluetooth, and LPWAN, supporting scalable data management.
| Feature | Benefit for Asset Tracking |
|---|---|
| Cloud integration | Centralized control, easy scaling |
| IoT connectivity | Real-time data, flexible expansion |
| rfid technology | Automated tracking, seamless growth |
You ensure your asset tracking system remains future-proof by leveraging rfid, IoT, and cloud technology. This approach supports continuous monitoring, efficient data management, and rapid adaptation to new business requirements.
Tip: Choose asset tracking solutions with robust IoT and cloud integration to support your business growth and maintain operational excellence.
Real-World Applications and Industry Impact of Electronic Tags

Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Inventory Management
You see rfid technology transforming inventory management in manufacturing and supply chain environments. When you deploy rfid tags, you automate tracking and replenishment processes, reducing manual labor and errors. You gain real-time visibility into stock levels, which helps you make lean inventory decisions and maintain product quality. For example, you can use rfid smart labels with cloud-based platforms to automate vendor-managed inventory. This approach ensures you avoid stock-outs and lower operational costs. Walmart and other major manufacturers rely on rfid to maintain accurate stock levels and streamline product lifecycle management.
You benefit from real-time location tracking of deliveries, environment sensing for perishable goods, and fleet management. These capabilities prevent misplaced shipments and ensure smooth production.
Loss Prevention
You reduce losses in your supply chain by integrating rfid tags with IoT systems. You monitor sensitive goods for temperature, humidity, and shock, receiving instant alerts if conditions change. E-paper displays replace traditional labels, allowing you to update information remotely and reduce waste. You improve logistics and fleet management by tracking vehicles and assets, ensuring safety and compliance. Cold chain logistics benefit from e-paper displays and sensors that monitor temperature-sensitive goods, such as pharmaceuticals and fresh food. You also use remote-updatable signage to guide warehouse traffic and communicate safety protocols, enhancing workplace safety.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Equipment Tracking
You improve equipment tracking in healthcare settings by attaching asset tags to mobile hospital equipment. These electronic tags provide real-time location and status data, allowing you to quickly locate devices and reduce time spent searching. You prevent asset hoarding and improve availability for clinical staff. Automated workflows support preventative maintenance and compliance with regulatory requirements. Alerts notify you of equipment status changes, such as PAR-level breaches, ensuring critical equipment remains available for patient care.
- You integrate rfid tags with CMMS to enhance maintenance scheduling and recall procedures.
- BLE-enabled tags support wireless deployments and precise room-level locating.
- Consulting and managed services help you optimize workflow design and system maintenance.
Compliance and Safety
You rely on rfid technology to ensure compliance with healthcare regulations, including FDA UDI. Automated tracking and detailed audit trails safeguard sensitive medical equipment and medications. You reduce loss, theft, and unauthorized access by using rfid solutions that scale across hospitals and clinics. Detailed records log device usage, servicing, and user information, supporting regulatory compliance. You monitor temperature and environmental conditions for sensitive medical assets, ensuring asset integrity. Automated inventory tracking minimizes discrepancies and prevents shortages or overstocking, boosting staff productivity and allowing focus on patient care.
- You integrate rfid tags into secure storage cabinets, access terminals, and management software.
- Authentication methods, such as swipe cards and biometrics, secure equipment check-in/out.
- Management software aggregates data into dashboards for real-time tracking, alerts, and compliance reporting.
Retail and Logistics with Electronic Shelf Price Tags
Automated Stock Replenishment
You transform retail operations by implementing electronic shelf price tags. These tags enable dynamic pricing that responds instantly to demand, competitor pricing, and stock levels. You turn pricing into a live data signal for supply chain decisions, shifting from efficiency-focused to flexibility-focused models. Real-time inventory tracking becomes critical to avoid stockouts or overstocking due to rapid sales changes triggered by a price update. You integrate electronic shelf price tags with automation and forecasting tools, allowing seamless data exchange between retailers and suppliers. This integration supports automated reordering and improves product availability.
- You reduce operational costs by eliminating expenses related to paper labels and manual labor for price updates.
- Electronic shelf price tags contribute to sustainability goals through reduced paper waste and energy-efficient designs.
Customer Experience Enhancement
You enhance customer engagement by using electronic shelf price tags to display additional product information and enable omnichannel communication. You improve price accuracy, building customer trust and reducing disputes. Integration with inventory systems allows real-time stock alerts, automated reordering, and timely product availability. Electronic shelf price tags facilitate an omnichannel experience by displaying stock levels, online competitor prices, product reviews, and enabling ordering via QR codes. You improve customer satisfaction and loyalty by integrating physical and online commerce.
Tip: You can use electronic shelf price tags to support dynamic pricing strategies, improve operational efficiency, and deliver a seamless shopping experience.
Construction and Heavy Equipment
Asset Utilization
You face constant pressure to maximize the use of every asset on your construction site. Electronic tags, especially RFID, give you real-time visibility into the location and status of tools, vehicles, and heavy machinery. When you attach passive RFID tags to hand tools, you track them efficiently across large sites. Active RFID tags, equipped with GPS, let you monitor high-value equipment and receive instant alerts if assets leave designated zones.
A leading construction firm in New York City installed RFID tags on all tools and equipment, placing readers throughout the site. This setup allowed you to locate tools quickly, reducing search time and operational costs. You also improve safety by ensuring workers have access to the right equipment when needed.
“The investment in RFID technology paid off exceedingly, not only in safeguarding our materials but also in boosting our operational efficiency,” said the project manager of the Chicago construction site.
You benefit from features such as:
- Real-time alerts when equipment moves outside approved areas, reducing downtime.
- Tool crib tracking that restricts equipment use to authorized personnel.
- Audit trails that show who used equipment and when, increasing accountability.
- Usage pattern monitoring that helps you optimize asset allocation and schedule maintenance.
Theft Reduction
Theft remains a major challenge in construction. You can address this risk by deploying tamper-proof RFID tags on valuable assets. These tags send automatic alerts if someone tries to remove or alter them. You also use active RFID tags to track heavy machinery and receive notifications if equipment leaves the site unexpectedly.
Consider the following real-world outcomes:
| Project | Problem | Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York Construction Co | Frequent equipment theft | RFID asset tags | Significant theft reduction and asset recovery |
| Chicago Construction | Material theft | Anti-theft RFID tags | Minimized theft and improved inventory tracking |
You see that RFID technology not only deters theft but also supports asset recovery and improves inventory tracking.
Transportation and Toll Payment
Automated Toll Collection
You streamline toll collection by using electronic tags on vehicles. These tags enable fast, contactless payments, reducing wait times and congestion. You benefit from enhanced security through encryption and authentication, which lowers the risk of theft and fraud. Automated toll systems also collect valuable data, helping you manage traffic and adjust pricing based on demand.
Key advantages include:
- Reduced cash handling and lower operating costs.
- Usage-based fees that encourage carpooling and public transport.
- Flexible pricing to influence traffic patterns and reduce congestion.
- Environmental benefits from less idling and fewer emissions.
You also gain scalability and easy integration with existing infrastructure, making it simple to expand coverage as your needs grow.
Fleet Tracking
You use electronic tags to monitor your fleet in real time. High-sensitivity RFID tags provide accurate vehicle identification and long reading distances, even at highway speeds. Fast reading and writing speeds improve traffic flow, while large memory capacity stores vehicle identity and permissions.
You benefit from:
- Strong data security that prevents unauthorized access.
- Reliable operation in harsh weather and high-interference environments.
- Integration with intelligent transport solutions, such as weigh-in-motion and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
- AI-driven analytics that optimize revenue, reduce costs, and support predictive maintenance.
Tip: By leveraging 5G connectivity, you enable seamless toll transactions and large-scale IoT deployments, ensuring your transportation operations remain efficient and future-ready.
Key Benefits of Electronic Tagging for Asset Tracking
Real-Time Asset Visibility
Location Tracking
You gain immediate insight into asset locations when you deploy electronic tagging systems. RFID tags transmit information wirelessly and contactlessly to readers, allowing you to track assets without physical scanning. This technology enables you to monitor asset movements within facilities and during transit. You see where every item is at any moment, which enhances security and automates processes like check-in and check-out. RFID technology uses radio waves to identify and track assets, providing continuous updates on asset whereabouts. You rely on dashboards and alerts that compile this data, ensuring you know the location of every asset 24/7.
Condition Monitoring
You monitor asset condition in real time with electronic tags. RFID tags capture and relay status data, such as temperature or humidity, to software systems. You receive instant alerts if an asset’s condition changes, allowing you to respond quickly and prevent damage. This capability supports compliance and quality control, especially in industries like healthcare and food logistics. You maintain asset integrity and reduce risk by acting on real-time information.
Tip: Real-time visibility helps you prevent losses and optimize asset utilization.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Error Reduction
You eliminate manual entry errors by automating data collection with RFID asset tracking. RFID readers scan multiple tags simultaneously from several meters away, which reduces scanning time compared to manual barcode methods. You avoid issues like dirt or wear that affect barcode readability, ensuring precise tracking. RFID tags store detailed asset information, which supports accurate recordkeeping and minimizes discrepancies.
Faster Audits
You complete audits faster with RFID technology. Automated systems provide immediate access to asset locations, saving you time and improving operational workflows. RFID tags are durable, waterproof, dustproof, and heat resistant, which ensures reliable long-term use in various environments. You scan assets quickly and efficiently, even in challenging conditions.
- RFID supports longer reading distances and multi-tag reading, which traditional methods lack.
- Automation reduces labor costs and human errors, increasing overall efficiency.
Cost Savings and ROI
Reduced Labor Costs
You save significant labor costs by switching to electronic tagging. Manual price updates require substantial staff time. For example, updating prices manually can take 50 hours weekly at $15 per hour, totaling $39,000 annually. RFID and ESL systems automate these processes, freeing your staff for higher-value tasks.
Lower Asset Losses
You reduce asset losses by improving tracking accuracy and automating alerts. Pricing errors cause losses estimated at $5,000 annually, which electronic shelf labels nearly eliminate. RFID technology ensures assets are accounted for, minimizing theft and misplacement.
| Benefit | Annual Savings | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Savings | $39,000 | Automated updates reduce manual work |
| Energy Savings | $10,000 | ESL systems use energy-efficient displays |
| Error Reduction | $5,000 | Fewer pricing and tracking mistakes |
| ROI | 54% | Payback period of about 1.85 years |
You see long-term benefits from durable hardware, reduced maintenance, and improved operational efficiency. Automated updates improve pricing accuracy and customer experience, supporting profitability.
Note: Investing in RFID and electronic tagging yields measurable returns through labor, energy, and error reduction.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Electronic tags have become essential tools for strengthening security and ensuring compliance in asset tracking. You gain the ability to monitor assets continuously and respond quickly to any irregularities. These systems help you protect valuable items and meet strict regulatory standards across industries.
Tamper Alerts
You can rely on electronic tags like RFID and NFC to provide real-time tamper alerts. When an asset moves unexpectedly or leaves a designated area, the system triggers an immediate notification. This feature helps you prevent unauthorized removal and reduces the risk of theft. Many organizations integrate electronic tags with security gates. If someone tries to remove an asset without permission, the system detects it and sends an alert to your management platform.
- Electronic tags enable continuous monitoring of assets, triggering alerts for unexpected movement.
- Integration with security gates allows automatic detection of unauthorized asset removal.
- Smart tracking systems can scan or weigh assets upon storage, sending alerts if items are missing or low.
- You can set up notifications for unreturned tools at the end of a shift, preventing loss.
You also benefit from smart locker storage solutions. These systems automate manual tasks and generate business intelligence, supporting both asset security and compliance. By authenticating users when they sign equipment in or out, you ensure only authorized personnel handle sensitive items.
Tip: Set up tamper alerts and access controls to protect high-value assets and maintain accountability within your organization.
Regulatory Reporting
Electronic tags simplify compliance with industry regulations. You can store critical data directly on the tag, such as maintenance history and warranty details. This information helps you follow maintenance schedules and meet regulatory requirements. NFC tags maintain individual access logs, recording who last interacted with an asset. This feature supports audit trails and ensures transparency.
- Tags store maintenance records and warranty information, aiding regulatory adherence.
- Access logs from NFC tags provide a clear record of asset interactions.
- Real-time reporting and analytics from tagged assets give you visibility into asset utilization and movement.
- Integration with networked management systems enables automated compliance practices.
Hospitals use RFID tagging to track valuable equipment, which significantly reduces loss rates and supports compliance with healthcare standards. You can generate detailed reports for audits, inspections, or internal reviews. Automated alerts and business intelligence tools help you identify compliance gaps and take corrective action quickly.
Note: Leveraging electronic tags for regulatory reporting not only streamlines audits but also strengthens your organization’s reputation for reliability and transparency.
Challenges and Future Trends in Electronic Tags and RFID
Barriers to Adoption
Cost of Implementation
You may encounter significant upfront costs when adopting electronic tags and rfid systems. These expenses include purchasing tags, readers, integration services, and comprehensive training for your staff. Many organizations hesitate to invest without a clear cost-benefit analysis. You must also consider the challenge of aligning diverse stakeholders, each with different priorities and expectations. Technical compatibility issues can arise when integrating rfid with your existing systems, which may require additional resources and expertise.
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy remains a top concern for many businesses. You need to address worries about unauthorized data collection and the potential for surveillance. Healthcare staff, for example, often express dissatisfaction with user interfaces and question the accuracy of tracking systems. Employee resistance can stem from comfort with traditional methods and fears about privacy. To overcome these barriers, you should invest in education and training, involve employees early, and conduct pilot tests to evaluate system performance.
Key barriers to adoption include:
- High initial investment costs for hardware, integration, and training.
- Privacy and security concerns regarding data collection.
- Technical challenges and compatibility with legacy systems.
- Lack of organizational buy-in and employee resistance.
- The need for thorough training and early performance evaluation.
Emerging Innovations
AI and Predictive Analytics
You see artificial intelligence and predictive analytics transforming electronic tag management. AI enables automated data collection, real-time analytics, and personalized experiences. For example, Walmart uses AI-powered tag management to personalize customer interactions, resulting in a 25% increase in sales. Adobe leverages AI-driven automation to reduce marketing costs by 30%. Predictive analytics helps you forecast asset behavior and optimize tracking strategies, allowing for efficient multi-step triggering and conditional logic.
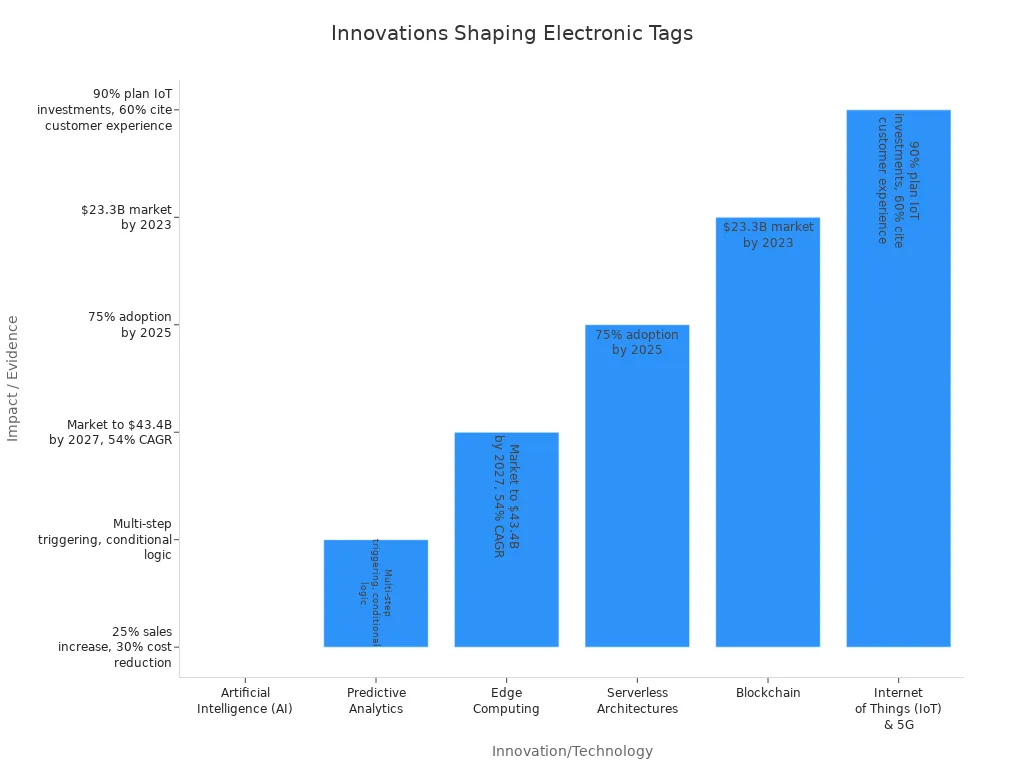
| Innovation/Technology | Impact on Electronic Tags and Tag Management Systems | Supporting Evidence/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Automated data collection, real-time analytics, predictive insights, and personalization. | Walmart saw 25% sales increase; Adobe reduced marketing costs by 30%. |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasts asset behavior, optimizes tag strategies, and improves operational efficiency. | AI-powered analytics enable multi-step triggering and conditional logic. |
| Edge Computing | Reduces latency and improves real-time decision making by processing data closer to the source. | Akamai explores edge computing; market expected to grow rapidly. |
| Blockchain | Enhances data security and transparency with tamper-proof records. | IBM developed blockchain-based tag management; market growth expected. |
| IoT & 5G | Expands connectivity and supports efficient, secure tag management for more devices. | Cisco survey: 90% of companies plan IoT investments. |
A recent survey shows that 92% of businesses plan to invest in generative AI, highlighting its growing importance in asset tracking and management.
Energy Harvesting Tags
You can expect energy harvesting tags to become more common. These tags draw power from environmental sources such as light, heat, or radio waves. This innovation reduces the need for battery replacements and lowers maintenance costs. Energy harvesting extends the lifespan of rfid tags, making them more sustainable and reliable for long-term asset tracking.
The Future of Asset Tracking
Universal Interoperability
You will benefit from universal interoperability as asset tracking systems evolve. Future rfid and electronic tag solutions will integrate seamlessly with IoT, AI, and cloud platforms. This integration enables you to manage assets across different locations and industries without compatibility issues. You will see the adoption of Industry 4.0 standards and cloud-based tracking systems, which expand the application scope of rfid technology.
Autonomous Asset Management
You can look forward to autonomous asset management powered by intelligent, self-organizing systems. Innovations such as biodegradable rfid tags, quantum security, and neural interfaces will drive this transformation. RFID-tagged items will optimize their own positioning and utilization, reducing manual intervention. Automation and predictive maintenance will become standard, supported by real-time analytics and AI-driven decision-making. As costs fall and technology advances, you will find rfid accessible to businesses of all sizes, fueling growth in logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail.
The future of asset tracking promises smarter, more sustainable, and highly integrated solutions that deliver operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
You now see electronic tags, including electronic shelf price tags, driving real-time, automated asset tracking across industries. You benefit from measurable improvements such as reduced labor costs, faster inventory audits, and enhanced pricing accuracy.
- Automated replenishment and real-time tracking help you maintain optimal inventory levels.
- Cost savings and sustainability goals become achievable as you eliminate manual processes.
Looking ahead, you will rely on intelligent, integrated systems powered by AI, IoT, and cloud platforms, making asset management smarter and more efficient.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using electronic tags for asset tracking?
You gain real-time visibility and automated updates. Electronic tags help you reduce manual errors, save time, and improve asset security. You can track assets instantly and make better business decisions.
How do RFID tags differ from Bluetooth tags?
RFID tags use radio waves for short-range identification. Bluetooth tags, especially BLE, offer longer range and support real-time location tracking. You choose RFID for inventory and Bluetooth for indoor positioning or theft prevention.
Can electronic tags work in harsh environments?
Yes. Many electronic tags feature waterproof, dustproof, and heat-resistant designs. You can use them in manufacturing, construction, and outdoor settings without worrying about durability.
Are electronic tags secure?
You benefit from advanced security features. Many tags use encryption and authentication to protect data. You can set up access controls and receive tamper alerts for sensitive assets.
How do electronic shelf price tags improve retail operations?
You update prices instantly across all shelves. Electronic shelf price tags reduce labor costs, eliminate pricing errors, and support dynamic pricing strategies. You also enhance the customer experience with accurate, real-time information.
What industries use electronic tags for asset tracking?
You find electronic tags in retail, healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, construction, and transportation. Each industry uses tags to improve efficiency, reduce losses, and ensure compliance.
Do electronic tags require batteries?
Some tags, like passive RFID, do not need batteries. Others, such as active RFID or Bluetooth tags, use batteries for extended range and real-time tracking. You select the type based on your tracking needs.
How can you integrate electronic tag data with existing systems?
You use APIs or middleware to connect electronic tag systems with ERP, inventory, or management platforms. This integration gives you unified data, real-time updates, and automated workflows.
Tip: Always consult your technology provider for the best integration practices.


