
Retailers increasingly turn to electronic price tags to enhance pricing accuracy and operational efficiency. These systems, which include solutions like the ESL Gateway AP and ESL Price Tag, enable rapid price updates and reduce labor costs compared to traditional price tags. The market for Electronic Shelf Labels reached USD 1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 5.8 billion by 2032, reflecting strong adoption in Esl Retail. Unlike traditional price tags, electronic price tags provide clear, real-time information, improving both store performance and customer satisfaction.
| Statistic | Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Market size (2023) | USD 1.5 billion | Demonstrates scale of electronic price tags in retail |
| Projected market size (2032) | USD 5.8 billion | Highlights rapid adoption and operational impact |
Understanding Electronic Price Tags and Digital Price Tag Technology
What Are Electronic Price Tags?
Electronic price tags represent a modern solution for retailers seeking to automate and streamline pricing. These devices, often called electronic shelf labels, replace traditional paper tags with digital price tag displays. Retailers use them to update prices instantly, synchronize information across channels, and reduce manual errors. According to industry research, 79% of grocery retailers already use electronic price labeling, and over half of food retailers plan to expand their use. This widespread adoption highlights the technology’s value in improving accuracy and efficiency.
How Electronic Price Tags Work
Wireless Communication and Connectivity
Most digital price tag systems rely on wireless communication technologies such as radio frequency (RF), infrared, or near-field communication (NFC). RF technology stands out for its reliability and ability to support real-time updates across large retail spaces. Infrared offers high precision but requires a direct line of sight. These wireless networks connect thousands of electronic shelf labels throughout a store, enabling centralized control and immediate price changes.
Tip: Reliable wireless coverage ensures that every digital price tag receives updates without delay, minimizing pricing discrepancies.
Integration with POS and Inventory Systems
Integration with point-of-sale (POS) and inventory management systems forms the backbone of electronic price tag technology. Retailers connect their digital price tag network to merchandise management and ERP software. This integration allows for real-time synchronization of prices, promotions, and stock levels. For example, when a product’s price changes online or in the POS system, the update appears instantly on the corresponding electronic shelf label. This process reduces manual labor, eliminates human error, and supports dynamic pricing strategies.
Types of Electronic Shelf Labels
E-paper Displays
E-paper displays have become the preferred choice for many retailers due to their energy efficiency and high readability. These digital price tags mimic the appearance of paper, offering clear visibility from various angles and under different lighting conditions. E-paper technology consumes power only when updating content, resulting in long battery life—an essential feature for large-scale retail deployments. Retailers favor e-paper displays for their sustainability benefits and ability to support frequent price changes.
LCD and Other Digital Price Tag Technologies
LCD-based digital price tags provide vibrant color displays and can show more complex information, such as promotional graphics or QR codes. Some advanced electronic shelf labels use ink screen technology, combining aesthetic appeal with low power consumption. The table below summarizes common features and technologies:
| Feature Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Type | LCD, E-Paper, Others |
| Technology | RF, Infrared, NFC |
| Key Features | High readability, energy efficiency, real-time updates |
| Operational Benefits | Enhanced efficiency, reduced labor, improved accuracy |
Regional trends show strong adoption in North America and Asia Pacific, driven by operational efficiency and sustainability goals. Retailers like Walmart and Lidl have implemented electronic shelf labels to support omnichannel pricing and improve customer experience. As technology advances, digital price tag solutions continue to evolve, offering greater durability, integration, and design flexibility.
Key Benefits of Electronic Shelf Labeling for Retailers

Dynamic Pricing and Real-Time Updates
Immediate Price Changes
Retailers gain a significant advantage with digital price tag systems that enable immediate price changes. These systems allow staff to update prices across thousands of products in seconds, rather than hours. Real-time pricing engines deliver instant updates to all sales channels, supporting rapid responses to market shifts. Automation reduces manual intervention by more than 80%, freeing employees to focus on customer service and strategic tasks. This seamless process ensures that every shelf reflects the latest prices, which helps maintain customer trust and satisfaction.
Competitive Pricing Strategies
Dynamic pricing powered by electronic shelf labels gives retailers the flexibility to adjust prices in response to competitor actions and customer behavior. Artificial intelligence and machine learning tools analyze data to optimize prices, increasing profit margins and improving inventory management. Retailers can implement hyper-personalized offers and real-time promotions, which boost customer engagement and promotional return on investment. For example, Amazon demonstrates the power of dynamic pricing by changing prices on millions of products every ten minutes. The table below highlights measurable impacts of dynamic pricing and real-time updates:
| Measurable Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Conversion Rates | Personalized pricing encourages more visitors to become buyers and fosters customer loyalty. |
| Revenue and Profit Growth | Tracks increases in revenue and gross profit, isolating pricing impact from other factors. |
| Profit Margins | Ensures profit margin goals are met by product or customer category. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Models long-term value from repeat purchases and loyalty. |
| Customer Satisfaction Scores | Uses sentiment analysis to gauge experience and identify improvement areas. |
| Inventory Turnover | Measures inventory days on hand to align pricing with operational goals. |
| Real-Time Dashboards | Provides immediate insights into key performance indicators for quick decision-making. |
| Periodic Reviews | Regular assessments optimize pricing strategy effectiveness. |
Labor Savings and Operational Efficiency
Reduced Manual Price Changes
Electronic shelf labeling eliminates the need for manual price tag replacement, which traditionally takes about three minutes per tag. In busy retail environments, staff may need to update 1,000 to 2,000 tags weekly, resulting in significant labor costs. By automating this process, retailers save hours of labor each week. Integration with POS and inventory systems further reduces errors and allows for real-time price and inventory updates. Battery life improvements, often lasting up to five years, also reduce maintenance labor compared to frequent paper tag replacements.
- ESLs significantly reduce labor and material costs by removing manual price updates and paper tag usage.
- Material costs associated with traditional paper tags, such as paper, ink, and printer maintenance, are eliminated.
- Retailers like Target and Amazon Go have demonstrated practical labor and efficiency benefits through successful ESL implementation.
Streamlined Store Operations
Digital price tag solutions streamline store operations by automating routine tasks and improving workflow. Integration with pricing, inventory, and POS systems enhances operational efficiency and customer interactions. Retailers benefit from faster market response and improved in-store agility. The long-term benefits of electronic price tags often outweigh the initial investment, as labor savings and operational improvements accumulate over time. Automation enables staff to focus on higher-value activities, such as customer engagement and merchandising.
Note: Automation not only saves time but also supports compliance with pricing regulations and helps manage rising labor costs.
Improved Pricing Accuracy and Consistency
Elimination of Human Error
Digital price tag technology nearly eliminates pricing errors by synchronizing directly with the store’s database. Automation removes the need for manual price updates, which are often error-prone. Retailers report a 95% reduction in the time required to update prices after implementing real-time electronic shelf labels. This improvement leads to more accurate pricing and fewer customer complaints at checkout.
Consistency Across Channels
Electronic shelf labels ensure that shelf prices always match checkout prices, reducing discrepancies and confusion. Real-time synchronization with POS systems guarantees consistency across all channels, including online and in-store. This alignment supports agile pricing strategies and helps retailers close the price gap with online competitors. The table below summarizes key metrics indicating improvements in pricing accuracy and consistency:
| Metric/Aspect | Evidence Description |
|---|---|
| Time Reduction in Price Updates | 95% reduction in time needed to update prices after implementing real-time electronic shelf labels. |
| Pricing Accuracy | Near elimination of pricing errors due to automation and direct database connection. |
| Pricing Consistency | Real-time synchronization ensures shelf prices always match checkout prices, reducing discrepancies. |
| Operational Efficiency | Automation removes manual price updates, minimizing human error and labor costs. |
Retailers using electronic shelf labeling experience smoother shopping experiences for customers, accurate pricing, and improved operational efficiency. These benefits support both short-term gains and long-term growth in the competitive retail landscape.
Enhanced Customer Experience with Digital Price Tags
Up-to-Date and Clear Information
Modern shoppers expect accurate and transparent pricing. Digital price tag systems deliver real-time updates, ensuring that every product displays the correct price and detailed information. This transparency meets the demand for convenience and personalized experiences in retail. Customers benefit from inventory alerts and dynamic pricing, which help them discover new products and take advantage of timely promotions. Staff can focus on meaningful interactions with shoppers because automated systems handle repetitive tasks. As a result, the overall shopping experience improves, and customers feel more confident in their purchases.
Digital price tags also reduce pricing errors by up to 100%. This accuracy eliminates customer complaints and government fines related to pricing discrepancies. Staff spend 80% less time updating prices, which allows them to dedicate more attention to customer service. These improvements increase customer satisfaction and reduce frustration, creating a more positive environment in the store.
Improved Store Presentation
Retailers using electronic shelf labels achieve a cleaner and more organized store appearance. Digital displays provide uniformity across shelves, eliminating the clutter of mismatched or outdated paper tags. The sleek design of electronic shelf labeling systems enhances the visual appeal of retail spaces, making it easier for customers to navigate aisles and find products. Clear and consistent signage supports brand image and helps stores stand out in a competitive market. Shoppers appreciate the professional look, which contributes to a more enjoyable and efficient visit.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Electronic Shelf Labels
Reduced Paper and Printing Waste
Retailers adopting electronic shelf labels eliminate the need for paper tags. This change leads to a significant reduction in paper waste and supports sustainability goals. By removing the constant cycle of printing and replacing paper labels, stores decrease their environmental footprint. These efforts align with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices in retail.
- Electronic shelf labels eliminate the need for paper labels.
- This elimination leads to reduced paper waste.
- The reduction in waste promotes sustainability.
- These benefits align with increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices.
Lower Carbon Footprint
Switching to digital price tag technology helps retailers lower their carbon footprint. The reduction in paper and ink usage means fewer resources are consumed and less waste is generated. Energy-efficient display technologies, such as e-paper, further minimize environmental impact by using power only during updates. Retailers demonstrate their commitment to sustainability by adopting these solutions, which can enhance their reputation among environmentally conscious shoppers.
Better Inventory and Stock Management
Faster Stock Rotation
Digital price tag systems connect directly to inventory management platforms, enabling real-time monitoring and automated replenishment. Retailers can track inventory turnover rates, days on hand, and stock-to-sales ratios with greater accuracy. This integration supports faster stock rotation, especially in grocery and perishable goods sectors. For example, grocery stores use digital shelf labels to display current stock levels and alert staff when items run low. This process supports first-in, first-out (FIFO) stock rotation, ensuring product freshness and reducing waste.
- Digital price tags enable real-time inventory monitoring and automated replenishment by linking to inventory management systems, improving stock rotation and reducing stockouts.
- Metrics used to verify improvements include inventory turnover rate, out-of-stock percentage, days on hand, and stock-to-sales ratio.
- In grocery retail, digital shelf labels display current stock levels and alert staff when items run low, supporting FIFO stock rotation and enabling timely restocking to prevent stockouts.
Improved Out-of-Stock Alerts
Retailers benefit from automated alerts and dashboards that notify staff when products reach reorder points. These systems help maintain optimal stock levels and prevent out-of-stock situations. AI-powered analytics and sensor technologies provide accurate recommendations for replenishment, reducing manual errors and improving supply chain efficiency. Companies like L’Oréal and Target use digital price tag solutions to track stock across channels and adjust replenishment schedules in real time. Staff receive timely notifications, allowing them to restock shelves quickly and maintain high product availability for customers.
- Digital Shelf Labels provide real-time inventory data synchronized with inventory management systems, enabling staff to monitor stock levels and receive alerts for low stock.
- Automated alerts from DSLs notify staff when reorder points are reached, preventing stockouts and improving customer satisfaction.
- Continuous monitoring and adjustment of minimum and maximum stock levels based on sales velocity and supplier lead times optimize stock rotation and reduce carrying costs.
- Visual management tools and dashboards help track real-time stock levels and sales trends, enabling proactive inventory decisions.
Retailers who invest in these technologies see measurable improvements in inventory turnover, reduced out-of-stock percentages, and better overall stock management. These benefits contribute to a more reliable and satisfying shopping experience for customers.
Main Drawbacks of Electronic Price Tags and Electronic Shelf Labels

High Upfront Costs and Investment
Hardware and Installation Expenses
Retailers face significant initial expenses when transitioning from traditional price tags to electronic price tags. Hardware costs include the purchase of digital shelf labels, wireless communication infrastructure, and display mounting systems. Installation often requires specialized labor, which adds to the total investment. Large retail environments may need thousands of digital tags, amplifying the upfront financial burden. These costs can deter smaller retailers or those with tight capital budgets from adopting the technology.
Note: Retailers must evaluate whether the long-term operational savings will offset the initial hardware and installation expenses.
Software and Integration Costs
Beyond hardware, software licensing and integration with existing systems present additional challenges. Retailers must invest in software platforms that synchronize electronic price tags with point-of-sale and inventory management systems. Custom integration work may be necessary, especially for stores with legacy IT infrastructure. Ongoing software updates and support contracts further increase the total cost of ownership. These expenses often exceed those associated with traditional price tags, making careful budgeting essential.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support Needs
Battery Replacement and Lifespan
Electronic shelf labels rely on batteries for power. Although e-paper displays offer long battery life, batteries still require periodic replacement. In large stores, staff must track and replace thousands of batteries over time. This maintenance task can disrupt operations and add to labor costs. Battery disposal also raises environmental concerns, which retailers must address as part of their sustainability efforts.
Technical Support Requirements
Digital price tag systems demand ongoing technical support. Retailers need IT staff or vendor support to troubleshoot connectivity issues, perform software updates, and resolve display malfunctions. System downtime can lead to pricing inconsistencies and customer dissatisfaction. Unlike traditional price tags, which rarely fail, electronic systems introduce new points of failure that require specialized expertise to manage.
Technology Adoption and Change Management Barriers
Staff Training and Adaptation
Introducing electronic price tags requires comprehensive staff training. Employees must learn to operate new software, manage digital displays, and respond to technical issues. Resistance to change often emerges, especially among staff accustomed to traditional price tags. The Harvard Business School case on Renault Group highlights the challenges legacy organizations face during technological disruption. Effective change management strategies become essential to align staff with new technology and minimize resistance.
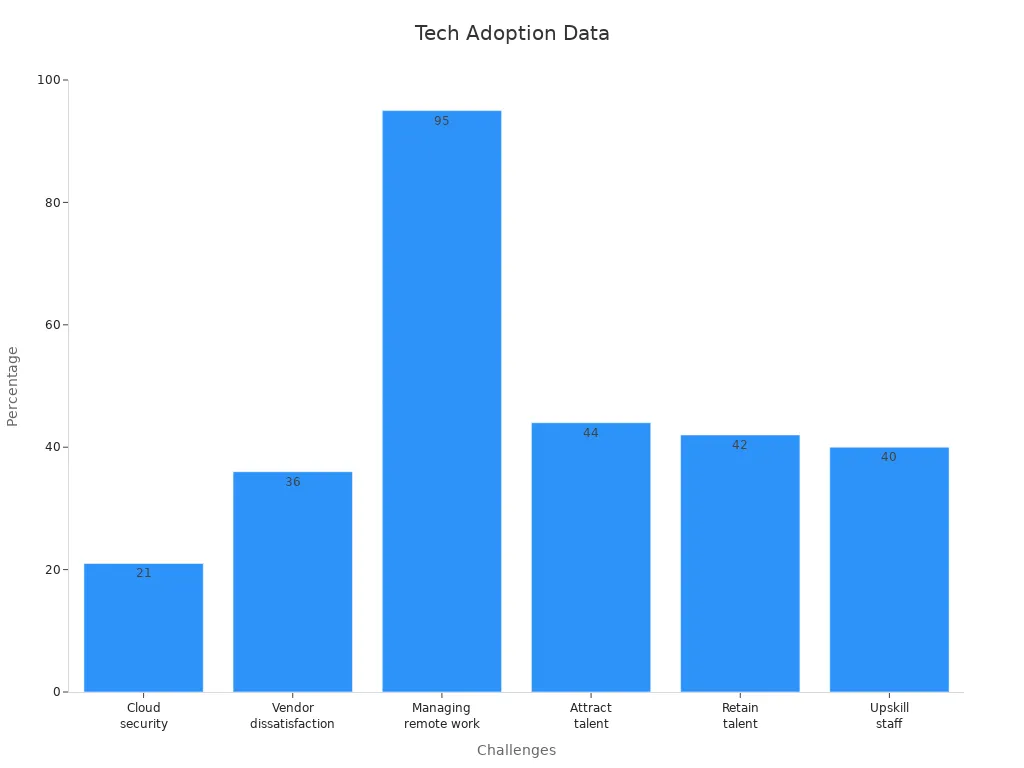
| Difficulty / Challenge | Supporting Data / Insight | Explanation / Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Disconnect in adoption methods | HR leaders report a gap between effective adoption methods and their actual use | Indicates challenges in implementing best practices for technology adoption among staff |
| Cloud security concerns | 21% of HR leaders cite security of HR data on cloud as a top challenge | Security fears hinder smooth cloud adoption and staff confidence |
| Skills shortages | 44% difficulty attracting cloud talent, 42% retaining, 40% upskilling existing employees | Lack of skilled staff slows technology adoption and change management |
| Vendor dissatisfaction | 36% likely to switch vendors after subscription ends | Problems with budget and integration cause frustration and instability in tech use |
| Managing remote work | 95% of HR leaders use or plan tech to manage remote work, but measuring output vs. login frequency is critical | Shows complexity in adopting technology to support new work models and staff engagement |
| Adoption of disruptive tech | Top barriers are implementation costs and lack of compelling use cases | Staff and leadership hesitation to adopt new technologies without clear benefits |
| Recommended approaches | Apply proven adoption methods, address security and skills early, take gradual steps for disruptive tech | Provides actionable strategies to overcome adoption and change management difficulties |
Implementation Complexity
Deploying electronic price tags involves complex planning and coordination. Retailers must integrate new hardware and software with existing systems, test wireless connectivity, and ensure compatibility with inventory and POS platforms. Implementation often disrupts daily operations, especially in large or multi-location retail chains. Project managers must address technical hurdles, manage vendor relationships, and oversee staff training. These complexities can delay full deployment and increase the risk of cost overruns.
Tip: A phased rollout and pilot testing can help retailers identify and resolve issues before full-scale implementation.
Retailers considering electronic price tags must weigh these drawbacks against the potential benefits. High upfront investment, ongoing maintenance, and change management challenges can impact the success of digital price tag projects. Careful planning and realistic budgeting remain critical for a smooth transition from traditional price tags to advanced electronic solutions.
Potential Technical and System Issues
Connectivity and Display Problems
Electronic price tags depend on stable wireless networks to function correctly. In a retail environment, interference from other devices or physical barriers can disrupt signal strength. When connectivity drops, price updates may not reach all shelf labels. This situation can lead to inconsistent pricing across the store. Retailers must monitor network health and address dead zones quickly.
Display malfunctions also pose challenges. E-paper and LCD screens can fail due to hardware defects or environmental factors such as humidity and temperature changes. A failed display may show outdated or blank information, confusing both staff and customers. Regular inspections help identify faulty units early. Retailers often keep spare labels on hand to replace malfunctioning ones without delay.
Tip: Investing in robust wireless infrastructure and conducting routine maintenance checks can reduce the risk of connectivity and display issues.
System Downtime and Reliability Concerns
System downtime can disrupt store operations and damage customer trust. If the central server or software platform goes offline, electronic price tags may stop receiving updates. During these outages, staff cannot adjust prices or promotions, which can result in lost sales opportunities. Some systems offer offline modes, but these features may have limited functionality.
Reliability remains a top concern for retailers considering digital price tag solutions. Hardware failures, software bugs, or power outages can all impact system performance. Retailers should implement backup procedures and disaster recovery plans. Regular software updates and vendor support contracts help maintain system stability.
A comparison of common reliability risks and mitigation strategies:
| Risk Factor | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Network Interference | Missed or delayed price updates | Upgrade wireless infrastructure |
| Hardware Failure | Blank or incorrect displays | Keep spare units for quick swap |
| Software Bugs | System crashes or errors | Schedule regular software updates |
| Power Outages | Total system downtime | Use backup power supplies |
Security and Data Privacy Risks
Hacking or Tampering Threats
Electronic price tags introduce new security risks in the retail sector. Hackers may attempt to access the wireless network to change prices or disrupt store operations. Unauthorized access can lead to incorrect pricing, financial losses, or reputational harm. Physical tampering with shelf labels also poses a threat, especially in high-traffic areas.
Retailers must secure their networks with strong encryption and authentication protocols. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. Staff should receive training to recognize suspicious activity and respond quickly to incidents.
Note: A layered security approach, including both digital and physical safeguards, offers the best protection against tampering and cyber threats.
Data Protection Compliance
Retailers handle sensitive data when integrating electronic price tags with inventory and point-of-sale systems. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is essential. These laws require businesses to safeguard customer and transaction data from unauthorized access or misuse.
Retailers should work closely with technology vendors to ensure that all systems meet regulatory standards. Data encryption, access controls, and regular compliance reviews form the foundation of a strong data protection strategy. Failure to comply can result in legal penalties and loss of customer trust.
A checklist for data protection compliance in retail:
- Encrypt all data transmitted between devices and servers.
- Restrict system access to authorized personnel only.
- Conduct regular audits of data handling practices.
- Stay updated on changes to relevant privacy laws.
Retailers who address these technical and security challenges position themselves for long-term success with electronic price tag technology.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of Electronic Shelf Labeling for Your Store
Assessing Store Needs and Readiness
Store Size and Complexity
Retailers must first evaluate the size and complexity of their stores before considering electronic shelf labeling. Large stores with thousands of products often benefit more from automation. Complex layouts or multiple departments may require advanced integration with inventory and point-of-sale systems. Smaller stores with limited product ranges might not see the same return on investment. A careful assessment of store layout, product variety, and operational needs helps determine if a digital price tag system fits the business.
Frequency of Price Changes
The frequency of price changes plays a critical role in the decision process. Stores that update prices daily or run frequent promotions gain significant efficiency from automation. In contrast, retailers with stable pricing may not justify the upfront investment. Analyzing historical pricing data can reveal patterns and help estimate potential labor savings.
Calculating ROI for Digital Price Tag Implementation
Cost-Benefit Analysis
A thorough cost-benefit analysis helps retailers understand the financial impact of adopting digital price tag technology. This analysis should include hardware, software, installation, and ongoing maintenance costs. Retailers must compare these expenses with projected labor savings, improved pricing accuracy, and enhanced customer experience. Many organizations use benchmarks such as the number and severity of problems found during pilot testing to measure effectiveness. Efficiency can be tracked by the number of issues resolved per unit time.
Payback Period Estimation
Estimating the payback period allows retailers to gauge how quickly the investment will deliver returns. By calculating the time needed for operational savings to offset initial costs, decision-makers can assess whether the project qualifies as a long-term investment. Most retailers seek a payback period that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance. A shorter payback period often signals a more attractive opportunity.
Decision Checklist for Retailers
Key Questions to Consider
A structured checklist supports informed decision-making. Retailers should address the following questions:
- Does the store require frequent price updates?
- Is the current system prone to pricing errors?
- Can the staff manage new technology with minimal training?
- Will the investment align with long-term business objectives?
- Are there clear benchmarks for measuring success?
Readiness Assessment Guide
A readiness assessment ensures the store can implement electronic shelf labeling smoothly. Effective checklists use a severity rating scale for potential problems, ranging from minor to catastrophic. Organizations often set strict limits, allowing no major or catastrophic issues before moving forward. Checklist items should be marked as Required, Recommended, or Optional, with response options such as Yes, No, Not Applicable, and Not Sure. Evaluation questions should confirm that all necessary steps are listed, terminology is clear, and troubleshooting guidance is available. Combining checklists with usability testing and user feedback helps identify core challenges. Continuous improvement and iterative feedback keep the checklist relevant and effective.
Tip: A well-designed checklist not only guides implementation but also supports ongoing evaluation and improvement.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Success Stories with Electronic Shelf Labels
Many leading retailers have adopted electronic shelf labels to streamline operations and improve customer experience. For example, Walmart introduced ESLs in select stores to automate price changes and synchronize shelf prices with online listings. This move allowed staff to update thousands of prices within minutes, reducing manual labor and minimizing pricing errors. Walmart reported improved pricing accuracy and faster response to market changes.
Lidl, a major European grocery chain, implemented ESLs across hundreds of locations. The company aimed to reduce paper waste and support sustainability goals. Lidl’s deployment resulted in significant labor savings and a cleaner store appearance. Staff spent less time on repetitive tasks and more time assisting customers. The company also achieved better compliance with pricing regulations.
A table below summarizes key outcomes from these implementations:
| Retailer | Key Benefit | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Walmart | Automated price updates | Faster price changes, fewer errors |
| Lidl | Sustainability | Reduced paper waste, labor savings |
Note: Retailers that invest in ESLs often see measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability.
Lessons Learned from Implementation Challenges
Retailers have encountered several challenges during ESL adoption. Integration with legacy systems often presents technical hurdles. Some stores underestimated the complexity of connecting ESLs to existing inventory and POS platforms. This oversight led to delays and additional costs.
Staff adaptation remains another common challenge. Employees sometimes resist new technology, especially when training resources are limited. Retailers found that clear communication and hands-on training sessions helped ease the transition. A phased rollout, starting with pilot programs, allowed teams to identify and resolve issues before full-scale deployment.
Connectivity issues also surfaced in large stores. Wireless dead zones caused some ESLs to miss updates. Retailers addressed this by upgrading network infrastructure and conducting regular maintenance checks.
A checklist for overcoming common challenges:
- Assess compatibility with current IT systems.
- Provide comprehensive staff training.
- Pilot test ESLs in select departments.
- Monitor wireless network performance.
- Establish a support plan for ongoing maintenance.
Tip: Retailers who plan carefully and address technical and human factors early achieve smoother ESL implementation and greater long-term success.
Best Practices for Implementing Electronic Price Tags
Planning and Vendor Selection
Choosing the Right Solution Provider
Selecting the right vendor for electronic price tags requires a structured approach. Retailers should evaluate vendors based on several critical factors. These include product quality, cost-effectiveness, on-time delivery, and customer service. Financial strength and regulatory compliance also play a significant role in ensuring a reliable partnership. Multi-departmental evaluation, involving engineering, finance, and procurement teams, helps ensure a thorough review. Many retailers use e-procurement systems to automate vendor identification and contract management. Strategic tools, such as the Kraljic Matrix, help classify vendors by risk and value.
| Factor / Metric | Description / Importance |
|---|---|
| Quality | Product or service must meet technical specifications critical for electronic price tag systems. |
| Cost and Value | Reasonable cost, including discounts and transportation costs, to ensure value for money. |
| On-time Delivery | Timely delivery is crucial to avoid production delays and ensure product launch schedules are met. |
| Financial Strength | Vendor’s financial viability to ensure reliability and long-term partnership. |
| Customer References | Multiple references to verify vendor reputation and past performance. |
| Customer Service | Responsiveness and problem-solving ability post-delivery. |
| Trustworthiness | Vendor reliability and integrity in business dealings. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to relevant laws and industry standards. |
| ESG Sustainability | Environmental, social, and governance factors valued by the purchasing company. |
| Performance Metrics | Includes adherence to specs, invoicing accuracy, delivery timeliness, and vendor knowledge. |
Retailers should also compare solution providers using criteria such as cost-effectiveness, customization, scalability, and industry reputation. Service quality and technological capabilities must align with business needs.
Pilot Testing and Evaluation
Before full-scale deployment, retailers benefit from pilot testing electronic price tag systems in select departments. This approach allows teams to track performance metrics, such as specification adherence, delivery timeliness, and customer service responsiveness. Ongoing reviews help identify issues early and maintain vendor quality. Retailers should implement contingency plans if vendors fail to meet expectations.
Staff Training and Change Management for Electronic Shelf Labeling
Training Programs and Resources
Comprehensive staff training programs play a vital role in successful digital adoption. Organizations with effective training and change management are up to seven times more likely to succeed in digital projects. Training should align with business outcomes, focusing on operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Personalized content that addresses diverse roles and skill levels improves employee engagement and tool usage. Ongoing feedback and analytics enable continuous improvement.
| Aspect | Evidence Supporting Benefits of Comprehensive Staff Training Programs for Digital Price Tag Adoption |
|---|---|
| Success Rate Increase | Organizations with effective change management and training are up to 7 times more likely to succeed in digital adoption projects. |
| Alignment with Business Outcomes | Training programs that link digital adoption to business goals improve KPIs such as operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. |
| Behavioral Focus | Training that cultivates required digital behaviors and uses analytics to tailor learning improves employee engagement and tool usage. |
| Personalization | Customized training content addressing diverse roles and skill levels enhances user ability to navigate and use digital tools effectively. |
Communication Strategies
Clear communication strategies support staff adaptation. Leaders and change advocates should build awareness, desire, and knowledge among employees. Structured frameworks, such as the Prosci ADKAR Model, help overcome resistance by reinforcing new behaviors and supporting sustained adoption.
Ongoing Management and Optimization of Digital Price Tags
Monitoring System Performance
Retailers must monitor system performance to ensure reliability. Key metrics include system uptime, update accuracy, and battery health. Regular audits and usage analytics help identify gaps and optimize operations.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement keeps electronic shelf labeling effective. Retailers should collect feedback, review analytics, and update training materials regularly. Iterative enhancements address emerging challenges and support long-term success.
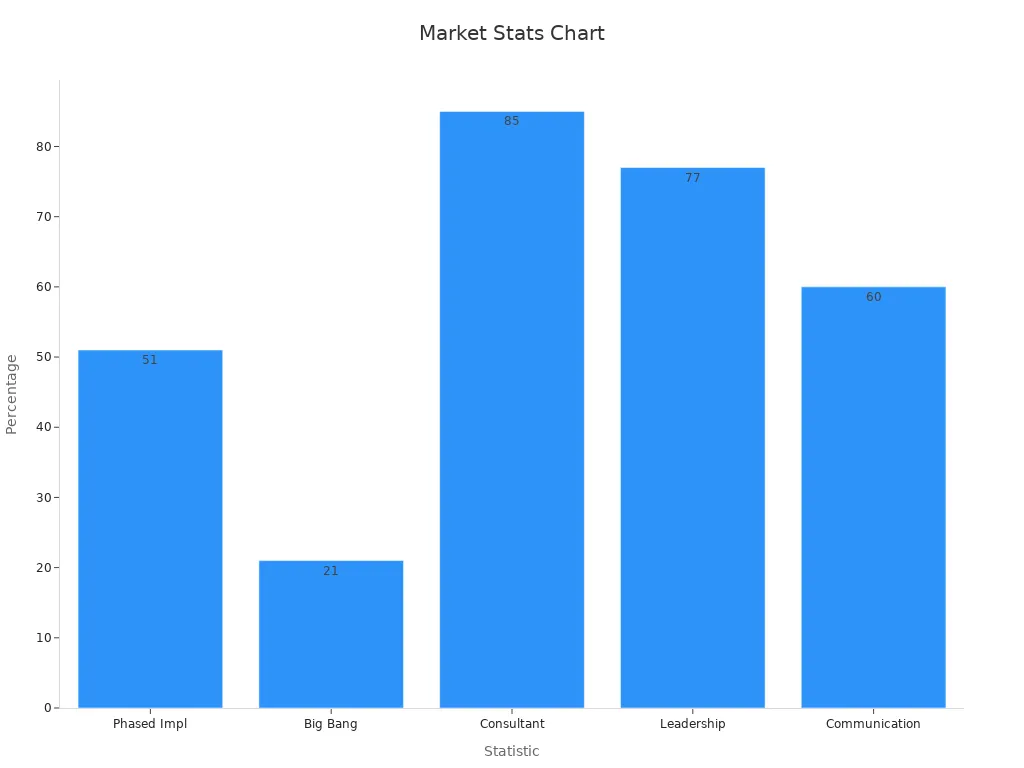
Electronic price tags deliver measurable gains in efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability. However, retailers must weigh these benefits against costs and operational complexity. A phased approach remains the most effective strategy, as shown by more than 50% of organizations preferring gradual rollouts and higher success rates with consultant support.
| Statistic Description | Data/Value |
|---|---|
| Percentage of organizations using phased implementation | More than 50% |
| Percentage using ‘big bang’ approach | About 21% |
| Success rate when hiring software consultants | 85% |
| Importance of leadership support for success | 77% of companies |
| Importance of effective communication | 60% of companies |
The electronic shelf label market continues to expand rapidly, with a projected CAGR of 12.7% through 2031. Many leading retailers, including Walmart and SPAR Austria, choose phased deployments to manage complexity and maximize results.
- Phased rollouts help retailers address technical challenges and stakeholder concerns.
- Gradual adoption supports better investment management and operational alignment.
- Pilot programs and vendor consultations enable tailored solutions for each business.
A well-planned, step-by-step implementation helps retailers minimize risks and realize the full value of electronic price tags.
FAQ
What is the typical lifespan of an electronic price tag?
Most electronic price tags last between 5 and 7 years. E-paper models often require battery replacement only once during their lifespan, depending on update frequency and store conditions.
Can electronic price tags integrate with existing POS systems?
Yes, most modern electronic price tag solutions offer integration with leading POS and inventory management systems. Retailers should confirm compatibility with their current software before implementation.
How secure are electronic price tag systems?
Vendors design electronic price tag systems with strong encryption and authentication protocols. Regular security audits and staff training help reduce risks of hacking or tampering.
What happens if the wireless network fails?
Electronic price tags may not receive updates during network outages. Most systems retain the last displayed price until connectivity restores. Retailers should monitor network health to prevent prolonged disruptions.
Are electronic price tags suitable for small retailers?
Small retailers can benefit from electronic price tags if they frequently change prices or manage many SKUs. However, high upfront costs may limit feasibility for stores with tight budgets.
How do electronic price tags support sustainability goals?
Electronic price tags eliminate paper and ink waste. Energy-efficient displays, such as e-paper, further reduce environmental impact. Retailers demonstrate commitment to sustainability by adopting these solutions.
What training do staff need for electronic price tags?
Staff require training on system operation, troubleshooting, and basic maintenance. Many vendors provide onboarding resources, including manuals and online tutorials, to support a smooth transition.


