
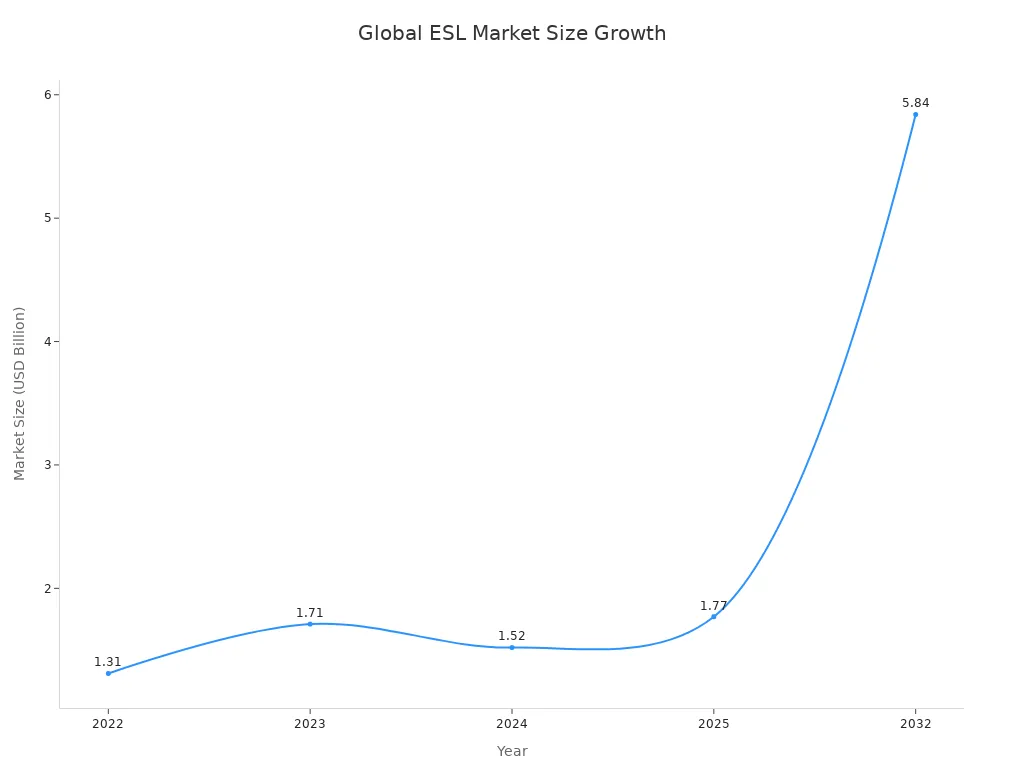
Electronic shelf labels represent a digital solution for displaying prices in a grocery store. Retailers rely on electronic shelf label systems, such as ESL Gateway AP and ESL Price Tag, to automate price changes and reduce manual errors. The adoption of electronic shelf labels in Esl Retail environments enables rapid updates, which improves accuracy and saves time. The global market size for electronic shelf labels reached USD 1.31 billion in 2022 and continues to expand due to technology advancements and rising demand for automated pricing.
Electronic shelf labels enhance the shopping experience by providing clear prices and supporting sustainability through reduced paper use in grocery stores.
Early Electronic Shelf Labels and Price Displays

The First Electronic Shelf Label Innovations
Retailers began experimenting with electronic shelf label technology in the early 1990s. The first generation of electronic shelf labels featured liquid-crystal display (LCD) screens that resembled calculator displays. These labels appeared in retail environments as a solution to automate the display of prices and reduce manual labor. Swedish company Pricer emerged as a pioneer, introducing electronic shelf labels in stores around the mid-1990s. The labels primarily displayed item prices and minimal product information due to limited display capacity. Although the technology offered basic automation, it marked a significant shift from traditional paper tags. Retailers could change prices more efficiently, setting the stage for future advancements in digital price management.
Early electronic shelf labels provided a glimpse into the future of retail automation, despite their limited functionality and slower data update speeds.
Challenges in Early Price Automation
The initial rollout of electronic shelf labels faced several technological and operational hurdles:
- Labels relied on simple LCD screens, which had poor readability under bright lighting conditions.
- Infrared communication required direct line-of-sight between transmitters and labels, restricting range and scalability.
- Price updating was slow and often required manual intervention, making real-time changes difficult.
- Risks in price updating included errors that could propagate across all labels, causing widespread pricing mistakes.
- Secure wireless networks were not yet available, leaving labels vulnerable to unauthorized price changes.
- Labels operated on low-power batteries, but these needed replacement every few years, highlighting limitations in power management.
- The cost and complexity of deploying hundreds of digital price tags posed practical challenges for retailers.
Retailers recognized the need for improved display technology and more reliable communication methods. The transition to radio frequency communication and the adoption of e-paper displays later addressed many of these issues, leading to better readability, longer battery life, and enhanced flexibility in managing prices.
First Generation Electronic Shelf Labels: LCD and Infrared
LCD-Based Electronic Shelf Label Technology
The first generation of electronic shelf labels introduced LCD display technology to retail environments. LCD screens allowed labels to present product information and prices in a clear, visually appealing format. Retailers found these displays easy to read, even from a distance, which improved the overall shopping experience. The LCD-based electronic shelf label system automated price updates, reducing the need for manual changes and minimizing errors.
A comparison between LCD-based electronic shelf labels and traditional paper labels highlights the benefits and trade-offs:
| Aspect | LCD-based Electronic Shelf Labels (ESLs) | Traditional Paper Labels |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | $5 to $10 per label; requires hardware, software, integration; total can reach thousands to millions for large retailers | Few cents per tag; minimal upfront cost |
| Long-term Savings | Labor costs reduced by up to 80%; eliminates price mismatch errors; lowers printing waste | Requires constant reprinting and manual updates |
| Update Efficiency | Instant, automated price updates across thousands of products with one click; saves hours of manual labor | Manual printing, cutting, and replacement; time-consuming and error-prone |
| Customer Experience | Ensures accurate pricing; frees staff to focus on customer service | Prone to pricing errors; staff distracted by label replacement |
| Overall Cost-effectiveness | Higher upfront investment but better operational efficiency and ROI over time, especially for frequent price changes or large inventories | Lower upfront cost but higher ongoing labor and error costs |
Traditional paper labels seem inexpensive at first, but they require significant labor for frequent price changes. In contrast, electronic shelf labels offer long-term savings and greater efficiency.
Infrared Communication for Price Updates
Infrared technology played a key role in the first electronic shelf label systems. Retailers used infrared signals to transmit price updates from a central system to each label. This method enabled timely and accurate updates, but it also introduced some limitations:
- Infrared communication required a direct line-of-sight between the transmitter and the labels.
- The transmission range was limited, and signals could not pass through barriers.
- Communication was typically one-to-one and lacked security features.
- Infrared transceivers were affordable and suitable for short-range use.
Note: Infrared communication made early electronic shelf label systems possible, but its limitations led to the development of more advanced wireless protocols in later generations.
Impact on Retail Price Management
The combination of LCD displays and infrared communication transformed how retailers managed prices. The new system enabled centralized control, allowing managers to change prices across thousands of labels instantly. Wireless updates reduced the need for manual labor and minimized errors. Every label could synchronize within seconds, ensuring price accuracy throughout the store.
- Centralized control allowed retailers to manage all prices from a single system.
- Wireless updates using infrared technology enabled real-time communication with each label.
- Instant synchronization eliminated delays and reduced pricing mistakes.
Electronic shelf labels improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced the customer experience. These innovations laid the groundwork for future advancements in electronic shelf label technology.
Second Generation Electronic Shelf Labels: E-Paper and Wireless Advances
E-Paper Displays and Enhanced Prices Visibility
Retailers adopted e-paper displays in electronic shelf label systems to address the limitations of LCD technology. E-paper displays use bi-stable technology, which consumes power only during updates. This feature allows labels to operate for years without frequent battery changes. The table below highlights the differences between e-paper and LCD displays:
| Feature | E-Paper ESLs | LCD ESLs |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | Very low; power only used when updating label | Higher; requires constant refreshing |
| Readability | High contrast, excellent in bright/direct sunlight | High resolution and color variety, but less readable in bright light |
| Durability | Long lifespan, minimal maintenance | Shorter lifespan, more maintenance |
| Use Case | Ideal for static info like prices in grocery/pharmacy | Better for dynamic/promotional content in fashion/electronics |
| Operational Cost | Lower due to energy efficiency and durability | Higher due to power and maintenance needs |
E-paper displays provide high contrast and clear visibility, even in direct sunlight. This improvement ensures that prices remain readable for customers at all times. Retailers benefit from reduced maintenance and lower operational costs, making e-paper labels ideal for grocery and pharmacy environments.
Wireless Communication and Real-Time Price Updates
Second-generation electronic shelf labels introduced advanced wireless communication technologies. Bluetooth Core 5.4 enables a single access point to broadcast updates to thousands of labels simultaneously. This capability allows retailers to update prices across the store in seconds. The label management software coordinates these updates, reducing manual intervention and errors.
- Bluetooth wireless standards support scalable, secure communication.
- Bidirectional communication lets labels confirm updates and report stock status.
- Interactive features, such as flashing labels, assist shoppers and staff.
- The open Bluetooth standard supports cost-efficient, flexible deployments.
E-paper ESLs with integrated Bluetooth chipsets use less material and energy, aligning with sustainability goals. Retailers can manage digital price tags and inventory efficiently, improving the overall shopping experience.
Improvements in Battery Life and Usability
E-paper displays and optimized wireless communication have extended battery life in electronic shelf labels. Modern labels can operate for five to ten years, depending on update frequency and environmental conditions. The label management software tracks battery status and schedules maintenance, reducing electronic waste and operational costs.
Retailers experience fewer battery replacements and less downtime. The digital price tag system supports frequent price changes without increasing maintenance. Enhanced usability and reliability make second-generation electronic shelf label systems suitable for large-scale deployments in retail chains.
Note: Advances in display quality, battery life, and wireless connectivity have made electronic shelf labels more affordable and flexible for retailers, supporting efficient label management software and scalable operations.
Third Generation Electronic Shelf Labels: Smart Features and Integration

Real-Time Prices and Cloud Connectivity
Third-generation electronic shelf label systems rely on cloud connectivity to deliver real-time price updates and advanced analytics. Retailers use centralized cloud software to manage prices across multiple locations. The system transmits updates wirelessly using Wi-Fi, RF, or Bluetooth Low Energy, depending on store infrastructure.
- Electronic shelf labels receive instant price changes for promotions, markdowns, or competitor-based adjustments.
- Cloud-based label management software enables remote control and automation, reducing manual labor and operational inefficiencies.
- Integration with data analytics and AI allows retailers to analyze product pricing trends and optimize promotions in real time.
- Customers benefit from consistent online and in-store pricing, which builds trust and loyalty.
- Automation ensures accurate shelf tags and checkout prices, eliminating costly errors.
Geo-Location and Personalized Pricing
Modern label management software supports geo-location features that enhance the shopping experience. Retailers can use Bluetooth beacons and sensors to detect customer locations within the store. This technology enables dynamic pricing and targeted promotions based on shopper proximity.
For example, a customer near a specific aisle may see a special offer displayed on the electronic shelf label. Personalized pricing strategies become possible, allowing retailers to respond quickly to changing demand and inventory levels.
Note: Geo-location and dynamic pricing help retailers maximize sales and improve customer engagement by delivering relevant offers at the right moment.
Integration with Retail Management Systems
Retailers achieve seamless operations by integrating electronic shelf labels with retail management systems.
- Label management software synchronizes with pricing databases, POS, and inventory systems for real-time updates.
- Automation ensures price consistency between shelf and checkout, reducing errors and supporting dynamic pricing.
- Interactive features, such as QR codes and NFC, enhance customer engagement and streamline product pricing information.
- Integration reduces labor costs, improves efficiency, and supports sustainability by minimizing paper waste.
- Ongoing optimization keeps the electronic shelf label system aligned with evolving retailer needs.
Retailers like Maple Grocers have improved price management accuracy and allowed staff to focus on customer service by integrating label management software with ERP and POS platforms.
The Impact of Electronic Shelf Labels on Retail and Prices
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
Retailers have transformed their operations by adopting electronic shelf label systems. These systems automate price updates, which eliminates the need for manual label changes and reduces labor costs. Staff can now focus on customer service instead of spending hours updating price tags. In a typical grocery environment, label management software enables rapid, large-scale updates across thousands of products, ensuring that grocery store prices remain accurate and consistent.
- Staff time is freed from repetitive tasks, allowing more attention to customer needs.
- Instant price updates synchronize prices across all locations, supporting dynamic pricing strategies.
- Bulk updates allow thousands of labels to change within minutes, drastically reducing labor costs.
- The risk of human error decreases, which minimizes discrepancies between shelf and checkout prices.
- Lower compliance risks result from accurate, up-to-date product information.
Major retailers have reported substantial cost savings after switching from paper labels to electronic shelf labels. For example, a mid-sized store managing 10,000 price tags can save about $54,000 annually by eliminating manual updates, reducing energy costs, and avoiding losses from pricing errors. The initial investment in electronic shelf label technology can be recovered in under two years, with larger grocery chains often seeing payback within a year, especially when label management software is combined with AI-based price optimization. These savings support smarter retail decision-making and improve overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Shopping Experience and Price Transparency
Electronic shelf labels have improved the shopping experience for consumers in several ways. Real-time updates and interactive features bridge the gap between online and offline shopping. Shoppers benefit from accurate, up-to-date prices and clear product information, which reduces confusion and builds trust.
- Real-time updates ensure that customers always see the correct prices, eliminating surprises at checkout.
- Flash promotions, time-sensitive discounts, and interactive QR codes engage shoppers and encourage purchases.
- Integration with label management software allows stores to display detailed product descriptions, user reviews, and stock status.
- Price transparency increases customer confidence and satisfaction, as prices on the shelf always match those at the register.
- Dynamic pricing and instant promotions help stores respond quickly to market changes, especially in grocery and food prices.
A research study involving over 300 participants found that electronic shelf label features positively influence customer well-being. Shoppers reported greater happiness and satisfaction, which led to positive postpurchase behaviors such as a willingness to pay premium prices and share positive experiences. In addition, stores using label management software experienced increased sales and stronger customer retention. By providing accurate, transparent pricing and interactive engagement, electronic shelf labels enhance the overall shopping experience.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
The adoption of electronic shelf labels supports sustainability in retail. Traditional paper labels require frequent replacement, generating significant waste and consuming resources such as wood pulp, ink, and adhesives. In contrast, electronic shelf labels use durable, reusable materials and energy-efficient e-ink technology.
| Environmental Aspect | Paper Labels | Electronic Shelf Labels (ESLs) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Use | Single-use, short-lived materials | Durable, reusable components; long lifespan |
| Waste Generation | High, frequent replacements | Minimal, long-lasting and recyclable |
| Carbon Emissions | High from production and transport | Reduced due to fewer replacements |
| Energy Consumption | Continuous for manufacturing/printing | Very low; e-ink uses power only during updates |
| Recycling & Reuse | Limited, often difficult | Up to 99% material recovery possible |
Electronic shelf labels reduce raw material consumption, waste generation, and carbon emissions. Batteries in these labels can last five to ten years, and most components are recyclable or refurbishable. By eliminating the need for continuous printing and frequent deliveries of paper and ink, stores lower their environmental footprint. Label management software further supports sustainable practices by enabling efficient, paperless operations. Grocery retailers, in particular, benefit from these environmental advantages as they manage large inventories and frequent price changes.
Electronic shelf labels not only improve operational efficiency and customer experience but also help retailers achieve their sustainability goals.
Technological milestones have transformed electronic shelf labels from simple digital price displays to advanced IoT devices with customizable features, real-time updates, and energy-efficient designs. Retailers continue to invest in automation and AI, driving rapid market growth and innovation. Understanding the evolution of electronic shelf labels helps both retailers and consumers appreciate improvements in pricing accuracy, operational efficiency, and customer engagement.
The future promises smarter, more connected store environments, where electronic shelf labels play a central role in shaping retail strategies.
- Key innovations include e-paper displays, Bluetooth connectivity, and integration with cloud management systems.
- Adoption patterns highlight the need for regulatory compliance, infrastructure readiness, and tailored solutions across regions.
FAQ
What is an electronic shelf label (ESL)?
An electronic shelf label is a digital display device that shows product prices and information on retail shelves. Retailers use ESLs to automate price updates and improve accuracy in stores.
How do electronic shelf labels receive price updates?
Most ESLs receive price updates wirelessly through radio frequency, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi. The store’s central system sends new prices directly to each label, ensuring fast and synchronized changes.
Are electronic shelf labels environmentally friendly?
Electronic shelf labels reduce paper waste and energy use. E-paper displays consume power only during updates. Most components are recyclable, which supports sustainability goals in retail environments.
Can electronic shelf labels display more than just prices?
Yes. ESLs can show product details, stock levels, QR codes, and promotional messages. Advanced models support interactive features that enhance the shopping experience for customers.


