
RFID technology transforms retail operations by enabling instant, remote updates to Electronic Shelf Labels. Retailers using RFID see a dramatic shift in efficiency. RFID allows staff to update every ESL Price Tag through a centralized system, eliminating manual labor. RFID connection through an ESL Gateway AP automates the process, saving up to 12 hours per week per store and reducing labor costs by approximately 52%. This RFID-driven improvement in Esl Retail means prices on shelves stay accurate in real time. Customers experience fewer discrepancies at checkout, while RFID technology maintains consistent pricing across locations.
Understanding RFID Connection in Electronic Price Tag Networks
What Is RFID?
Radio-frequency identification, or RFID, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track objects automatically. In retail, RFID enables stores to manage inventory and pricing with greater speed and accuracy.
How RFID Works
RFID systems rely on three main components:
- RFID tags: Each tag contains a microchip and antenna. The microchip stores unique data, while the antenna enables wireless communication.
- RFID readers: These devices send out radio waves to power passive tags and receive data from them. Readers can be fixed in place or mobile, depending on the store’s needs.
- Software: Middleware and dashboards collect, aggregate, and integrate data from readers with central retail systems.
When an RFID reader emits a signal, it activates the tag’s microchip. The tag then transmits its stored information back to the reader. The reader forwards this data to the network, where software processes and stores it for further use.
Types of RFID Used in Retail
Retail environments typically use three types of RFID tags:
- Passive tags: Powered by the reader’s signal, these tags are cost-effective and suitable for most product tracking network applications.
- Battery-assisted passive tags: These tags use a small battery to boost signal strength, increasing read range.
- Active tags: Equipped with their own power source, active tags offer the longest range and are used for high-value assets.
Most retail RFID systems operate in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) range, between 860 MHz and 960 MHz. This frequency supports fast data transfer and longer read distances, making it ideal for inventory and price management.
What Are Electronic Price Tags?
Electronic price tags, also known as electronic shelf labels, display product prices and information digitally. These tags connect to a central network, allowing stores to update prices instantly and accurately.
Key Features of Electronic Price Tags
- Low energy consumption, often using e-paper technology for long battery life.
- Real-time price updates, supporting dynamic pricing strategies.
- Enhanced readability with wide viewing angles and multi-color displays.
- Support for promotions, QR codes, and inventory status.
- Sustainability benefits, reducing paper waste and operational costs.
Electronic price tags play a vital role in the digital transformation of retail. They help stores adapt to changing consumer behavior and support sustainable business practices.
How Electronic Price Tags Communicate
Electronic price tags communicate through a wireless network, often using RFID technology. Each tag receives updates from a central system via RFID readers and antennas. The network ensures that every price change reaches the correct tag in real time. This process eliminates manual updates and reduces errors, improving operational efficiency.
Note: RFID tags in electronic price tag systems store unique identifiers and communicate wirelessly, enabling fast and accurate data collection.
RFID Connection to Price Tag Networks
Integration Methods
Retailers integrate RFID connection into price tag networks using several methods:
- Direct integration with existing ERP or inventory systems.
- Middleware that manages data flow between RFID readers and central databases.
- Cloud-based dashboards for remote monitoring and control.
These methods ensure seamless communication between RFID tags, readers, and retail management systems.
System Architecture Overview
A typical RFID-enabled price tag network includes:
- RFID tags attached to products or shelves.
- Antennas and readers positioned throughout the store.
- A central software platform that collects, processes, and displays data.
- Secure network connections to transmit information between devices and systems.
This architecture supports real-time product tracking, price updates, and inventory management. RFID microchips in tags enable instant identification, while the network ensures data flows smoothly from the sales floor to the back office.
The RFID-Enabled Price Update Process

Step-by-Step Workflow
Initiating a Price Change
Retailers often need to adjust prices quickly to stay competitive. The process begins when a manager or pricing team decides to update product prices. They enter new pricing information into the central management system. This system connects directly to the rfid network, which manages all electronic price tags in the store. The rfid system ensures that every change starts from a single, secure point of control.
RFID Tag Communication
Once the system receives the new price, it sends the update through the rfid network. Antennas and readers broadcast the information wirelessly to the rfid tags on the shelves. Each tag contains rfid microchips that store unique identifiers and product data. The rfid tags receive the new price and update their displays almost instantly. This process eliminates the need for staff to walk the aisles and change prices by hand.
Tip: RFID tags use secure communication protocols to prevent unauthorized access during updates.
Network Synchronization
After the rfid tags receive the new data, the network synchronizes all tags to ensure consistency. The rfid readers scan each tag to confirm that the update succeeded. If a tag does not respond, the system flags it for further review. The network architecture allows for rapid, store-wide synchronization, so every shelf displays the correct price at the same time.
Confirmation and Error Handling
The rfid system provides real-time confirmation for every price update. The central dashboard displays the status of each tag. If an error occurs, such as a tag failing to update, the system alerts staff immediately. They can then troubleshoot the issue, often by resending the update or replacing the tag. This error handling process ensures that pricing remains accurate and reliable.
Real-Time and Remote Capabilities
Centralized Control
A major advantage of rfid technology lies in its centralized control. Retailers manage all price changes from a single platform, whether for one store or hundreds of locations. The rfid network connects every tag to the central system, allowing instant updates across the entire chain. This approach reduces the risk of inconsistent pricing and streamlines operations.
Store-Level Flexibility
While centralized control offers efficiency, rfid also supports store-level flexibility. Managers can adjust prices for local promotions or inventory changes. The rfid tags respond to both global and local commands, updating displays as needed. This flexibility helps stores react quickly to market trends and customer demand.
Note: RFID tags can support dynamic pricing, enabling retailers to adjust prices throughout the day based on sales data or competitor activity.
The rfid-enabled price update process transforms retail pricing. It combines speed, accuracy, and flexibility, ensuring that every tag displays the correct price in real time. Retailers benefit from reduced labor costs, while customers enjoy up-to-date information and fewer checkout surprises.
Key Benefits of RFID Technology for Retailers
Labor and Cost Savings
Reduced Manual Updates
RFID technology automates price updates, removing the need for staff to manually replace paper tags. Retailers use RFID tags to update prices across thousands of products in seconds. This automation frees employees from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on customer service and store presentation. NFC-enabled electronic price tags further streamline operations by eliminating manual stock checks and reducing labor time.
- Staff no longer spend hours walking aisles to change prices.
- RFID tags enable instant updates, even across multiple locations.
- Employees can dedicate more time to customer engagement.
Lower Operational Costs
Retailers experience significant cost reductions after implementing RFID technology. The use of RFID tags lowers reliance on external service bureaus and reduces printing and paper expenses. Passive RFID tags cost between $0.10 and $0.50 each, making them affordable for large-scale deployment. Apparel retailers often see payback periods of 6 to 12 months due to rapid labor and cost savings. Inventory accuracy improvements also lead to less shrinkage and stock loss, further increasing profitability.
RFID technology reduces retail loss by 20-30% through improved inventory visibility and theft prevention.
Improved Pricing Accuracy
Elimination of Human Error
RFID tags support automated data capture, which reduces errors common in manual barcode scanning. Traditional price tag updates rely on staff to enter data and scan barcodes, which can result in mistakes. RFID technology allows tags to be read without line-of-sight, ensuring faster and more accurate updates. This automation improves accuracy and minimizes discrepancies between shelf and checkout prices.
- Automated updates eliminate manual entry errors.
- RFID tags ensure every price change is applied correctly.
Consistent Pricing Across Locations
Retailers achieve consistent pricing across all stores by using RFID tags and electronic price tags. The central system updates every tag in real time, ensuring that promotions and discounts appear uniformly. ESLs (electronic shelf labels) support dynamic pricing and real-time updates, which traditional tags cannot match. This consistency builds trust with customers and enhances the overall shopping experience.
Real-time tracking and integration with inventory management systems provide up-to-date information and accuracy.
Enhanced Flexibility and Responsiveness
Dynamic Pricing Strategies
RFID technology gives retailers the flexibility to implement dynamic pricing strategies. RFID tags enable real-time product tracking, allowing stores to adjust prices based on sales trends, inventory levels, or competitor activity. This capability supports innovative promotions and rapid response to market changes.
- RFID tags allow for instant price adjustments.
- Retailers can launch flash sales or targeted promotions with ease.
Fast Response to Market Changes
Retailers using RFID technology can respond quickly to supply chain disruptions or shifts in demand. Real-time visibility into inventory and pricing enables faster replenishment and streamlined operations. RFID tags provide the foundation for agile pricing and inventory management, helping retailers stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
RFID technology underpins flexible, responsive retail strategies by improving inventory accuracy and operational efficiency.
RFID and Inventory Management Advantages
Real-Time Stock Tracking
Automated Inventory Updates
RFID technology transforms inventory management by enabling automated updates throughout the retail environment. RFID tags attached to products, cases, or pallets communicate wirelessly with readers, capturing data instantly and accurately. Employees use handheld RFID devices to scan multiple tags at once, which speeds up inventory counts and reduces manual labor. RFID tags do not require line-of-sight scanning, so staff can complete audits in minutes rather than hours. This automation reduces errors and ensures that inventory records stay current.
- RFID tags store unique identifiers and transmit data via radio waves.
- RFID readers in warehouses and on the sales floor detect tagged items automatically.
- The system updates inventory levels in real time, eliminating the need for manual barcode scanning.
- Integration with warehouse management systems and ERP platforms streamlines product tracking from receipt to distribution.
Retailers benefit from improved inventory accuracy, which often reaches over 99%. This level of precision supports better decision-making and reduces operational costs.
Reduced Out-of-Stock Situations
RFID-driven inventory management helps retailers maintain optimal stock levels. Real-time tracking aligns inventory with consumer demand, improving product availability and customer satisfaction. RFID tags provide instant updates on stock movement, allowing staff to identify low-stock items before they run out. The technology also supports faster inventory reconciliation, helping resolve discrepancies quickly.
- RFID tags enable continuous monitoring of inventory on shelves and in backrooms.
- Real-time tracking reduces the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
- Enhanced visibility into inventory levels supports timely replenishment and better shelf availability.
Retailers experience fewer out-of-stock situations, which leads to increased sales and improved customer loyalty.
Integration with Pricing Systems
Synchronized Inventory and Pricing Data
RFID technology enables seamless integration between inventory management and pricing systems. RFID tags update both inventory and price information simultaneously, ensuring consistency across all channels. Staff gain instant access to accurate stock data, which supports efficient replenishment and customer assistance. This synchronization improves inventory accuracy and reduces errors in pricing or stock levels.
- RFID tags communicate with central databases to update inventory and pricing in real time.
- Integration with pricing systems accelerates asset and inventory management processes.
- Retailers achieve enhanced omnichannel fulfillment and stock visibility.
This approach leads to measurable benefits, such as faster restocking, improved operational agility, and significant reductions in losses and shrinkage.
Streamlined Replenishment Processes
RFID-powered inventory management streamlines replenishment by providing real-time visibility into stock levels. RFID tags attached to logistics assets offer precise location information, improving product handling efficiency. Staff can respond quickly to supply chain needs, reducing downtime and excess inventory. Automated inventory checks save time and free employees to focus on customer service.
- RFID tags support predictive maintenance and faster inventory turnover.
- Asset tracking with RFID reduces lease costs and improves equipment utilization.
- Retailers achieve a payback period for RFID investment in as little as a few months, with long-term ROI.
RFID technology delivers a comprehensive solution for inventory management, combining real-time tracking, accurate data, and efficient replenishment to drive retail success.
Key Benefits for Customers
Always Up-to-Date Pricing
Accurate Shelf Prices
Customers expect shelf prices to match what they pay at checkout. rfid-enabled electronic price tags deliver this accuracy by connecting wirelessly to a central pricing database. Every price tag receives instant updates from the system, which eliminates the need for manual changes. Store managers can adjust prices remotely, ensuring that every shelf reflects the latest information. Digital price tags use e-paper displays, which show real-time pricing and promotional details. This technology prevents outdated prices from lingering on shelves.
- rfid systems synchronize shelf prices with point-of-sale systems.
- Automated alerts notify staff if a tag fails to update, maintaining price accuracy.
- E-paper displays remain clear and readable, even in bright lighting.
Customers benefit from knowing that the price they see is always the price they pay.
Fewer Checkout Discrepancies
rfid technology reduces the risk of pricing errors at checkout. When the system updates prices across the store, it ensures that shelf prices and register prices match. This integration minimizes confusion and disputes at the register. Automated processes also reduce human error, which often causes discrepancies in traditional pricing systems. Customers experience smoother transactions and greater confidence in store operations.
Improved Shopping Experience
Clearer Promotions and Discounts
rfid-enabled electronic price tags support dynamic promotions. Stores can launch flash sales or update discounts instantly, displaying new offers on e-paper tags. Customers see accurate, up-to-date promotions as they shop. This clarity helps shoppers make informed decisions and take advantage of deals without confusion. The system also tracks inventory in real time, so promotions only appear on items in stock.
- Promotions update automatically across all relevant products.
- rfid integration ensures that discounts are applied consistently.
Increased Trust in Store Pricing
Trust forms the foundation of a positive shopping experience. rfid technology builds this trust by providing consistent, accurate pricing. Customers no longer worry about mismatched prices or outdated tags. The seamless connection between shelf labels and central systems assures shoppers that stores value transparency. As a result, customers feel more confident in their purchases and more likely to return.
rfid-driven automation creates a seamless, reliable environment for every shopper.
Real-World Examples of RFID Connection in Retail

Carrefour’s RFID-Enabled Electronic Price Tag Network
Implementation Process
Carrefour stands as a leader in retail technology by deploying an RFID-enabled electronic price tag network across more than 1,700 stores worldwide. The company partnered exclusively with Pricer to integrate RFID tags into its digital shelf label system. This process involved connecting RFID tags to a centralized platform, allowing instant price updates and seamless rfid connection throughout each store. Staff placed RFID tags on shelves and products, linking them to the store’s inventory and pricing systems. The network supports real-time communication between RFID tags, readers, and management software, enabling automated workflows and dynamic pricing strategies.
Results and Impact
Carrefour’s RFID connection produced significant improvements in retail operations:
- Pricing accuracy increased to over 90%, cutting pricing errors by 50%.
- Automation of price updates and workflows boosted operational efficiency by more than 60%.
- Staff spent less time on manual price tag updates, focusing on higher-value tasks.
- Real-time, centralized price updates enabled instant storewide changes, supporting dynamic promotions.
- Customers benefited from accurate pricing, interactive features like QR codes, and improved in-store navigation.
- Integration with inventory management improved product availability and reduced out-of-stock incidents.
- Carrefour’s scalable and secure RFID solution positioned the company as an innovator in digital retail.
Carrefour’s RFID tags and rfid connection deliver a seamless, automated pricing environment that enhances both operational efficiency and customer experience.
Walmart’s Use of RFID for Price and Inventory Management
Deployment Strategy
Walmart began its RFID journey in 2003, aiming to improve operational efficiency and cost savings. The company now uses RFID tags at the item level, especially in apparel. Managers attach RFID tags to products, enabling real-time tracking and bulk scanning without line of sight. The rfid connection links tags to inventory and pricing systems, allowing instant updates and accurate stock visibility. Walmart mandates suppliers to tag items, ensuring consistent tracking from manufacturing to the sales floor. The RFID network supports proactive replenishment and streamlines supply chain operations.
Measurable Outcomes
Walmart’s RFID deployment produced measurable results:
- RFID tags provide real-time inventory visibility, achieving accuracy rates up to 95%.
- The technology reduces out-of-stock situations by enabling proactive replenishment.
- RFID tags streamline supply chain operations, improving logistics and reducing costs.
- Enhanced inventory accuracy and order fulfillment improve customer experience by minimizing delays and supporting better product availability.
Walmart’s RFID connection reduces inventory errors, improves replenishment efficiency, and supports better price management. The system helps limit excess inventory, reduces the Bull-whip effect in the supply chain, and ensures correct pricing based on real-time data. RFID tags play a critical role in Walmart’s retail strategy, supporting both operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Addressing Challenges in RFID Technology Integration
Security and Privacy
Data Protection Measures
Retailers face several security and privacy concerns when deploying rfid in stores. These concerns include unauthorized access, cloning, spoofing, inventory manipulation, eavesdropping, and denial-of-service attacks. Attackers may attempt to read rfid tag data without permission, clone tags to create counterfeit products, or manipulate inventory records. Eavesdropping on rfid signals can reveal sensitive store activities or customer behavior. Some rfid tags lack encryption due to limited computing power, making them more vulnerable to attacks.
To address these risks, retailers use a combination of strategies:
- Encryption of rfid tag data to prevent cloning and misuse.
- Authentication protocols and strict access controls for rfid infrastructure.
- Regular software updates and physical security for rfid readers and antennas.
- Locking memory banks and using middleware to block man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Real-time monitoring and inventory audits to detect suspicious activity.
Retailers also comply with regulations such as GDPR, which require transparency and user consent when rfid tags can link to individuals. Most rfid applications focus on tracking products, not personal data, which helps reduce privacy concerns.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
Preventing unauthorized access remains a top priority for retailers using rfid. They implement kill commands to disable tags after purchase, use blocker tags, and apply cryptographically unlinkable pseudonyms. These technical measures help prevent unwanted tracking and protect consumer privacy. Staff receive training to recognize and respond to security threats. Industry experts recommend ongoing dialogue between retailers, technology providers, and consumer advocates to balance efficiency with privacy protection.
Tip: Regular employee training and real-time monitoring help retailers stay ahead of emerging security threats in rfid environments.
Integration with Existing Systems
Compatibility Issues
Integrating rfid with existing retail management and IT systems presents technical challenges. Many retailers must modify software platforms or develop custom middleware to ensure compatibility. The complexity of rfid technology often requires careful planning and testing. Compatibility checks help identify potential conflicts with legacy systems. Retailers may need to update hardware or software to support seamless data exchange between rfid and other business applications.
Staff Training and Change Management
Successful rfid integration depends on effective staff training and change management. Employees must learn how to operate rfid readers, interpret data, and respond to system alerts. Training programs cover both technical skills and security best practices. Change management strategies help staff adapt to new workflows and responsibilities. Clear communication and ongoing support ensure a smooth transition to rfid-enabled operations.
- Staff training addresses technical complexity and security awareness.
- Change management supports adoption and maximizes the benefits of rfid.
Cost of Implementation
Upfront Investment
Retailers encounter significant upfront costs when implementing rfid. Expenses include purchasing tags, readers, antennas, and software. Infrastructure upgrades and integration work add to the initial investment. Despite these costs, many retailers view rfid as a strategic investment that delivers long-term value.
Long-Term ROI
The return on investment for rfid-enabled electronic price tag solutions proves compelling. Industry data shows an average ROI of 182% within 18 months for broad rfid retail implementations. Dynamic pricing applications, which rely on rfid-enabled price tags, achieve ROI in about 11 months. Retailers report substantial reductions in labor costs, improved inventory accuracy, and significant savings from loss prevention.
| RFID Application Area | ROI / Financial Impact | ROI Timeframe | Notes on RFID Price Tag Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall RFID Implementation | Average ROI of 182% | Within 18 months | Broad RFID retail tech ROI including price tags |
| Dynamic Pricing (Sainsbury’s) | Waste reduction 87%, Margin improvement 12%, Labour cost reduction 45% | ROI in 11 months | Dynamic pricing uses RFID-enabled electronic price tags |
| Inventory Accuracy (Marks & Spencer) | £2.8M stock cost reduction, 9.2% sales increase | ROI in 14 months | RFID improves inventory, indirectly supporting pricing |
| Loss Prevention (Next) | £18M shrinkage savings, 75% theft reduction | ROI in 8 months | RFID reduces losses, improving overall ROI |
Retailers who invest in rfid benefit from faster price updates, better inventory management, and increased operational efficiency. These advantages help offset the initial investment and drive long-term profitability.
Future Trends in RFID and Inventory Management
Advancements in RFID Technology
Improved Range and Speed
RFID technology continues to evolve, offering improved range and faster data transmission. New generations of RFID tags and readers now support longer read distances, which allows retailers to track inventory across larger areas with fewer devices. Enhanced speed means that stores can process thousands of items in seconds, making inventory tracking more efficient. These improvements help retailers maintain accurate stock levels and respond quickly to changes in demand. As a result, stores experience better supply chain visibility and smoother operations.
Lower Power Consumption
Manufacturers now design RFID tags with lower power requirements. This advancement extends battery life for active tags and reduces maintenance costs. Passive RFID tags, which do not require batteries, have also become more energy-efficient. Lower power consumption supports sustainable retail practices and allows for the deployment of more tags throughout the supply chain. Retailers benefit from reduced operational expenses and improved environmental impact.
Expanding Use Cases
Beyond Pricing—Inventory and Analytics
RFID now plays a critical role beyond electronic price tag updates. Retailers use RFID tags for real-time inventory tracking across the entire supply chain, from manufacturer to store shelves. This capability provides accurate visibility into stock levels and helps prevent out-of-stock situations. RFID accelerates checkout by automatically detecting every item in a customer’s cart, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction. Stores also combine RFID with computer vision to monitor how products move within the store, such as tracking items left in fitting rooms or misplaced on shelves. This integration enhances inventory tracking, restocking decisions, and promotional strategies.
Retailers leverage RFID data to monitor product quality by linking sales and returns, which helps identify manufacturing issues. Loss prevention improves as RFID tracks product movement and pinpoints where shrinkage occurs. Specialized RFID tags now accommodate diverse product types, including metal objects and liquids, expanding the technology’s reach. Wearable RFID readers for staff further streamline operational workflows in warehouses and stores.
Note: RFID’s expanding use cases support unified commerce, customer experience enhancement, and sustainability efforts.
Integration with Mobile and IoT
The integration of RFID with mobile devices and IoT platforms transforms retail operations. Retailers gain real-time inventory and asset tracking, which improves inventory accuracy and reduces stockouts. Companies like Old Navy use RFID-enabled systems to monitor inventory and fulfill online orders efficiently. This technology streamlines manual inventory checks, supports loss prevention, and enhances customer service.
RFID combined with IoT enables smarter retail operations, such as real-time restocking alerts and personalized mobile promotions. Retailers achieve greater supply chain visibility and operational efficiency. Although challenges remain, including data security and integration complexity, the benefits position retailers for growth and competitive advantage.
RFID technology revolutionizes electronic price tag updates by delivering speed, accuracy, and automation. Retailers achieve real-time inventory tracking, supply chain transparency, and improved customer experiences, as shown below:
| Feature / Aspect | RFID-enabled Electronic Price Tags | Traditional Systems (Paper/Barcode) |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Real-time, automatic updates | Manual, error-prone |
| Customer Experience | Faster checkout, personalized marketing | No impact |
| Maintenance and Costs | Higher initial, lower long-term costs | Lower initial, higher ongoing costs |
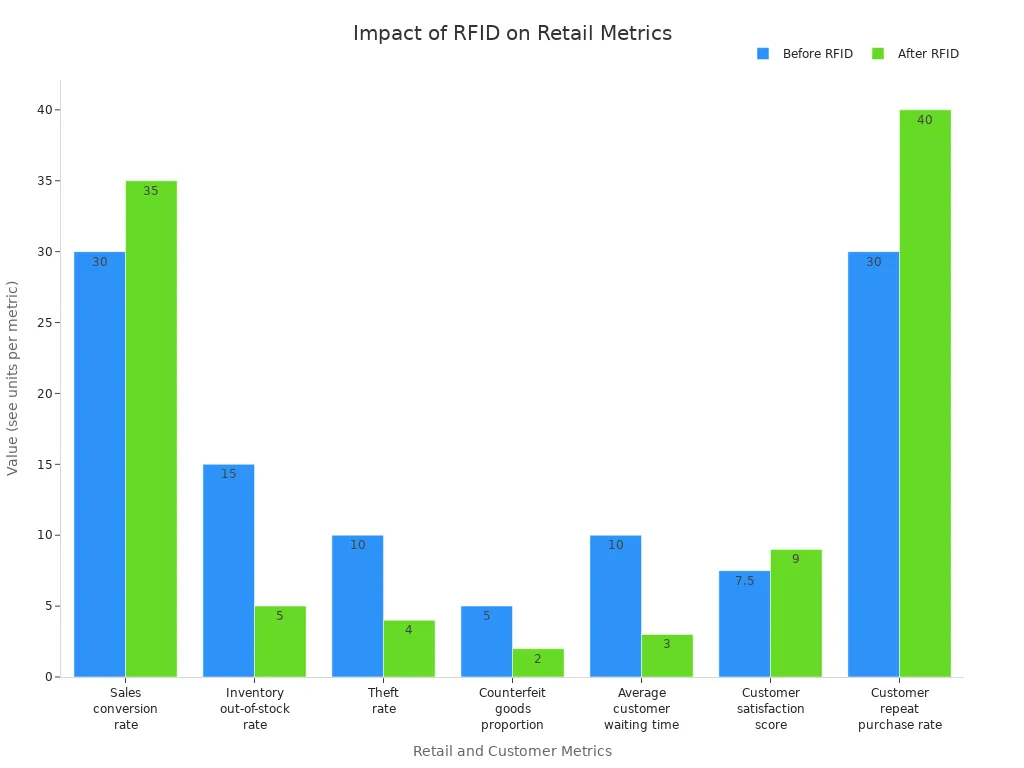
As RFID and electronic price tag networks evolve, retailers can expect innovations such as smart shelves, automated shopping carts, and seamless omnichannel experiences. This ongoing transformation will continue to boost efficiency and customer satisfaction across the retail sector.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using RFID for electronic price tag updates?
RFID enables instant, automated price changes across all shelves. Retailers save time and reduce errors. Customers see accurate prices every time they shop.
How secure is RFID technology in retail environments?
Retailers use encryption, authentication, and regular monitoring to protect RFID systems. These measures help prevent unauthorized access and keep pricing and inventory data safe.
Can RFID electronic price tags integrate with existing store systems?
Most RFID solutions offer middleware or APIs for integration. Retailers can connect RFID tags to inventory, POS, and ERP systems for seamless data flow.
Does RFID technology increase operational costs?
Initial investment in RFID hardware and software can be significant. Over time, retailers often see lower labor costs, reduced errors, and improved efficiency, which offset the upfront expense.
How do RFID price tags improve the customer experience?
RFID tags ensure shelf prices match checkout prices. Customers benefit from fewer pricing errors, clearer promotions, and faster service.
What happens if an RFID tag fails to update?
The system flags the tag for review. Staff receive alerts and can resend updates or replace the tag. This process maintains pricing accuracy throughout the store.
Are RFID tags reusable or recyclable?
Many RFID tags are designed for single use, especially in retail. Some manufacturers offer recyclable or reusable options to support sustainability goals.


