
You face several challenges when deploying electronic price tag systems in Esl Retail environments. Interference from electromagnetic interference, physical barriers, and environmental factors can disrupt signal reliability. Proper rfid antenna placement and careful management of rfid interference help you maintain accuracy. You should consider the impact of signal obstacles in store design and always use shielding to minimize electromagnetic interference. Consistent maintenance of Electronic Shelf Labels, ESL Price Tag units, and ESL Gateway AP devices reduces unexpected disruptions in your rfid network.
Tip: Regularly inspect rfid hardware and adjust placement for optimal performance.
Electronic Price Tag Signal Interference: Causes and Solutions
Electromagnetic Interference in Electronic Price Tags
Common EMI Sources in Retail
You encounter electromagnetic interference from many sources in retail environments. These sources disrupt the signal between your electronic price tag and its reader. The most common sources include:
- Wireless computer networks
- Wireless phones
- Microwave ovens
- Neon lights
- Security alarms
Security tags often trigger false alarms due to electromagnetic interference. Improper deactivation or tag malfunction can also cause issues. You improve customer experience by understanding and addressing these causes. AM (Acousto Magnetic) technology resists electromagnetic interference better than RF (Radio Frequency) systems. RF systems often experience false alarms from electronic devices and metallic objects, such as shopping carts or store fixtures. AM systems perform more reliably in areas with high metal content or strong electromagnetic fields.
Filtering and Shielding Solutions
You reduce electromagnetic interference by using effective filtering and shielding. Filtering removes unwanted frequencies from the signal path. You can use passive filters to maintain signal purity and prevent noise from entering sensitive circuits. Shielding blocks external electromagnetic fields from reaching your electronic price tag system. You should select conductive or magnetic shielding materials for displays and cables. Display wraps and bond line gap shielding further protect your devices from electromagnetic interference.
Proper Grounding Techniques
Grounding provides a safe path for stray electromagnetic energy. You must separate digital and analog grounds on your printed circuit boards. This separation prevents interference between different types of signals. Proper grounding strategies ensure that electromagnetic energy does not disrupt your electronic price tag system. You should connect all metal parts to a common ground point to minimize electromagnetic interference.
Cable Routing and Management
Cable routing plays a key role in reducing electromagnetic interference. You should keep signal cables away from power lines and sources of electromagnetic noise. Twisted pair wiring helps cancel out electromagnetic fields and maintains signal integrity. You must avoid running cables near neon lights, microwave ovens, or wireless routers. Organized cable management reduces the risk of interference and improves the reliability of your electronic price tag system.
Physical Obstructions and Their Impact
Store Layout and Building Materials
Physical barriers in your store can weaken or block the signal between electronic price tags and readers. Thick walls, metal shelves, and reinforced concrete create significant obstacles. You should consider the impact of building materials when planning your store layout. Open spaces and non-metallic fixtures allow signals to travel more freely. You improve system performance by minimizing obstructions in key areas.
Best Practices for Tag and Reader Placement
Proper placement of electronic price tags and readers ensures reliable communication. You should position readers at elevated locations with a clear line of sight to the tags. Avoid placing tags near dense clusters of metal objects or electronic devices. Spacing readers evenly throughout the store prevents signal overlap and reduces electromagnetic interference. You maintain strong connections by regularly reviewing and adjusting tag and reader placement.
Environmental Factors Affecting Electronic Price Tags
Temperature and Humidity
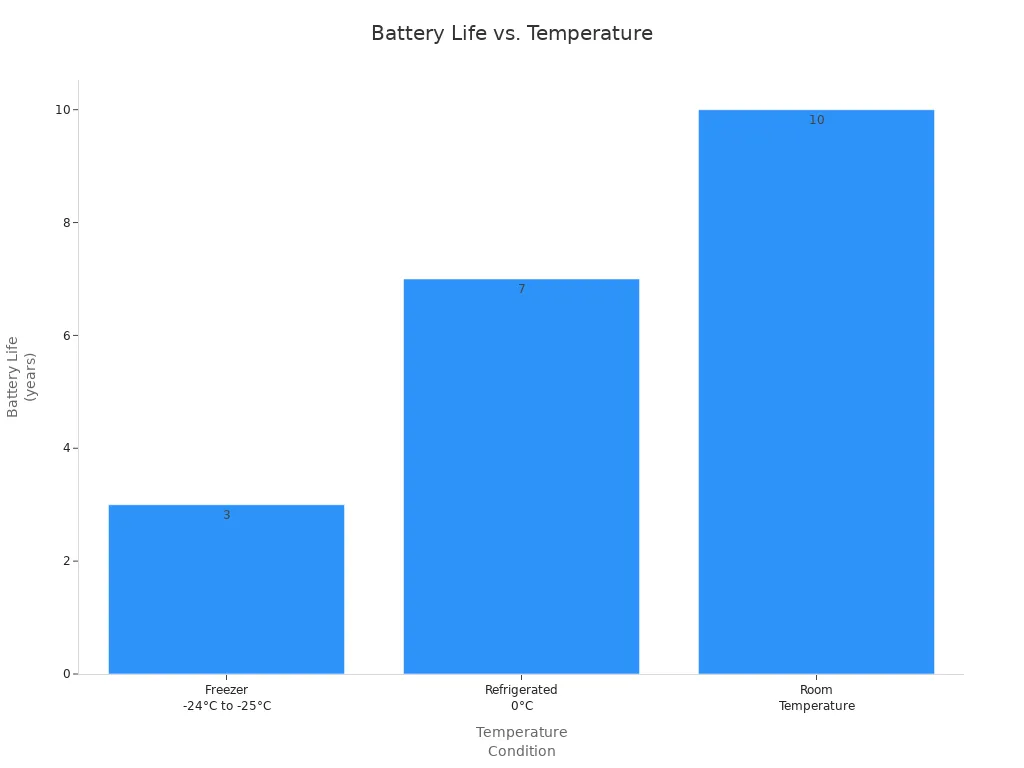
Environmental conditions directly affect the reliability of your electronic price tag system. Temperature changes impact battery life and signal quality. For example, freezer conditions (-24°C to -25°C) reduce battery life to about 3 years. Refrigerated environments (around 0°C) extend battery life to 7 years. Room temperature conditions provide up to 10 years of battery life. Tags designed for freezer use often include IP67 protection to resist dust and moisture. High humidity can damage battery chemistry and internal electronics, reducing reliability. High temperatures accelerate battery self-discharge, while extreme cold lowers battery capacity. You should place tags away from direct sunlight and heat sources to maintain performance.
| Environment | Approximate Battery Life | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| Freezer (-24°C) | 3 years | IP67 protection |
| Refrigerated (0°C) | 7 years | Moisture resistance |
| Room Temperature | 10 years | Standard protection |
Seasonal and Temporary Interference
Seasonal changes introduce new sources of electromagnetic interference. Holiday decorations, temporary lighting, and additional electronic displays can disrupt your signal. You should monitor your system during peak seasons and adjust placement as needed. Temporary construction or store rearrangements may also affect signal quality. Regular inspections help you identify and resolve new sources of electromagnetic interference quickly.
RFID Interference in Electronic Price Tag Systems

RFID interference presents a significant challenge in electronic price tag systems. You often encounter disruptions caused by electromagnetic interference generated by both RFID tags and readers. This interference can impact the accuracy and reliability of your pricing displays. Technical literature highlights that EMI from RFID transmissions, including differences in modulation rates, stands as a primary cause of performance issues in these systems. You must address these challenges to maintain seamless retail operations.
Overlapping Frequencies and Channel Management
Assigning Non-Overlapping Channels
Incorrect RFID frequency selection increases the risk of interference between devices. You should assign non-overlapping channels to each RFID reader in your store. This approach prevents signals from colliding and ensures that each reader communicates with its tags without disruption. Channel management becomes especially important in environments with many RFID devices operating simultaneously. You reduce the likelihood of rfid interference by carefully planning your frequency assignments.
Frequency-Hopping and Timing Protocols
RFID frequency and protocol adjustments play a crucial role in minimizing rfid interference. Frequency-hopping protocols allow your system to switch between different frequencies, reducing the chance of persistent interference on a single channel. Timing protocols further help by scheduling transmissions so that readers and tags do not communicate at the same time. These strategies ensure that your electronic price tag system remains robust, even in busy retail environments.
Reader-to-Reader Interference Solutions
Optimal Reader Spacing
Reader-to-reader interference occurs when multiple RFID readers operate too closely together. You can prevent this by spacing your readers strategically throughout the store. Proper placement avoids crosstalk and signal overlap, which often lead to rfid interference. You should also consider the layout of your tags to prevent simultaneous reading and data collisions. Optimizing tag and reader positions reduces the risk of interference and improves system performance.
Adjusting Transmission Power
You control rfid interference by adjusting the transmission power of your RFID readers. Lowering the power setting minimizes the range of each reader, reducing the chance of overlapping signals. This adjustment helps you target specific areas without causing unnecessary interference in adjacent zones. Installing filters to block unwanted signals and using shielding materials further contain the RFID signal within designated areas. Improved anti-collision protocols enable your system to read multiple tags sequentially, preventing data collisions and enhancing reliability.
Tip: Regularly review your RFID reader layout and power settings to adapt to changes in your store environment.
You maintain a high-performing electronic price tag system by combining these strategies. Addressing rfid interference through careful planning, technology selection, and ongoing adjustments ensures accurate pricing and smooth retail operations.
Proper RFID Antenna Placement for Reliable Performance

Strategic Antenna Positioning
Elevation and Line-of-Sight Considerations
You maximize the reliability of your electronic price tag system by focusing on strategic RFID antenna positioning. Elevating antennas above aisles or shelving units allows you to create a clear line of sight between the antenna and RFID tags. This approach ensures that tags pass directly through the antenna’s field of view, which increases read accuracy and reduces missed scans. You should orient antennas to direct the strongest signal toward the tags, sometimes by tilting or aiming them for optimal coverage. Adjusting antenna parameters, such as impedance and polarization, further enhances signal transmission. Performance testing with professional RFID tools helps you fine-tune antenna position, angle, and distance for the best results.
Tip: Always test different antenna placements and orientations before final installation to identify the most effective configuration for your store layout.
Avoiding Dense Clusters and Metal Surfaces
You avoid poor RFID antenna placement by keeping antennas away from dense clusters of metal objects and sources of electromagnetic interference. Metal shelves, shopping carts, and electronic equipment can reflect or absorb radio waves, causing signal disruption. You should maintain a moderate distance between antennas and RFID tags to prevent signal attenuation. Placing antennas away from wireless devices and electrical equipment also minimizes interference. When you use multiple antennas, space them at least half a wavelength apart to reduce crosstalk and increase tag read reliability.
Antenna Selection for Challenging Environments
Tags for Metal and High-Moisture Areas
You face unique challenges when deploying RFID in environments with high metal content or moisture. Metal and liquid interference can significantly reduce read range and reliability. On-metal or metal-mount RFID tags use spacers or shielding to maintain signal integrity on metal surfaces. In areas with high moisture, such as refrigerated sections or near liquids, you select RFID tags with special coatings or those designed for use in liquids. These tags operate on frequency bands less affected by water absorption, ensuring stable performance. Adjusting reader transmit power and frequency settings further optimizes antenna performance in these demanding conditions.
- Metal environments: Use on-metal or metal-mount tags with built-in shielding.
- Moisture-rich areas: Choose tags with protective coatings or those designed for liquid environments.
- Adjust reader settings: Modify transmit power and frequency to suit the environment.
Single-Hop Network Architecture
You improve system reliability in complex retail spaces by considering single-hop network architecture. This design reduces the number of communication steps between the RFID tag and the reader, which minimizes the risk of signal loss or interference. Strategic placement of readers and antennas ensures that each tag communicates directly with a nearby reader, even in areas with high electronic noise or physical obstructions. You achieve optimal read rates and maintain accurate pricing information throughout your store by combining proper rfid antenna placement with the right tag technology.
Solutions for Electromagnetic Interference in Electronic Price Tags
Shielding and Display Wraps
Conductive and Magnetic Shielding Materials
You can significantly reduce electromagnetic interference in your electronic price tag installations by selecting the right shielding materials. Advanced shielding materials, such as pre-tin plated steel, aluminum, and copper, offer strong electromagnetic compatibility and durability. Each material provides unique benefits for electromagnetic protection. The table below outlines the most effective options for electromagnetic shielding:
| Material | Key Properties | Typical Use Cases and Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Tin Plated Steel | Conductive, corrosion resistant, affordable | Electronic housings needing durability and shielding |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, highly conductive | Consumer electronics, reflection and absorption |
| Copper | Very high conductivity, absorbs EMI as heat | Sheets, foils, meshes; effective but more costly |
| Copper Alloy 770 | Moderate conductivity, corrosion resistant | Connectors, enclosures with aesthetic appeal |
| Film, Tape & Foil | Thin, flexible metallic layers (Al, Cu) | Wrap cables and irregular shapes without adding weight |
| Silicone (with metal) | Flexible, moldable, durable | EMI shielding with environmental sealing, temperature tolerant |
| Carbon Foam | Lightweight, flexible, corrosion resistant | Panels, inserts for EMI and thermal management |
| EMI Shielding Fabric | Polyester/nylon with conductive metal fibers | Mild EMI protection, flexible for irregular shapes |
Copper and aluminum stand out for their high conductivity and effectiveness in electromagnetic compatibility applications. You should match the material to your store’s needs and budget.
Display Wraps and Bond Line Gap Shielding
Display wraps and bond line gap shielding provide flexible solutions for electromagnetic interference. You can use metallic films, tapes, or foils to wrap cables and cover irregular components. These wraps block electromagnetic fields and prevent signal leakage. Silicone-based wraps with embedded metal particles offer both electromagnetic shielding and environmental protection. Bond line gap shielding fills small gaps in device enclosures, stopping electromagnetic energy from escaping or entering. You improve electromagnetic compatibility by applying these wraps and seals to your electronic price tag displays.
Filtering and Twisted Pair Wiring
Passive Filters for Signal Purity
You maintain signal purity by using passive filters in your electronic price tag systems. Filtering removes unwanted electromagnetic noise from your signal lines. Passive filters, such as capacitors and inductors, block high-frequency electromagnetic interference and allow only the desired signals to pass. You should place these filters close to sensitive components for maximum effectiveness.
Twisted Pair Signal Wiring
Twisted pair wiring offers a practical solution for reducing electromagnetic interference. By twisting two conductors together, you cancel out electromagnetic fields from external sources and between pairs. Adding foil shielding to twisted pairs further limits crosstalk and enhances signal purity. You can also use overall cable shielding, such as foil or braided shields, to create a barrier against electromagnetic noise. These rfid shielding techniques ensure reliable communication between your electronic price tags and readers.
- Twisted pair wiring reduces crosstalk and electromagnetic noise.
- Foil shielding on cables blocks external electromagnetic interference.
- Proper grounding of cable shields diverts unwanted energy away from signal lines.
Grounding and PCB Design
Digital and Analog Ground Separation
You improve electromagnetic compatibility by separating digital and analog grounds on your printed circuit boards. Grouping related subcircuits and keeping trace lengths short prevents noise from spreading. You should avoid splitting ground planes under distributed lines, as this can increase electromagnetic interference. Decoupling capacitors placed near IC power and ground pins help smooth voltage and reduce electromagnetic noise.
Proper Grounding Strategies
Effective grounding strategies protect your electronic price tag hardware from electromagnetic interference. Use a single common ground point, known as a star ground, to prevent ground loops. Solid, dedicated ground planes improve both power and signal integrity. You should minimize the number of vias in ground paths and keep sensitive routing on a single PCB layer when possible. Metal enclosures act as Faraday cages, shielding your circuits from external electromagnetic fields. By following these solutions, you ensure robust electromagnetic compatibility and reliable operation for your electronic price tag systems.
Selecting and Maintaining Interference-Resistant Electronic Price Tags
Choosing the Right Tag Technology
Enhanced Interference Immunity Features
You need to select electronic price tags that offer strong resistance to interference. Start by evaluating the communication modules in your rfid tags. Look for models that support a minimum average transmission distance of 30 meters. This feature helps maintain signal integrity across your retail space. Choose tags that operate on multiple RF channels—over 60 channels is ideal. This capability allows your rfid system to optimize communication and avoid crowded frequencies. Reliable rfid tags use advanced transmission types and encryption security. These features ensure your data remains accurate and protected from external interference. Durable hardware also plays a role. Select tags that withstand shock, dust, and water. These qualities help your rfid devices maintain stable signals even in challenging environments.
Note: Durable rfid tags reduce the risk of signal loss caused by accidental drops or exposure to moisture.
Compatibility with Store Infrastructure
You must ensure your rfid tags and devices work seamlessly with your store’s infrastructure. Assess the physical layout of your store. Open spaces allow radiofrequency signals to travel freely. Avoid placing rfid devices near thick walls or metal shelves, which can block signals. Select tags that synchronize quickly with your rfid network. Fast and efficient updates help your system maintain accurate pricing and reduce communication errors. Compatibility with your existing rfid readers and access points ensures smooth integration. Always verify that your chosen rfid devices support the protocols and frequencies used in your store.
| Selection Criteria | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Minimum 30m transmission distance | Maintains signal strength across large areas |
| Multiple RF channels (>60) | Reduces interference and optimizes communication |
| Durable, water/dust-resistant tags | Ensures reliability in harsh environments |
| Fast update support | Keeps pricing accurate and synchronized |
| Encryption and secure transmission | Protects data from external interference |
Maintenance and Firmware Updates
Scheduled Inspections and Testing
You keep your rfid devices performing at their best through regular inspections. Schedule routine checks to identify weak signals, battery issues, or physical damage. Test your rfid tags and readers in different store zones. This practice helps you spot areas with potential interference. Replace or repair any faulty rfid devices immediately. Consistent testing ensures your pricing remains accurate and your system stays reliable.
- Inspect rfid tags and devices weekly.
- Test signal strength in all store sections.
- Replace damaged or weak devices promptly.
Keeping Software and Firmware Up to Date
You maintain system reliability by updating the software and firmware on your rfid devices. Manufacturers release updates to improve interference immunity and fix bugs. Set reminders to check for new firmware versions regularly. Apply updates during low-traffic hours to avoid disrupting store operations. Updated rfid devices adapt better to changing interference sources and store layouts. You also gain access to new features that enhance security and performance.
Tip: Always back up your rfid system settings before performing firmware updates.
Troubleshooting Checklist and Quick Solutions
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Initial Checks and Diagnostics
You should start troubleshooting by performing a thorough site survey. Walk through your store and look for potential sources of interference. Other electronic devices, power sources, and even large physical structures can disrupt your electronic price tag system. Use signal tracing tools or spectrum analyzers to pinpoint areas where the signal drops or becomes unstable. Check all devices for visible damage or loose connections. Make sure each device is powered on and communicating with the network. If you find any disconnected or malfunctioning devices, reconnect or replace them immediately.
Isolating the Source of Interference
Once you complete your initial checks, focus on isolating the specific source of interference. Follow these steps to identify and address the problem:
- Conduct a site survey to locate possible interference sources, such as nearby electronic devices or large metal fixtures.
- Use signal tracing and spectrum analysis to pinpoint the exact location of the interference.
- Apply shielding by wrapping affected devices or cables in conductive material to block unwanted signals.
- Install filters on power supplies or signal lines to remove unwanted frequencies.
- Implement proper grounding by connecting devices to a ground plane or rod, which reduces electromagnetic radiation and improves performance.
Tip: Document each step as you go. This record helps you track changes and identify recurring issues.
Quick Solutions for Immediate Resolution
Resetting Devices and Systems
If you need a fast fix, try resetting your devices and systems. Power cycling often clears temporary glitches and restores normal operation. You can also switch to dedicated RF frequencies to reduce interference from other wireless equipment. Deploying multiple base stations improves coverage and stabilizes the signal, especially in large or crowded areas.
Contacting Technical Support
When quick fixes do not resolve the issue, contact your technical support team. Provide them with details about the interference, the devices affected, and the steps you have already taken. Many modern electronic price tag systems, such as the ESL Maple Series, use advanced frequency-hopping technology. This feature helps maintain stable performance even in environments with high levels of interference. Technical support can guide you through additional troubleshooting or recommend system upgrades if needed.
Note: Regular system monitoring allows you to detect and resolve connectivity issues before they impact your store’s operations.
Best Practices for Preventing Signal Interference in Electronic Price Tags
Proactive Maintenance and Regular Testing
Routine EMI Audits
You protect your electronic price tag system from electromagnetic interference by conducting routine EMI audits. These audits help you identify sources of electromagnetic noise before they disrupt your operations. You should inspect all signal and data lines, checking for proper shielding and grounding. Regularly review your PCB layout to ensure minimal loop areas, which reduces magnetic emissions. Place decoupling and bypass capacitors close to IC power pins to filter high-frequency electromagnetic noise. Apply EMI filters at power inputs and data lines, using capacitors and inductors tailored to the specific interference frequencies. You also need to verify that all components use solid ground planes to avoid ground loops, which can amplify electromagnetic disturbances.
Tip: Schedule EMI audits at least once per quarter to catch emerging electromagnetic issues early.
Staff Training and Awareness
You strengthen your defense against electromagnetic interference by training your staff. Teach your team how to recognize signs of electromagnetic disruption, such as display flickering or inconsistent price updates. Provide clear instructions on how to handle and position electronic price tags to minimize electromagnetic exposure. Encourage staff to report any unusual device behavior immediately. When your team understands the importance of electromagnetic compatibility, you reduce the risk of accidental interference. Staff awareness ensures that everyone contributes to maintaining a stable and interference-free environment.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Adapting to Store Changes
You maintain optimal performance by adapting your electronic price tag system to changes in your store layout or operations. When you move shelves or introduce new electronic equipment, reassess the placement of tags and readers. Use process mapping to visualize electromagnetic bottlenecks and identify redundant steps that may increase electromagnetic exposure. Collaborate with employees to share best practices and recommendations for reducing electromagnetic interference. Implement both incremental improvements, such as repositioning a reader, and strategic overhauls, like upgrading to new electromagnetic shielding materials.
Leveraging High-Quality Electronics
You achieve long-term reliability by selecting high-quality electronic components designed for electromagnetic compatibility. Choose low-emission devices and position them to reduce electromagnetic coupling. Use conductive or magnetic shielding materials to enclose sensitive components, considering the material’s thickness and frequency response. Integrate your electronic price tag system with back-office software to automate updates and monitor electromagnetic performance in real time. Analytics dashboards help you track key performance indicators and detect electromagnetic quality challenges early. By leveraging advanced electronics and automation, you ensure your system remains resilient against electromagnetic threats.
Note: Compliance with standards such as FCC Part 15 and MIL-STD 461 ensures your system meets legal and performance requirements for electromagnetic compatibility.
You can achieve reliable electronic price tag performance by focusing on these proven strategies:
- Place RFID antennas strategically for optimal coverage and accurate scanning.
- Maintain your system with regular inspections and prompt repairs.
- Troubleshoot issues proactively using alerts and reporting tools.
Industry leaders recommend that you:
- Embrace new technology and automation.
- Monitor performance with key indicators.
- Adapt quickly to changes in your retail environment.
Staying vigilant and flexible ensures your pricing remains accurate and your operations run smoothly.
FAQ
What causes the most signal interference in electronic price tags?
You often face interference from electromagnetic sources, physical barriers, and environmental changes. Wireless networks, metal shelves, and seasonal displays can disrupt signals. Regular system checks help you identify and address these issues quickly.
How can you reduce electromagnetic interference in your store?
You can use shielding materials, proper cable management, and grounding techniques. Place antennas away from metal objects and electronic devices. Schedule EMI audits to catch new sources of interference early.
Why do electronic price tags sometimes lose connection?
You may see connection loss due to battery failure, physical obstructions, or overlapping RFID frequencies. Check for damaged tags, blocked signals, or nearby wireless devices that could cause interference.
What is the best way to place RFID antennas for reliable performance?
You should elevate antennas and maintain a clear line of sight to tags. Avoid placing antennas near dense metal clusters or electronic equipment. Test different positions to find the most effective setup for your store.
How often should you inspect and maintain your electronic price tag system?
You should inspect your system weekly. Test signal strength in all store areas and replace weak or damaged devices immediately. Regular maintenance ensures accurate pricing and reliable operation.
Can you fix signal interference issues yourself?
You can resolve many issues by resetting devices, checking connections, and moving antennas. For persistent problems, contact technical support. Keep a troubleshooting log to track recurring issues and solutions.
What features should you look for in interference-resistant electronic price tags?
You should choose tags with multiple RF channels, strong encryption, and durable construction. Look for models that support long transmission distances and fast updates. Compatibility with your store’s infrastructure is essential.


