
Retailers face a choice between what are digital price tags and traditional price tags, each presenting key differences that influence business outcomes. Digital price tags, such as ESL Price Tag systems connected by an ESL Gateway AP, deliver instant updates and reduce human error, while traditional price tags require manual changes and generate more waste. The following table highlights operational and financial impacts that Esl Retail professionals should consider:
| Aspect | Traditional Price Tags | Electronic Shelf Labels (ESL) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low | High; includes tag and infrastructure costs |
| Update Speed | Slow; manual | Instant; automated |
| Error Rate | High; manual errors | Low; automated updates |
| Environmental Impact | High; paper waste | Low; sustainable |
Understanding these key differences helps retailers align technology choices with cost, efficiency, and sustainability goals.
What Are Digital Price Tags and Electronic Shelf Tags?

Definition and Core Features of Digital Price Tags
Retailers often ask, what are digital price tags? These tags, also known as electronic shelf labels, use advanced technology to display product prices and information on digital screens attached to store shelves. Electronic pricing labels connect wirelessly to a central system, allowing retailers to update prices across thousands of products instantly. Core features include real-time price synchronization, integration with inventory systems, and support for dynamic promotions. Many electronic shelf tags offer additional capabilities, such as displaying QR codes or NFC for customer engagement. The adoption of esl technology continues to rise as retailers seek more efficient and accurate pricing solutions.
How Electronic Shelf Labels Work in Retail
Electronic shelf labels operate by linking each tag to a store’s central pricing and inventory management system. When a retailer needs to change a price, the system sends an update to the relevant electronic pricing labels, which then display the new price within seconds. This process eliminates manual updates and reduces the risk of pricing errors. Electronic shelf tags also provide real-time stock data, alerting staff when inventory runs low and guiding them during restocking. In practice, esl systems streamline operations, improve price accuracy, and ensure that shelf prices always match those at checkout. For example, Walmart plans to expand esl to 2,300 stores by 2026, enabling price updates that once took days to complete in just minutes. SPAR Austria has equipped 200 stores with multicolor electronic shelf labels, enhancing both accuracy and visual appeal for customers.
Advantages of Digital Price Tags Over Traditional Price Tags
The shift toward what are digital price tags stems from their clear advantages over traditional paper tags. Electronic shelf labels enable real-time, automated price changes, which significantly reduce labor costs and minimize human error. Retailers benefit from improved operational efficiency, as staff can focus on higher-value tasks instead of manually replacing tags. Electronic pricing labels also support dynamic pricing strategies, allowing stores to adjust prices based on demand, seasonality, or competitor activity. This agility leads to better inventory turnover and optimized margins. Customers experience greater price transparency and consistency, which fosters trust and satisfaction. The global market for esl is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 18.3% from 2024 to 2034, reaching $1.4 billion in 2024. This rapid adoption reflects the value that esl brings to both retailers and shoppers. Additionally, electronic shelf labels contribute to sustainability by reducing paper and ink waste, especially when powered by renewable energy sources.
Note: A field experiment in a large supermarket found that shoppers perceive electronic shelf labels as easy to use and helpful for identifying prices. These labels enhance the store’s image and improve customer experience, supporting their growing adoption in retail.
What Are Traditional Price Tags?
Definition and Types of Traditional Price Tags
Traditional price tags have served as the standard method for displaying product prices in retail for decades. These tags usually consist of paper price tags printed with product information and pricing details. Retailers often place these tags in plastic holders or attach them directly to shelves. The most common types include adhesive paper price tags, hanging tags, and shelf-edge labels. Some stores use laser-printed paper price tags, while others rely on handwritten tags for quick changes. Each type of traditional price tag offers a simple and direct way to communicate pricing to customers.
Retailers choose traditional price tags because they are easy to produce and require minimal technology. Printing paper price tags can be done in-store using standard printers and label forms. This approach allows for flexibility in design and quick adaptation to new promotions or product changes. However, the reliance on paper price tags means that stores must manage a steady supply of printing materials and plastic holders.
How Traditional Price Tags Are Used in Stores
In most retail environments, staff members print batches of paper price tags and manually place them on shelves or products. Employees often walk the aisles to replace outdated tags or update prices during sales events. This process requires careful attention to detail to ensure that each traditional price tag matches the correct product and reflects the current price.
Stores typically schedule regular updates for traditional price tags, especially during weekly promotions or seasonal changes. Staff may spend several hours each week printing, sorting, and installing new paper price tags. The process can become labor-intensive, especially in large stores with thousands of products. Retailers must also monitor for damaged or missing tags, which can lead to pricing confusion for customers.
Note: The manual nature of traditional price tags increases the risk of errors and inconsistencies, especially during busy periods or large-scale price changes.
Limitations of Traditional Price Tags Compared to Electronic Shelf Labels
Traditional price tags present several challenges for modern retailers. The use of paper price tags leads to significant ongoing costs, including printer cartridges, label forms, and maintenance for printing equipment. Employees must repeatedly travel between the office and sales floor to print and replace tags, which increases labor expenses. This manual process also results in wasted paper and plastic, raising environmental concerns.
Traditional price tags cannot match the speed or accuracy of electronic shelf labels. Price updates take longer to implement, and errors can occur if staff miss a tag or enter incorrect information. In contrast, electronic shelf labels allow for instant, automated updates across all products. While ESLs require a higher initial investment, they often recoup costs within a few years due to reduced labor and material expenses. Retailers who rely on traditional price tags may struggle to keep up with dynamic pricing strategies and real-time inventory changes.
A table below summarizes the key limitations:
| Limitation | Traditional Price Tags | Electronic Shelf Labels |
|---|---|---|
| Update Speed | Slow, manual | Instant, automated |
| Labor Costs | High | Low |
| Material Waste | Significant | Minimal |
| Pricing Accuracy | Prone to errors | Highly accurate |
Cost Comparison: Digital Price Tags vs Traditional Price Tags
Initial Investment and Setup Costs
Hardware and Installation for Electronic Shelf Tags
Retailers who choose digital price tags face a higher upfront investment. Each electronic shelf label requires a digital display, wireless communication module, and battery. Stores must also install access points and a central control system to manage the network. Installation often involves configuring each tag and integrating it with existing store layouts. These steps demand both time and technical expertise. The initial cost may seem steep, but it lays the foundation for automation and future savings.
Printing and Material Costs for Traditional Price Tags
Traditional price tags rely on paper price tags, printers, and plastic holders. Retailers must purchase printers capable of handling large volumes of labels. They also need a steady supply of paper price tags and ink cartridges. The cost of these materials adds up quickly, especially in stores with frequent price changes. Staff spend hours printing, cutting, and placing tags on shelves. While the initial outlay for traditional price tags appears low, the recurring expenses for paper price tags and supplies can become significant over time.
Software and Integration for Digital Price Tags
Digital price tags require specialized software to connect with point-of-sale and inventory systems. Retailers must invest in licenses, updates, and integration services. The software enables real-time price updates and ensures that shelf prices match checkout prices. Integration may involve custom development or third-party solutions. Proper setup ensures smooth operation and maximizes the benefits of automation.
Ongoing and Maintenance Costs
Maintenance and Support for Electronic Shelf Labels
Electronic shelf labels need regular maintenance to ensure reliable performance. Batteries in digital price tags last several years but eventually require replacement. Retailers may need technical support for software updates or troubleshooting. Most vendors offer maintenance contracts to cover these needs. The cost of support remains predictable and often lower than the ongoing labor required for traditional systems.
Labor and Time Expenses for Traditional Price Tags
Traditional price tags demand constant attention from staff. Employees must print new paper price tags, replace outdated ones, and check for missing or damaged tags. This manual process consumes valuable time, especially during promotions or seasonal changes. Labor costs rise as staff spend hours each week managing paper price tags. The repetitive nature of these tasks can also lead to fatigue and errors.
Replacement and Upkeep for Both Systems
Both systems require periodic replacement of components. Digital price tags need new batteries and occasional hardware upgrades. Traditional price tags require fresh paper price tags, ink, and replacement of worn plastic holders. The environmental impact of disposing of paper price tags and plastic holders adds to the long-term cost of traditional systems. Digital price tags, while requiring some electronic waste management, reduce the volume of disposable materials.
Long-Term ROI and Value
A thorough cost-benefit analysis helps retailers understand the long-term value of each system. Digital price tags deliver significant labor savings by automating price updates for thousands of products. Retailers report a 95% reduction in the time needed to update prices after switching to electronic shelf labels. Automation nearly eliminates pricing errors, which improves customer satisfaction and reduces complaints. Integration with inventory and POS systems streamlines operations and supports real-time updates.
The following table summarizes key ROI outcomes:
| Aspect | Evidence and Outcome |
|---|---|
| Labor Savings | Digital price tags eliminate manual price changes, saving hours weekly for 1,000-2,000 tags. |
| Time Efficiency | Retailers report a 95% reduction in time needed to update prices after ESL implementation. |
| Pricing Accuracy | Automation nearly eliminates pricing errors by synchronizing with store databases. |
| Operational Efficiency | Integration with POS and inventory systems streamlines operations and reduces errors. |
| Sustainability | Retailers like Lidl reduced paper and ink waste, supporting environmental goals. |
| Real-World Examples | Walmart achieved faster price changes and fewer errors; Lidl realized labor savings. |
| Payback Period | Retailers estimate payback periods by comparing operational savings against initial investment. |
| Implementation Success | Leadership, staff training, and infrastructure upgrades are critical for ROI. |
Retailers who use paper price tags face ongoing material and labor costs. Digital price tags, while requiring a higher initial investment, often pay for themselves within a few years through operational savings. A strategic approach—focusing on quick wins, regular audits, and staff training—ensures that digital price tags continue to deliver value over time. Retailers who prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability find that digital price tags offer a compelling long-term return on investment.
Note: A cost-benefit analysis should consider both tangible benefits, such as labor savings and improved efficiency, and intangible benefits, such as enhanced customer experience and sustainability.
Update Speed and Pricing Accuracy with Electronic Shelf Labels
Real-Time Price Changes Using Digital Price Tags
Electronic shelf labels transform how retailers manage pricing. These esl systems allow stores to make real-time updates across thousands of products with a single command. Staff no longer walk aisles to replace tags by hand. Instead, the central system pushes new prices instantly to every shelf. This process ensures that customers always see the correct price, even during busy sales events or rapid market changes.
Dynamic Pricing Capabilities
Retailers gain a competitive edge with dynamic pricing strategies. Electronic shelf labels support dynamic updates based on demand, time of day, or competitor activity. For example, a store can lower prices on perishable goods as closing time approaches or match a competitor’s flash sale within minutes. This flexibility helps maximize revenue and reduce waste. The esl platform enables dynamic promotions and targeted discounts, which drive both sales and customer satisfaction.
Manual Update Limitations of Traditional Price Tags
Traditional price tags rely on manual labor for every change. Staff must print, cut, and place each tag, which slows down the process. During large promotions, updates can take hours or even days. This delay often leads to mismatched prices between shelves and registers. Manual updates also limit a retailer’s ability to respond quickly to market trends or inventory changes. As a result, stores miss opportunities for dynamic pricing and risk customer frustration.
Error Reduction and Compliance
Accurate pricing remains critical for both customer trust and regulatory compliance. Electronic shelf labels deliver a high level of accuracy by automating updates and syncing directly with inventory systems. This automation nearly eliminates the risk of human error.
Human Error Risks with Traditional Price Tags
Manual processes introduce significant risks. Staff may overlook tags, enter incorrect prices, or forget to update certain products. A 2024 audit found that 24% of retail prices went unchecked, leading to frequent mistakes. These errors can result in lost sales, customer complaints, and even regulatory fines. The annual cost to retailers from pricing mistakes reaches $112 billion, highlighting the impact of inaccuracy.
Automated Accuracy with Electronic Shelf Tags
ESL systems use real-time updates and AI-powered verification to maintain pricing accuracy. These platforms scan over 1,000 tags per minute to detect mismatches instantly. From deployment, digital price tag systems achieve over 90% accuracy. Automation also helps retailers avoid fines, which can reach up to $10,000 per violation. By fixing errors before they affect sales, stores save thousands of dollars each month. The table below summarizes key statistics:
| Statistic / Fact | Description |
|---|---|
| 24% | Percentage of retail prices not checked in a 2024 audit, leading to mistakes |
| 1,000+ tags/minute | Speed at which AI-powered systems scan price tags for mismatches |
| 90%+ accuracy | Initial accuracy rate of digital price tag systems from deployment |
| $112 billion | Annual cost to retailers due to pricing mistakes |
| Thousands of dollars/month | Savings from automating price verification |
| Up to $10,000 | Potential fine per violation avoided through real-time price verification |
Note: Automated esl solutions not only improve compliance but also protect retailers from costly errors and penalties.
Labor and Operational Impact of Choosing Between ESLs and Traditional Price Tags
Staff Workload and Efficiency
Manual Tag Updates for Traditional Price Tags
Traditional price tags require staff to print, cut, and place each tag by hand. Employees spend hours walking aisles, checking for outdated or missing tags, and making sure prices match at checkout. This manual process increases the risk of errors and slows down store operations. Changing paper price tags can take about three minutes per tag, which adds up to several hours for large stores. Staff often need to double-check prices during busy periods, leading to higher labor costs and reduced efficiency.
Automated Updates with Electronic Shelf Labels
ESL systems automate price changes, reducing manual labor and streamlining workflows. Staff can update thousands of prices instantly from a central system. This automation leads to a 60% reduction in workload for price updates, shelf management, and order picking. ESLs also eliminate the need for frequent price checks and overrides at checkout, which speeds up front-end operations. Real-time product status checks via smartphones further reduce manual inventory management. The table below highlights key differences in staff workload and efficiency:
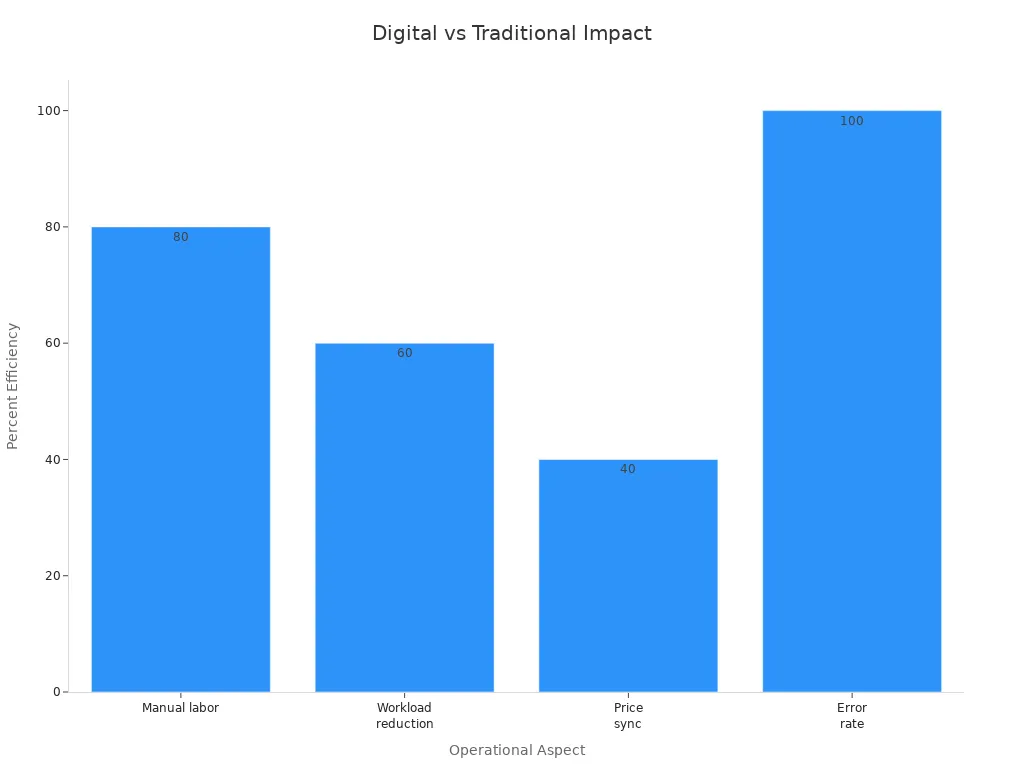
| Aspect | Digital Price Tags (ESLs) Impact | Traditional Price Tags Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Manual labor for price updates | Up to 80% reduction | High manual labor required |
| Workload reduction | 60% reduction in price update, shelf management, order picking | Higher workload due to manual updates |
| Price synchronization speed | 40% faster price synchronization | Slower, manual synchronization |
| Error rate | Elimination of manual errors | Manual errors common |
| Price change implementation | Reduced from hours to seconds | Hours required for manual changes |
Store Operations and Process Streamlining
Time Savings with Digital Price Tags
ESL technology transforms store operations by enabling price updates across the entire store within seconds. Retailers no longer need large teams to handle price changes. Fewer staff can manage more tasks, which reduces labor costs and increases operational efficiency. Integration with inventory systems allows real-time display of stock levels, minimizing out-of-stock situations and reducing the time staff spend checking inventory. Dynamic pricing becomes possible, letting stores quickly match competitor prices or adjust prices based on demand.
- ESLs improve pricing accuracy by minimizing human error and allowing quick corrections.
- Bluetooth Low Energy integration with ESLs provides customer heat mapping, offering insights into customer behavior and store layout optimization.
- Sustainability benefits include elimination of paper use and reduced printer maintenance costs, with ESL batteries lasting up to five years.
Retailers like Target and Amazon Go have adopted ESLs to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Training and Transition Considerations
Transitioning to ESLs requires initial staff training on new systems and processes. Employees must learn to operate the central management software and understand how ESLs integrate with inventory and POS systems. Most staff adapt quickly, as ESL interfaces are designed for ease of use. Ongoing support ensures that employees can troubleshoot minor issues and maximize the benefits of automation. Over time, the reduction in manual tasks allows staff to focus on customer service and other high-value activities.
Tip: Investing in comprehensive training during the transition phase helps staff embrace new technology and ensures a smooth shift to automated pricing.
Customer Experience: Digital Price Tags vs Traditional Price Tags
Price Transparency and Accuracy
Up-to-Date Information with Electronic Shelf Labels
Electronic shelf labels provide real-time information to shoppers. When retailers update prices, the new information appears instantly on every shelf. This ensures that consumers always see accurate pricing, which reduces confusion at checkout. Staff can focus on helping customers instead of spending hours changing tags. Consistent information across all channels builds trust and supports customer satisfaction. Market research shows that these systems also help retailers align with eco-friendly practices, which many consumers value.
Mismatched Pricing Issues with Traditional Price Tags
Traditional price tags often lead to mismatched information between shelves and registers. Manual updates can result in outdated or missing tags, especially during busy sales events. Shoppers may feel frustrated when the price at checkout does not match the shelf. This situation can damage customer satisfaction and reduce trust in the store. Inconsistent information also increases the risk of complaints and lost sales.
Interactive Features and Customer Engagement
QR Codes, Promotions, and Product Information
Digital price tags offer interactive features that enhance customer engagement. Many ESLs display QR codes, allowing shoppers to access detailed product information or special promotions with their smartphones. This instant access to information supports informed purchasing decisions. Retailers can update promotions quickly, ensuring that consumers always see the latest offers. These features create new opportunities for engagement and make the shopping experience more dynamic.
Impact on Shopper Trust and Satisfaction
Customer engagement increases when shoppers receive accurate information and interactive options. However, reactions to digital price tags remain mixed. CivicScience survey data reveals that only 14% of U.S. adults believe digital price tags would improve their experience, while 40% think it could have a negative effect. Younger consumers, such as Gen Z and Millennials, show more optimism about these changes. Older adults express more skepticism, often due to concerns about dynamic pricing. Despite these concerns, ESLs help retailers deliver consistent pricing and reduce errors, which supports customer satisfaction over time. As staff spend less time on manual tasks, they can focus more on direct engagement with shoppers, further improving the overall experience.
Note: Retailers should consider demographic preferences and communicate clearly about how digital price tags work to maximize customer satisfaction and engagement.
Environmental Impact: Electronic Shelf Labels vs Traditional Price Tags
Paper and Plastic Waste Reduction
Retailers who switch from traditional price tags to electronic shelf labels see a dramatic reduction in waste. Traditional paper tags generate large amounts of paper waste, require excess ink, and need frequent shipping for replacements. These processes contribute to chemical pollution and increase carbon emissions. Digital price tags eliminate the need for paper and ink, which lowers the environmental impact from both production and logistics.
- Traditional labels contribute to deforestation and toxic ink waste.
- Digital price tags reduce the frequency of label replacements, as European supermarkets report a 60% drop in manual pricing errors.
- An Asian grocery brand saved thousands of dollars each year by removing disposable paper tags from their operations.
- A U.S. retail chain cut labor costs by 30% through automated price adjustments, which also led to less waste.
- Over five years, stores using electronic pricing solutions saved 40% more energy compared to those using traditional methods.
Modern digital price tags use batteries that last five to ten years, which minimizes battery waste. By reducing the need for continuous paper production and transport, retailers help lower their carbon footprint and support sustainability goals.
Energy Consumption and Sustainability
Digital price tags offer significant improvements in energy efficiency. These systems require power only during updates, which drastically reduces ongoing energy consumption. Advanced LED and OLED technologies in digital shelf labels use up to 50% less energy than older display types. Retailers can program these displays to power off when not in use, further lowering energy usage.
A recent sustainability study on retail technology found that supply chain operations improved efficiency by 15–20% on average, with some stores reaching 30% in optimization and 25% in waste reduction. These gains support the claim that digital price tags promote sustainability in retail environments. By reducing both direct and indirect energy use, retailers can achieve better environmental impact outcomes.
Long-Term Environmental Considerations
The long-term environmental impact of electronic shelf labels extends beyond immediate waste reduction. Traditional price tags require ongoing production, shipping, and disposal, which leads to persistent environmental challenges. Digital price tags, on the other hand, reduce pollution and help retailers meet sustainability targets over time.
Retailers who invest in digital price tags contribute to lower deforestation rates and less toxic ink entering the environment. The extended battery life of modern tags means fewer replacements and less electronic waste. As more retailers adopt these solutions, the industry moves closer to a circular economy model, where sustainability becomes a core operational value.
Tip: Retailers who prioritize sustainability can use digital price tags as a visible commitment to reducing waste and improving their environmental impact.
Technical Considerations for Electronic Shelf Tags and Traditional Price Tags
System Integration and Compatibility
POS and Inventory Sync for Digital Price Tags
Retailers must evaluate how electronic shelf tags and electronic pricing labels fit into their existing technology landscape. Integration with point-of-sale (POS) and inventory management systems is essential for real-time price accuracy. Many esl solutions offer flexible compatibility with various POS configurations, allowing seamless updates across all channels. Retailers often collaborate with esl vendors to verify that electronic shelf labels can synchronize with current software and hardware. This process ensures that price changes on electronic pricing labels reflect instantly at checkout and in inventory records.
A successful integration strategy includes several steps:
- Assess the current IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, and networking.
- Work with esl vendors to confirm integration capabilities with POS and inventory systems.
- Select esl systems that adapt to different POS setups.
- Choose wireless communication technologies, such as sub1 GHz frequency, to prevent interference with store Wi-Fi.
- Consider battery life and maintenance needs for electronic shelf tags.
- Use cloud-based content management platforms for centralized, real-time updates and dynamic pricing.
- Conduct pilot testing in select store areas to validate performance before a full rollout.
- Maintain ongoing vendor support for troubleshooting, updates, and system maintenance.
- Enforce security protocols to protect data integrity and system access.
This approach helps retailers avoid costly disruptions and ensures that electronic shelf labels deliver consistent performance.
IT Infrastructure Needs for Electronic Shelf Labels
Implementing esl technology requires a robust IT foundation. Retailers must ensure their networks can handle the additional wireless traffic from thousands of electronic shelf tags. Reliable connectivity supports real-time updates and minimizes downtime. Cloud-based management platforms, such as ComQi’s EnGage, allow centralized control of electronic pricing labels across multiple locations. Battery life also plays a role in operational efficiency, as longer-lasting batteries reduce maintenance demands. Retailers should plan for regular system updates and technical support to keep esl technology running smoothly.
Reliability and Security
Power Outages and Failures
Reliability remains a top concern for both electronic shelf labels and traditional price tags. Electronic shelf tags depend on stable power and network connections. During power outages, most esl devices retain their last displayed price, but updates pause until service resumes. Retailers should develop contingency plans to address potential disruptions and ensure that staff can respond quickly to failures.
Data Protection and Privacy
Security is critical when deploying esl technology. Retailers must enforce strict protocols to protect sensitive pricing and inventory data. Secure wireless communication prevents unauthorized access to electronic pricing labels. Regular software updates and vendor support help address vulnerabilities. By prioritizing data protection, retailers maintain customer trust and safeguard business operations.
Tip: Regularly review security settings and conduct audits to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table: Digital Price Tags vs Traditional Price Tags
Retailers often seek a clear, direct comparison between digital price tags and traditional price tags. A side-by-side analysis helps decision-makers understand which system aligns best with their business needs. The following table summarizes the most important features and differences:
| Feature | Traditional Price Tags | Electronic Shelf Labels (ESL) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Low upfront cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Maintenance | Manual updates required | Occasional battery replacement |
| Update Speed | Slow, manual price changes | Instant, wireless updates |
| Environmental Impact | High due to paper waste | Low, sustainable digital solution |
| Error Rate | High, prone to manual errors | Low, automated updates reduce errors |
| Customer Engagement | Basic, static information | Advanced, dynamic content possible |
| Long-Term Cost | Higher due to ongoing printing and labor | Lower after initial investment |
This table highlights the operational and financial contrasts between the two systems. Traditional price tags offer a low initial cost, making them attractive for small, independent retailers. These businesses often choose paper tags because they require minimal setup and work well when price changes are rare. However, manual updates increase labor costs and the risk of errors over time.
Electronic shelf labels require a higher upfront investment. Retailers must install digital displays and integrate them with store systems. Despite the initial expense, ESLs provide instant, wireless updates and reduce the need for manual labor. Automated updates improve pricing accuracy and help stores avoid costly mistakes. Over time, the lower maintenance and labor costs can offset the initial investment.
Note: Sustainability-conscious businesses often prefer ESLs. Digital price tags reduce paper waste and support green initiatives, helping retailers meet environmental goals.
Customer engagement also differs between the two systems. Traditional tags display only basic, static information. ESLs enable dynamic content, such as real-time promotions or QR codes, which can enhance the shopping experience.
Retailers should consider their size, operational needs, and sustainability priorities when choosing a pricing system. The following points summarize which businesses benefit most from each option:
- Small, independent retailers often select traditional price tags for simplicity and low cost.
- Medium to large retailers gain efficiency and accuracy from ESLs, especially when managing frequent price changes.
- Businesses focused on sustainability value the reduced waste and energy efficiency of digital price tags.
- Tech-savvy retailers use ESLs to enable dynamic pricing and interactive customer features.
A side-by-side comparison provides a practical foundation for retailers evaluating their next steps in pricing technology.
Choosing Between ESLs and Traditional Price Tags for Your Store
Small Retailers: Cost and Simplicity
Small retailers often prioritize simplicity and cost-effectiveness when evaluating pricing systems. Traditional price tags offer a low upfront investment and require minimal technical expertise. Staff can print and place tags using standard office equipment, making this approach accessible for stores with limited resources. However, manual updates consume significant labor time, especially during frequent promotions or inventory changes. Digital price tags, while requiring a higher initial investment, streamline operations by automating price updates. This automation reduces the time needed for changes from days to minutes and cuts paper waste by about 40%. Digital labels also help staff locate products quickly, improving efficiency. Features such as QR codes on digital tags provide customers with instant access to product details, enhancing the shopping experience. Although most documented efficiencies come from large retailers, small businesses can still benefit from improved inventory management and reduced operational overhead. When choosing between esls and traditional price tags, small retailers must weigh the balance between upfront costs and long-term savings.
Large Retailers: Scale and Efficiency
Large retailers manage thousands of products across multiple locations, making operational efficiency a top priority. Digital price tags deliver significant advantages at scale. E-paper technology in ESLs uses power only during price changes, supporting battery life of up to five years. Scheduled refresh cycles and low-power modes further reduce energy consumption. Battery-powered ESLs are easy to install and maintain, even in extensive deployments. Advanced models, such as the HA154, support large-scale environments with production capacities exceeding 100,000 units per month. These systems use secure, low-latency communication and allow a single base station to manage unlimited tags. Real-time centralized updates minimize compliance risks and labor costs by eliminating manual price changes. Integration with POS, ERP, and WMS systems ensures consistent pricing across all channels. As a result, large retailers achieve greater accuracy, lower maintenance costs, and improved customer satisfaction. The rapid adoption of ESLs in this segment reflects the need for operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Tech-Savvy vs Traditional Businesses
Tech-savvy businesses lead the way in adopting digital innovations. These retailers often view technology as integral to their brand and customer experience. High-end fashion stores and smart retail environments use technologies such as RFID, IoT, and augmented reality to enhance shopping. Digital price tags fit seamlessly into these ecosystems, providing real-time pricing updates and supporting omnichannel strategies. Consumers in this segment show strong readiness for new technology, with many willing to pay full price for the latest tech products. Their mobile-first behavior and preference for integrated online and offline experiences make digital price tags a natural fit. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of technology-driven retail models, emphasizing efficiency and reduced human contact. In contrast, traditional businesses may prefer the familiarity and simplicity of paper tags, especially if their customer base values consistency over innovation. Each business must assess its technological readiness and customer expectations before making a decision.
Tip: Retailers should consider industry benchmarks, such as the growing global ESL market and the increasing adoption rate, when evaluating which system aligns best with their operational goals.
Budget-Conscious Stores
Budget-conscious retailers often face tough decisions when selecting a pricing system. They seek solutions that minimize upfront costs and ongoing expenses. Traditional price tags appeal to these stores because of their low initial investment. Staff can print and place paper tags using basic office equipment. This approach works well for small stores with limited budgets and infrequent price changes.
However, ongoing costs can add up over time. Paper, ink, and plastic holders require regular replenishment. Staff must spend hours each week updating prices, which increases labor expenses. Mistakes during manual updates can lead to pricing errors and customer dissatisfaction. These hidden costs may outweigh the initial savings.
Digital price tags, while requiring a higher upfront investment, offer long-term savings. Automated updates reduce labor costs and minimize errors. Stores can avoid recurring expenses for printing supplies. Over several years, the total cost of ownership for digital price tags often becomes lower than that of traditional tags. Retailers who plan for growth or frequent promotions may find that digital price tags align better with their long-term financial goals.
Tip: Budget-conscious stores should calculate both initial and ongoing costs before choosing a pricing system. Factoring in labor, materials, and potential errors helps reveal the true cost over time.
High-Turnover or Dynamic Pricing Environments
Retailers operating in high-turnover environments, such as grocery or electronics stores, require fast and accurate price changes. Digital price tags provide a clear advantage in these settings. Automated pricing tools use AI to adjust prices in real time, reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency. Customer segmentation and behavior analysis enable personalized pricing strategies that target frequent and price-sensitive buyers.
Dynamic pricing helps minimize waste by adjusting prices as products near expiration. This approach boosts sales and reduces unsold inventory. Gradual price adjustments protect profit margins by optimizing revenue without excessive discounting. Predictive analytics improve inventory turnover rates by forecasting demand and enabling timely price changes.
The following table highlights key benefits for high-turnover and dynamic pricing environments:
| Metric/Benefit | Statistic/Outcome | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Label maintenance time | 80% reduction (Carrefour) | Greater operational efficiency |
| Pricing errors | 50% fewer errors (Carrefour) | Improved pricing accuracy |
| Real-time price updates | Enabled by ESLs in groceries, electronics | Supports dynamic pricing |
| Inventory turnover | Improved through faster price adjustments | Higher turnover rates |
| Customer satisfaction | Increased due to accurate and timely pricing | Enhanced loyalty and competitive position |
| Dynamic pricing algorithms | AI-powered, adjust prices based on real-time data | Quick response to market and competitor moves |
Real-time data integration from POS, CRM, and IoT sensors supports accurate and responsive pricing decisions. Retailers gain a competitive advantage by quickly responding to market changes and competitor pricing. Enhanced customer satisfaction results from fair, transparent pricing and the availability of discounted perishable goods.
Note: Retailers in fast-moving sectors benefit most from digital price tags, as these systems enable dynamic pricing and rapid adaptation to changing market conditions.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Between ESLs and Traditional Price Tags
Business Size and Scale
Retailers must assess their business size and operational scale before selecting a price tag system. Large stores with thousands of products often benefit from electronic shelf labels. These systems allow centralized control and instant updates, which reduce manual labor. Staff can focus on customer service instead of spending hours changing tags. Smaller retailers may find traditional price tags more practical due to lower upfront costs and simpler installation. However, as a business grows, the time and resources needed for manual updates increase. Market trends show that supermarkets and hypermarkets in Asia Pacific rapidly adopt ESLs, driven by digital transformation and rising consumer spending. Technological advances, such as high-resolution e-paper displays, make ESLs adaptable for both large and small formats. Retailers should match their choice to their current needs and future growth plans.
Frequency of Price Changes
The rate at which a store updates its pricing plays a crucial role in system selection. Stores with frequent promotions or dynamic pricing strategies gain significant advantages from ESLs. These digital tags enable real-time updates across all shelves, ensuring accuracy and consistency. Staff can adjust prices remotely, which minimizes errors and improves operational efficiency. Traditional price tags require manual changes, which can become time-consuming and error-prone during busy periods. In environments where prices change daily or weekly, ESLs help maintain up-to-date information and reduce the risk of mismatched prices at checkout. However, stores with stable pricing and infrequent updates may find traditional tags sufficient. Retailers must evaluate their promotional calendar and pricing strategy to determine the best fit.
Customer Expectations and Experience
Modern shoppers expect accurate and transparent information when making purchasing decisions. ESLs support this demand by providing real-time pricing and product details directly on the shelf. Integration with omnichannel retail ensures that online and in-store prices match, which builds trust and enhances the shopping experience. Digital tags can display additional information, such as QR codes or product specifications, offering customers more value. Traditional price tags, while familiar, may lead to inconsistencies if not updated promptly. Errors or outdated tags can frustrate shoppers and damage a retailer’s reputation. As e-commerce continues to grow, physical stores face pressure to upgrade in-store experiences. ESLs help retailers meet these expectations by delivering consistent and accurate information, supporting both customer satisfaction and operational goals.
Tip: Retailers should regularly review customer feedback and monitor market trends to ensure their pricing systems align with evolving shopper expectations.
Budget and ROI Goals
Retailers often evaluate pricing systems based on budget constraints and expected return on investment (ROI). Traditional price tags require a low initial outlay. Many small stores choose this option to minimize upfront expenses. However, ongoing costs for paper, ink, and labor can accumulate quickly. Digital price tags, or electronic shelf labels (ESLs), demand a higher initial investment. This includes hardware, software, and installation. Over time, ESLs can reduce labor costs and improve pricing accuracy. Retailers who update prices frequently may see a faster payback period.
A simple ROI analysis helps decision-makers compare both systems:
| Factor | Traditional Price Tags | Digital Price Tags (ESLs) |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | Low | High |
| Ongoing Labor | High | Low |
| Material Expenses | Recurring | Minimal |
| Payback Period | Long | Short (with frequent updates) |
Retailers should consider their pricing strategy and store size. High-turnover environments benefit more from automation. A clear understanding of total cost of ownership supports better financial decisions.
Tip: Retailers can use pilot programs to estimate actual savings before a full rollout.
Environmental Priorities
Environmental impact plays a growing role in retail decision-making. Traditional price tags generate significant paper and plastic waste. Frequent updates increase the volume of discarded materials. Digital price tags offer a more sustainable alternative. These systems reduce paper use and minimize ink waste. ESLs use batteries that last several years, which lowers the frequency of replacements.
Sustainability-conscious businesses often select digital price tags to support their environmental goals. They recognize the value of reducing waste and promoting responsible resource use. Many retailers also highlight their use of digital tags in marketing to appeal to eco-minded customers.
- Traditional tags: High paper and plastic waste
- Digital tags: Reduced waste, longer lifespan
Retailers who prioritize sustainability should weigh the long-term environmental benefits of ESLs against their initial cost.
Technical Readiness and Support
Technical readiness determines how smoothly a retailer can implement a new pricing system. Traditional price tags require minimal technical infrastructure. Staff need only basic training to print and place tags. Digital price tags, in contrast, depend on reliable wireless networks and integration with point-of-sale systems. Retailers must assess their current IT capabilities before investing in ESLs.
Support and maintenance also differ. ESLs require periodic software updates and battery replacements. Vendors often provide technical support and training. Retailers should plan for ongoing system monitoring to ensure consistent performance.
A checklist for technical readiness:
- Assess current network infrastructure
- Evaluate compatibility with existing POS systems
- Plan for staff training and ongoing support
- Establish a maintenance schedule for hardware and software
Note: Early planning and vendor collaboration help retailers avoid technical challenges during deployment.
Retailers face a pivotal choice between digital price tags and traditional price tags. Digital price tags offer automation, accuracy, and sustainability, while traditional tags provide simplicity and low upfront costs. Key decision factors include store size, update frequency, budget, and technical readiness.
Tip: Retailers should assess operational needs and long-term goals before selecting a pricing system. The right choice supports efficiency, customer satisfaction, and business growth.
FAQ
What is the lifespan of electronic shelf labels?
Most electronic shelf labels last between five and ten years. Battery life depends on update frequency and display technology. Retailers should plan for periodic battery replacement to maintain system reliability.
Can digital price tags integrate with existing POS systems?
Many digital price tag solutions offer integration with popular POS and inventory management systems. Retailers should confirm compatibility with their current software before implementation.
How secure are electronic shelf label systems?
Vendors design ESL systems with strong encryption and secure wireless protocols. Regular software updates and network monitoring help protect sensitive pricing and inventory data from unauthorized access.
Do digital price tags require internet access at all times?
Most ESL systems operate on local wireless networks. Internet access supports remote management and cloud-based updates, but basic price changes can occur offline through the store’s internal network.
Are there hidden costs with traditional price tags?
Traditional price tags incur ongoing expenses for paper, ink, and labor. Frequent updates increase these costs. Retailers should also consider the environmental impact of continuous material use.
How do digital price tags handle power outages?
Electronic shelf labels retain the last displayed price during power outages. Updates resume automatically when power returns. Retailers should develop contingency plans for extended outages.
Can retailers customize the appearance of digital price tags?
Retailers can often customize digital price tags with logos, colors, and promotional messages. Many systems support multiple display templates to match store branding and marketing needs.
What training do staff need for electronic shelf labels?
Staff require training on the central management software and basic troubleshooting. Most employees adapt quickly due to user-friendly interfaces. Ongoing vendor support ensures smooth operation.


