
When you walk through a modern store, you see digital price tags on every shelf. These tags use wireless technologies to keep your price information accurate and up to date. Communication distance often ranges from 13 to 30 meters indoors, but some digital systems reach up to 2 kilometers. The most common wireless options for electronic price tags include RF, NFC, BLE, and Wi-Fi. Each tag stays connected through careful network design, with solutions like the ESL Gateway AP supporting thousands of tags in Esl Retail environments. Electronic Shelf Labels and the ESL Price Tag both rely on reliable communication distance to ensure you always see the correct price.
| Wireless Technology | Usage Context | Key Advantages | Typical Retail Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF (Radio Frequency) | Most widely used communication protocol | Reliable, cost-effective, large area coverage, supports thousands of tags per base station | Supermarkets, hypermarkets, large-scale deployments |
| NFC (Near Field Communication) | Close-proximity interactions, enhanced security | Contactless transactions, detailed product info, interactive promotions | Specialty stores, premium retail environments |
| BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) | Real-time location tracking, data synchronization | Low power consumption, high data rates, proximity-based services | High-traffic retail environments, IoT-enabled smart stores |
| Wi-Fi | Environments with robust wireless infrastructure | Seamless network integration, remote management, analytics | Modern retail stores, shopping malls |
Communication Distance of Digital Price Tags
Understanding how digital price tags communicate across your store helps you make informed decisions about retail technology investments. The communication distance between tags and central systems determines how reliably you can update price information and manage your inventory. Let’s explore the wireless technologies that power these systems, the typical distances you can expect in retail environments, and real-world examples from different store types.
Wireless Technologies Used in Digital Price Tags
You will find several wireless technologies supporting digital price tags. Each technology offers unique advantages and limitations for your retail environment.
2.4GHz Radio Frequency Systems
2.4GHz RF systems remain a popular choice for digital price tags. These systems provide a balance between communication distance and data transfer speed. You can deploy them in most retail settings, but interference from Wi-Fi or other devices may affect performance. The technology supports flexible tag placement and broad coverage, making it suitable for supermarkets and department stores.
Sub-GHz and LoRa Protocols
Sub-GHz and LoRa protocols extend the communication distance well beyond standard RF systems. You can use these technologies in large retail spaces or warehouses where you need to cover long aisles or multiple floors. Sub-GHz frequencies avoid much of the interference found in the 2.4GHz band, while LoRa offers low power consumption and reliable long-range communication. These features make them ideal for stores with complex layouts or significant physical obstacles.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) stands out for its low power consumption and strong security. BLE5.0, in particular, delivers a high communication rate, long battery life (up to five years), and robust anti-interference features. You can benefit from over-the-air firmware upgrades and stable connections, which are essential for maintaining thousands of tags. BLE4.2 also provides international standards and better stability than older RF systems, though it offers lower performance than BLE5.0.
Tip: BLE5.0 supports a communication distance up to three times greater than traditional RFID 2.4G, making it a strong choice for modern digital price tags.
Near Field Communication (NFC)
NFC enables close-proximity communication between your digital price tags and mobile devices. You can use NFC for interactive promotions, contactless transactions, or detailed product information. While the communication distance is limited to a few centimeters, NFC excels in specialty retail environments where security and customer engagement matter most.
Proprietary RF Solutions
Some retailers choose proprietary RF solutions tailored to their specific needs. These systems may use custom frequencies or protocols to optimize communication distance, security, or integration with existing infrastructure. You should consider the trade-offs, as proprietary systems may lack international standards or broad compatibility.
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| BLE5.0 | High communication rate, long communication distance, strong security, excellent anti-interference, supports firmware upgrades, international standards, low power, stable, long battery life | None significant mentioned |
| BLE4.2 | International standard, better stability and security than 433MHz and RFID 2.4G | Lower performance than BLE5.0 |
| RFID 2.4G | Frequency modulation, used in custom protocols | Limited anti-interference, fewer channels, single-frequency, less secure |
| 433MHz | Simple, used in custom protocols | Poor security, unreliable, no international standard |
| ZigBee | N/A | Low rate, limited range, high latency, unsuitable for low-power tags |
| WiFi | N/A | High power, high cost, complex, unsuitable for low-power tags |
Typical Communication Distance in Retail Environments
You need to consider the communication distance when planning your digital price tag deployment. The effective range depends on the technology, store layout, and physical obstacles.
Indoor Range for Digital Price Tags
Most digital price tags achieve a minimum average transmission distance of about 30 meters indoors. This range allows you to cover most aisles and shelving units in a typical retail store. However, walls, metal shelves, and other obstacles can reduce the effective communication distance. You should always evaluate your store’s physical layout to ensure reliable coverage.
- Digital price tags typically reach 30 meters indoors.
- Store layout and obstacles can impact signal strength.
- Proper planning ensures consistent communication for all tags.
Open Area and Extended Range Capabilities
In open areas or stores with fewer obstacles, you can extend the communication distance significantly. Sub-GHz and LoRa-based systems may reach up to 2 kilometers in ideal conditions, making them suitable for large warehouses or multi-level retail spaces. You can use repeaters or mesh networking to further enhance coverage and reliability.
Note: The communication distance you achieve depends on both the wireless technology and your store’s design. Always conduct a site survey before installation.
Real-World Examples of Communication Distance
You can see how communication distance plays out in different retail settings.
Supermarkets and Grocery Stores
Supermarkets often use RF or BLE-based digital price tags to cover wide aisles and dense shelving. You can expect reliable communication within 30 meters, even in busy environments. Strategic placement of gateways and careful network design help you maintain accurate price updates across the entire store.
Department Stores and Large Retailers
Department stores and large retailers may require extended communication distance due to their size and complex layouts. Sub-GHz or LoRa protocols enable you to connect tags across multiple floors or distant sections. Cloud-based ESL solutions offer scalability and remote management, making it easier for you to expand coverage as your store grows.
When you choose the right technology and plan your network carefully, you ensure every retail price tag stays connected and up to date, no matter the size of your store.
How Digital Price Tags Maintain Connection Across the Store

You need a robust network architecture to keep your digital shelf labels connected and reliable. The right setup ensures that every electronic price label receives updates quickly and accurately, no matter where you place it in your store.
Network Architecture for Digital Shelf Labels
Gateways and Access Points
Gateways and access points form the backbone of your electronic price label network. You install these devices throughout your store to manage wireless communication between your central system and all tags. High-performance solutions, such as Silicon Labs’ FG22 Wireless 2.4 GHz SoC, offer ultra-low power consumption and strong radio performance. This technology supports large-scale deployments, letting you manage hundreds of thousands of electronic price labels from a single server. Providers like RAINUS design their systems for scalability, so you can expand your network as your store grows.
Repeaters and Range Extenders
You can use repeaters and range extenders to boost your network’s reach. These devices help you overcome obstacles like thick walls or metal shelving that can block signals. By placing repeaters in strategic locations, you ensure that every digital shelf label receives a strong, stable connection. This approach keeps your electronic price tags updated and maintains price accuracy across your entire store.
Mesh Networking for Tags
Mesh networking allows your tags to communicate with each other, not just with gateways. If one tag loses its direct connection, it can relay data through neighboring tags. This self-healing network increases reliability and reduces the risk of communication gaps. Mesh technology also supports scalability, making it ideal for stores with thousands of electronic price labels.
Communication with Central Systems
Data Synchronization for Electronic Price Labels
Your digital shelf labels rely on seamless data synchronization with your central management system. Wireless connections—such as RF, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi—enable real-time communication. Integration methods include API-based solutions, middleware, and file-based interfaces. You benefit from robust error handling, automated validation, and end-to-end encryption, which protect your data and ensure the integrity of every price update.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Communication Methods | Wireless connections: RF, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi enable real-time communication with central systems. |
| Integration Approaches | API-based (RESTful and SOAP), middleware solutions, file-based interfaces (CSV, XML). |
| Real-time Updates | Real-time synchronization with ERP systems ensures instant pricing and inventory updates. |
| Data Integrity Mechanisms | Robust error handling, idempotent operations to avoid duplicate updates, automated validation. |
| Security Protocols | End-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, access restrictions. |
| Monitoring & Logging | Continuous monitoring, detailed logs, audit trails, latency alerts, and error detection systems. |
| Middleware Role | Acts as a bridge simplifying integration, supports data mapping, transformation, and workflow automation. |
| API Protocol Details | RESTful APIs use stateless web protocols for scalability; SOAP APIs use XML messaging for complex validation and error handling. |
| Update Optimization | Batch updates during low-activity periods, incremental processing to reduce system load. |
Real-Time Updates and Monitoring
You maintain price accuracy and product information by using real-time monitoring systems. These systems collect and analyze data from all electronic price labels. Automated alerts notify you when errors or anomalies occur, so you can correct issues before they affect your customers. Continuous monitoring ensures that your digital shelf labels always display the correct pricing and product information. This approach builds trust and keeps your store running smoothly.
Tip: Real-time pricing and automated monitoring help you prevent misinformation and maintain the highest standards of accuracy for your electronic price tag technology.
Factors Affecting Communication Distance of Digital Shelf Labels

When you deploy digital shelf labels in your retail environment, you must consider several factors that influence how well your tags stay connected. These factors include your store layout, physical obstacles, wireless interference, environmental conditions, and the placement of both tags and gateways. Understanding these elements helps you maintain reliable communication for your electronic shelf labels and ensures accurate pricing across your store.
Store Layout and Physical Obstacles
Impact of Walls and Shelving
Walls and shelving units in your store can block or weaken wireless signals. Thick walls, especially those made of concrete or brick, absorb or reflect radio waves. Metal shelves and racks present even greater challenges. Metal surfaces reflect signals, which can cause multipath interference, leading to duplicate or missed reads from your tags. You may notice that tags placed behind or between metal objects experience reduced connectivity. To minimize these issues, you should map out your store and identify areas where obstacles might disrupt communication.
Building Materials and Store Design
The materials used in your store’s construction play a significant role in signal propagation. Stores with open layouts and non-metallic materials allow signals to travel farther. In contrast, environments with dense shelving, glass, or metal partitions can create dead zones for your digital shelf labels. You should also consider ceiling height and the presence of pillars or other architectural features. These elements can block or scatter signals, making it harder for your electronic shelf labels to maintain a stable connection.
Wireless Interference and Environmental Factors
Competing Wireless Devices
Your store likely contains many wireless devices, such as Wi-Fi routers, security systems, and handheld scanners. These devices can operate on similar frequencies as your digital shelf labels, causing electromagnetic interference (EMI). EMI disrupts communication between your tags and gateways, leading to misreads or lost updates. Industrial machinery and power lines can also generate unwanted electromagnetic signals. You should monitor your environment for sources of interference and adjust your network settings to avoid conflicts.
Environmental Noise and Signal Degradation
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and moisture can degrade the performance of your electronic shelf labels. For example, high humidity or water absorption can weaken RFID signals, making some tags unreadable. Extreme temperatures may also affect the reliability of your digital price tags, especially in cold chain logistics or outdoor retail settings. Multipath interference, where signals bounce off surfaces and create duplicate reads, further complicates communication. You need to account for these variables when planning your network.
Tip: Regularly check for new sources of interference as your store’s technology evolves. Adjust your network configuration to maintain optimal performance.
Here is a summary of common interference and environmental factors:
| Interference/Factor Type | Description | Impact on Digital Shelf Labels Connectivity | Example Causes/Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) | Disruption caused by unwanted electromagnetic signals interfering with RFID communication. | Causes misreads or no reads, reducing reliability and accuracy. | Power lines, industrial machinery, electronic devices. |
| Physical Obstructions | Barriers that absorb or reflect RFID signals, weakening or blocking communication. | Reduced read range and poor signal quality. | Metal surfaces, water, dense materials. |
| Reader-to-Reader Interference | Interference when multiple RFID readers operate on similar frequencies nearby. | Data inconsistency and communication conflicts. | Overlapping read zones, similar frequency operation. |
| Multipath Interference | Signal reflections causing duplicate or ghost reads. | False reads and reduced accuracy. | Signal bouncing off surfaces causing multiple signal paths. |
| Environmental Factors | Conditions like temperature, humidity, and moisture affecting RFID tag and reader performance. | Degraded tag performance and reader accuracy. | Temperature extremes, high humidity, moisture exposure. |
| Metal and Liquid Interference | Metal reflects signals; liquids absorb them, disrupting signal propagation. | Inconsistent read rates and reduced reliability. | Metal shelves, water-containing containers, liquids. |
| Poor Antenna Placement | Incorrect positioning leading to weak signal coverage. | Weak or no signal reception, poor read accuracy. | Antenna angle, location relative to tags and obstructions. |
Placement of Tags and Gateways
Height and Positioning of Digital Price Tags
The height and positioning of your tags directly affect their ability to communicate with gateways. Placing tags too low or behind large objects can block signals. You should install digital shelf labels at a height that allows a clear line of sight to the nearest gateway or repeater. Avoid placing tags near sources of interference, such as large electronic devices or metal fixtures. Proper positioning ensures that your electronic shelf labels receive updates without delay.
Density and Distribution of Electronic Price Labels
The number and distribution of tags in your store also impact network performance. High-density deployments, where many tags are clustered in a small area, can lead to reader-to-reader interference. Overlapping communication zones may cause data conflicts or missed updates. You should plan the layout of your electronic shelf labels to avoid overcrowding and ensure even coverage. Strategic placement of gateways and repeaters helps you maintain strong connections throughout your retail space.
Note: Conduct a site survey before installation to identify potential dead zones and optimize the placement of your digital shelf labels and gateways.
Solutions for Reliable Connectivity of Electronic Price Labels
Strategic Placement of Gateways and Repeaters
Coverage Planning for Digital Shelf Labels
You can achieve reliable connectivity for electronic price labels by carefully planning the placement of gateways and repeaters. When you position these devices strategically, you ensure stable wireless connections throughout your store and eliminate dead zones.
- Test signal strength in every area, especially in corners and behind fixtures.
- Identify weak spots and reposition access points or add repeaters to address them.
- Overlapping access points create redundancy, so your network continues to operate even if one device fails.
- Use backup power supplies for gateways and network switches to further enhance reliability.
By following these steps, you support accurate, real-time updates for digital shelf labels and improve overall network coverage.
Overlapping Communication Zones
Overlapping communication zones play a key role in maintaining continuous operation for electronic price labels. When you design your network with overlapping coverage, you build in redundancy. If one gateway or repeater goes offline, another device can take over, preventing data delays and ensuring your electronic price labels always display the correct price.
Mesh Networking and Self-Healing Systems
Mesh networking offers a powerful solution for large or complex retail environments. You create a self-organizing, self-healing wireless network where each node communicates with others. This setup provides reliable, scalable, and flexible coverage for electronic price labels. Mesh networks automatically adjust routes if a node fails, so your system maintains stable wireless communication.
Scalability for Large Stores
You can easily scale mesh networks by adding more nodes. Each new node increases the number of available data routes, which supports thousands of electronic price labels without reducing efficiency. Mesh systems use affordable technologies like LoRa and Bluetooth, which helps you control costs while expanding your network.
Redundancy and Reliability
Mesh networking ensures redundancy for your electronic price labels. Self-healing algorithms reroute data if a node fails, so your network remains stable. Mesh systems also provide robust security with industry-standard encryption and automatic updates. However, managing many devices can become complex, so choose systems with user-friendly interfaces for easier maintenance.
| Aspect | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Self-healing algorithms dynamically reroute data if nodes fail, ensuring stable network operation. | Locating malfunctioning nodes is challenging and time-consuming. |
| Scalability | Easy to scale by adding nodes without affecting network efficiency; more nodes create more data routes. | Managing routing and load balancing becomes complex as network size and data volume increase. |
| Configuration & Management | New nodes auto-calibrate and connect, simplifying setup and management. | Requires intelligent nodes capable of route building and adjustment, increasing complexity. |
| Cost Efficiency | Uses affordable technologies (e.g., LoRa, Bluetooth) and fewer gateways, reducing overall costs. | Signal power and data transfer limitations exist with some low-cost technologies. |
| Performance | Flexible routing paths maintain connectivity even in complex environments. | Large data volumes over long routes can degrade network performance. |
Network Monitoring and Optimization
Performance Tracking for Tags
You maintain high performance for electronic price labels by using advanced network monitoring and optimization techniques. Continual network monitoring gives you real-time insights, so you can detect and resolve issues before they cause downtime. Load balancing distributes network traffic to prevent bottlenecks and maintain efficiency, especially during peak usage.
| Technique | Description and Role in Digital Price Tag Systems Performance and Downtime Minimization |
|---|---|
| Load Balancing | Distributes network traffic intelligently across servers or paths to prevent bottlenecks, improve scalability, and maintain performance during peak usage. Enhances resilience by avoiding single points of failure. |
| Regular Maintenance & Upgrades | Includes firmware/software updates, hardware health checks, and performance testing to prevent failures and ensure smooth operation. Proactive maintenance reduces unexpected downtime. |
| Network Segmentation | Divides the network into isolated segments (e.g., VLANs, subnets) to contain issues and reduce broadcast traffic, improving robustness and faster recovery from problems. |
| Caching and Content Delivery | Stores frequently accessed data locally or via CDNs to reduce redundant data transfers, freeing bandwidth and improving response times. DNS caching speeds up domain resolution. |
| Bandwidth Management | Uses traffic shaping, throttling, and prioritization to allocate bandwidth efficiently, ensuring critical applications maintain performance even under heavy load. |
| Network Protocol Configuration | Fine-tunes protocol settings (e.g., TCP window size, MTU, DNS resolution) to optimize data flow and reduce latency, enhancing overall network efficiency. |
| Network Security | Implements firewalls, intrusion detection, DDoS protection, encryption, and regular audits to prevent disruptions caused by attacks, thereby maintaining network availability and performance. |
| Continual Network Monitoring | Provides real-time insights to detect and resolve issues proactively, minimizing downtime and maintaining high service quality. |
| Capacity Planning | Prepares the network for future growth by anticipating demand and scaling resources accordingly, preventing performance degradation. |
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
You keep your electronic price labels running smoothly by performing regular maintenance and upgrades. Update firmware and software, check hardware health, and test performance to prevent failures. Use network segmentation to contain issues and recover quickly. Employ bandwidth management and protocol configuration to optimize data flow and maintain efficiency. Strong network security, including firewalls and encryption, protects your system and ensures your electronic price labels remain available and accurate.
Proactive monitoring and maintenance help you minimize downtime and maximize the efficiency of your electronic price label network.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Coverage of Digital Price Tags
Best Practices for Installation
Conducting Site Surveys
You set the foundation for reliable electronic price labels by conducting thorough site surveys before installation. Assign a dedicated leader to oversee the pre-installation phase. Break the project into manageable tasks and assign clear responsibilities to your team. Evaluate the store layout, network infrastructure, and power supply. Use digital tools such as SAi OnSite to standardize survey templates, track progress, and integrate maps for precise planning. Capture all critical data before leaving the site to prevent costly mistakes and rework. Maintain clear communication with stakeholders through professional survey reports. This structured approach helps you avoid errors, save time, and optimize the installation process for digital price tags.
Avoiding Dead Zones in Store Layout
You improve the customer experience by ensuring every electronic price label receives a strong signal. Identify potential dead zones by testing signal strength in all areas, especially behind fixtures or in corners. Place gateways and repeaters strategically to cover weak spots. Overlapping communication zones provide redundancy, so your network remains stable even if one device fails. Avoid placing electronic price labels near large metal objects or electronic devices that may cause interference. Careful planning ensures that customers always see accurate pricing, which builds trust and satisfaction.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Digital Shelf Labels
Regular System Checks and Updates
You maintain the reliability of your electronic price labels by performing regular system checks. Choose systems with simple installation mechanisms, such as magnetic or card slot designs, to make maintenance tasks quick and efficient. Prioritize electronic price labels with long battery life, especially those using E-Ink technology, which can last five to seven years. Ensure your system operates reliably under various conditions, including extreme temperatures and high humidity. Durable electronic price labels withstand daily wear and tear, reducing the need for frequent replacements and supporting a seamless customer experience.
Firmware and Software Maintenance
You keep your digital system running smoothly by updating firmware and software regularly. Select suppliers who offer comprehensive technical support and training. Prompt troubleshooting and efficient problem resolution become possible with quality after-sales services, including warranties and quick repair options. These measures help you maintain long-term system reliability and minimize disruptions for your customers. Consistent maintenance ensures that electronic price labels always display accurate information, enhancing the overall customer experience and supporting your store’s reputation for reliability.
Future Trends in Communication Distance for Digital Price Tags
As you look ahead, you will see rapid innovation shaping the future of digital price tags. New wireless protocols, smarter integration, and a focus on sustainability are transforming how you manage pricing and connectivity in retail environments.
Advancements in Wireless Technology for Tags
New Protocols and Standards
You now have access to advanced wireless technology such as LTE-Advanced (4G+) and 5G. These protocols increase communication distance and reliability for digital price tags. LTE-Advanced uses carrier aggregation and higher-order MIMO, which boost network capacity and reduce congestion. This means you can support more devices with less latency, even in busy stores. 5G takes this further, offering ultra-low latency and the ability to connect up to a million devices per square kilometer. These improvements allow you to deploy dynamic pricing strategies and real-time updates across large retail spaces, supporting your digital transformation goals.
With Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE 5.0) and mesh networking, you can extend coverage and maintain stable connections in complex store layouts. These protocols also support low power consumption, which is essential for long-term efficiency.
Improved Battery Life and Efficiency
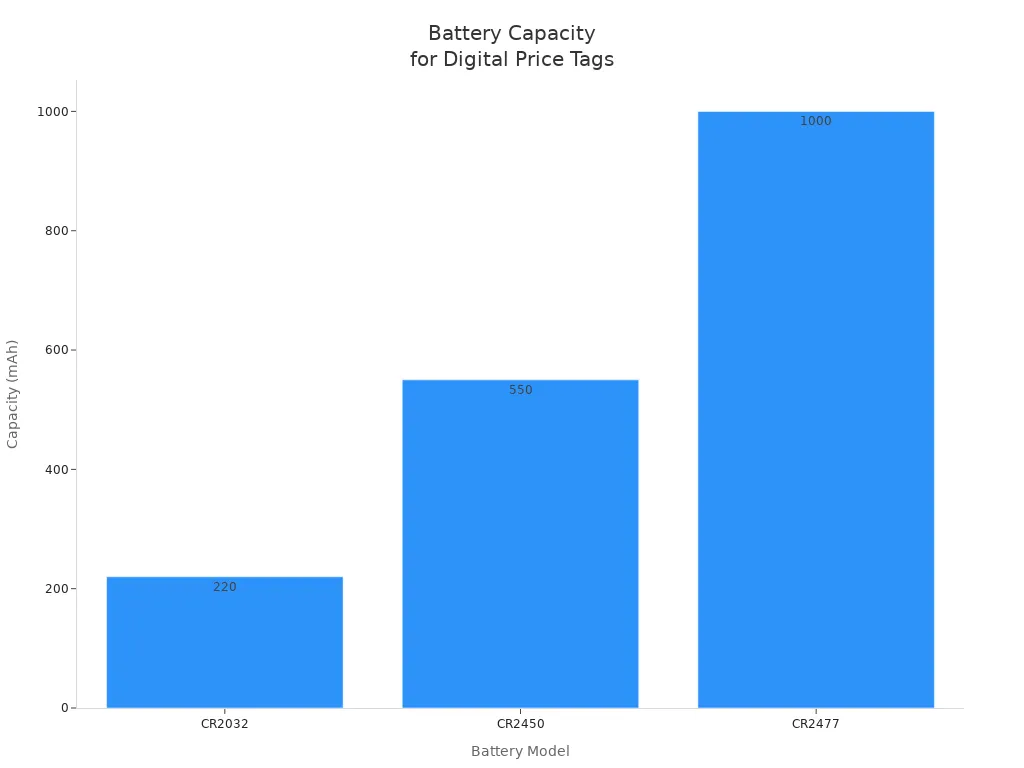
Battery innovation plays a crucial role in the reliability of digital price tags. Modern coin cell batteries like CR2032, CR2450, and CR2477 offer capacities from 220 to 1000 mAh, supporting different use cases from standard to feature-rich tags. These batteries have low self-discharge rates and can last up to ten years, reducing maintenance and operational disruptions. E-paper display technology further enhances battery life by consuming power only during updates. You benefit from low power consumption, which supports sustainability and lowers total cost of ownership.
| Battery Model | Voltage (V) | Capacity (mAh) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR2032 | 3 | 220 | Standard ESLs with frequent updates |
| CR2450 | 3 | 550 | ESLs using Bluetooth, high-traffic environments |
| CR2477 | 3 | 1000 | Feature-rich ESLs, demanding environments |
You also gain flexibility with replaceable or sealed batteries, ensuring consistent performance in various retail conditions. These advancements support your sustainability initiatives and help you maintain efficient operations.
Integration with Smart Store Systems
IoT and Automation for Electronic Price Labels
You can now integrate digital price tags with smart store systems, creating a connected ecosystem. IoT acts as the digital nervous system, linking your price tags to inventory robots, smart lighting, and security systems. Edge computing processes data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth costs. This setup enables real-time tracking, automated inventory management, and dynamic pricing adjustments. You improve efficiency and responsiveness, which enhances the customer experience and supports your digital transformation journey.
- Digital price tags connect wirelessly to centralized management software for real-time updates.
- Omnichannel communication links physical displays with online platforms, showing stock levels, competitor prices, and QR codes.
- Cloud-based platforms enable you to manage devices and pricing labels from anywhere, supporting nationwide updates.
- Automated alerts and demand forecasting improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Data Analytics and Insights
Modern digital price tag systems provide you with powerful data analytics. You can implement dynamic pricing strategies based on supply, demand, and competitor activity. Real-time inventory control automates replenishment, reducing stockouts and excess inventory. Edge computing and 5G technology enable faster, privacy-preserving data processing. These systems deliver actionable insights, helping you optimize operations and improve profitability.
Companies that excel in personalization see up to 40% more revenue, according to industry research. You can use these insights to enhance the customer journey and drive loyalty.
Sustainability remains a core focus. You benefit from eco-materials, ultra-low power consumption, and modular system designs. These features align with your corporate responsibility goals and support long-term innovation in retail.
You ensure digital price tags and shelf labels stay connected by using robust wireless technologies and smart network design. When you plan your system, you optimize communication distance for every customer. Strategic placement and regular maintenance help you deliver accurate pricing and a seamless customer experience. As technology evolves, you will see even greater reliability and reach, helping you serve each customer better.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of using wireless shelf labels in stores?
You gain the ability to update information instantly across your entire store. This reduces manual labor and helps you keep information consistent for every shopper.
How do wireless shelf labels receive updates?
You connect shelf labels to a central system through gateways or access points. The system sends updates wirelessly, ensuring each label displays the latest information.
Can you install these systems in stores with thick walls or metal shelves?
Yes, you can. You may need to use repeaters or mesh networking to overcome obstacles. Site surveys help you identify the best placement for reliable coverage.
How long does a typical shelf label battery last?
You can expect most shelf labels to operate for several years on a single battery. Battery life depends on update frequency, display type, and environmental conditions.
What happens if a label loses connection?
If a label loses connection, it usually continues to display the last received information. Once the connection restores, the label updates automatically.
Are these systems secure from unauthorized access?
You benefit from strong security protocols, including encryption and authentication. These measures help protect your system from unauthorized changes or data breaches.
Can you scale the system as your store grows?
You can expand your network by adding more gateways or nodes. Modern systems support thousands of labels, making it easy to scale as your needs change.
Tip: Always consult with your technology provider before expanding your system to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.


