
When you compare lcd vs led, you find that LED displays usually provide superior picture quality, longer lifespan, and greater energy efficiency. You might notice that LCDs remain more affordable, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers. In real-world environments like Esl Retail, Electronic Shelf Labels, and even architectural applications, you often see LED technology leading the way, supported by solutions such as ESL Gateway AP and ESL Price Tag systems. Your best choice depends on what matters most to you—cost or performance.
LCD vs LED: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the differences between lcd and led monitors helps you make an informed decision when choosing a display. Both technologies dominate the market, but each offers unique features and performance characteristics.
LCD: Definition and Technology
LCD stands for liquid crystal display. You find this technology in many monitors, televisions, and digital devices. LCD monitors use a layer of liquid crystals sandwiched between two sheets of glass or plastic. These crystals do not emit light directly. Instead, they manipulate light from a backlight to create images.
How LCD Displays Work
You see images on an lcd monitor because of several key components working together:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Backlight | Provides the necessary light source for the display. |
| Liquid Crystal Layer | Manipulates the light from the backlight to create images by changing the orientation of crystals when an electric current is applied. |
| Color Filters | Adds color to the images by using red, green, and blue filters for each pixel. |
The liquid crystals align in response to electric fields, controlling how much light passes through each pixel. Color filters and polarizers enhance image clarity and vibrancy. Most lcd monitors use thin-film transistor (TFT) technology, which allows precise control over each pixel.
Tip: LCDs require a constant light source, so they use either cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) or, in newer models, led backlighting.
Types of LCD Panels
You encounter several types of lcd panels, each with distinct characteristics:
- Twisted Nematic (TN): Offers fast response times, making it popular for gaming monitors. However, it has limited color accuracy and viewing angles.
- In-Plane Switching (IPS): Delivers better color reproduction and wider viewing angles, ideal for creative work and office use.
- Vertical Alignment (VA): Balances color performance and contrast, suitable for general-purpose displays.
Each panel type affects how you experience color, contrast, and motion on your lcd monitor.
LED: Definition and Technology
LED stands for light emitting diode. When you choose led monitors, you select a display that uses light-emitting diodes as the light source. This technology has transformed the display industry by offering brighter images, improved energy efficiency, and longer lifespan.
How LED Displays Work
An led monitor uses an array of light-emitting diodes to illuminate the screen. Each diode can emit light directly or from the edges, depending on the design. The display controls the brightness and color of each pixel using digital signals, often through pulse width modulation (PWM). This approach ensures high brightness and clarity.
You find several essential components in an led display:
- LED module: Contains multiple led lamp beads, a circuit board, power supply, and control chip.
- Drive circuit: Delivers stable current and voltage to the leds.
- Auxiliary structures: Include frames, radiators, and dust covers for protection and support.
- Data lines and cables: Connect components for data and power transmission.
- Housing and screen: Protects internal parts and influences the viewing experience.
Note: Each led acts as a pixel, and the display arranges them in a grid. This structure allows for high brightness, making led monitors suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
Types of LED Backlighting
You encounter different led backlighting methods in monitors:
- Edge-lit LED: LEDs are placed along the edges of the screen. Light diffuses across the display, resulting in a slim profile.
- Direct-lit LED: LEDs are positioned directly behind the screen. This setup provides more uniform brightness and better local dimming, enhancing contrast.
- Full-array LED: A grid of leds covers the entire back of the display. This method offers precise control over brightness and contrast, delivering superior image quality.
These backlighting techniques influence the performance and price of led monitors.
LCD vs LED: Key Distinctions
When you compare lcd vs led, you notice several important differences in performance, design, and serviceability.
| Feature | LCD Displays | LED Displays |
|---|---|---|
| Backlighting | Uses fluorescent or led backlighting | Uses light-emitting diodes (LED) |
| Image Quality | Lower sharpness, less vibrant | Sharper, brighter, and clearer images |
| Lifespan | Shorter, around 30,000 hours | Longer, up to 50,000 hours |
| Response Time | Slower, potential motion blur | Faster, smoother motion |
| Viewing Angles | Limited, color shifts from sides | Wide, up to 160°, consistent brightness and color |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient | More efficient, lower operational costs |
| Serviceability | Often requires full replacement | Built for quick fixes with spare parts |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost, better long-term value |
- LCD monitors rely on backlighting, which can limit brightness and visibility in bright environments.
- LED monitors use light-emitting diodes for direct illumination, resulting in vibrant images and suitability for outdoor displays.
- Two-thirds of industry experts believe led issues are less likely to require full replacement compared to lcd issues.
- 73% of users report trouble with lcd displays within three years, while only 68% experience issues with led displays in the same period.
- LED malfunctions require replacement less than 25% of the time, compared to lcd monitors.
You see that led technology offers significant advantages in image quality, energy efficiency, and durability. However, lcd monitors remain a cost-effective choice for many users. When you weigh lcd vs led, consider your priorities for performance, longevity, and budget.
LCD vs LED: Image Quality Comparison

When you compare lcd vs led, you quickly notice that image quality stands out as a major difference. The way each display handles brightness, contrast, color, and viewing angles shapes your experience, whether you use a monitor for work, gaming, or entertainment.
Brightness and Contrast
Black Levels and Local Dimming
You want deep blacks and strong contrast for a clearer image and a more immersive picture. LCD monitors use a backlight that shines through liquid crystals. This design makes it hard for lcd displays to achieve true black levels. Light often leaks through, causing blacks to appear grayish, especially in dark scenes.
LED monitors, especially those with full-array or direct-lit backlighting, use local dimming. This feature lets the display dim specific zones behind dark areas of the picture. You get deeper blacks and higher contrast, which improves picture quality in movies and games. Edge-lit led displays offer some dimming, but not as precise as full-array models.
Note: If you watch movies in a dark room, led monitors with local dimming provide a noticeable improvement in black levels and overall quality.
Performance in Bright Rooms
Ambient light can wash out the picture on many displays. LCD monitors often struggle in bright rooms because their backlights cannot reach high brightness levels. LED displays, on the other hand, excel in these conditions. The light-emitting diodes produce higher peak brightness, making the picture stand out even in sunlit spaces. You see more detail and color, and reflections become less distracting.
Color Accuracy and Vibrancy
Color Gamut Differences
Color accuracy matters when you want lifelike images. LCD displays use liquid crystal pixels with backlighting, which limits how precisely they can reproduce colors. LED displays, especially those with advanced backlighting like quantum dot or high color saturation technology, deliver better color accuracy and sharper images.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Display Type | Color Accuracy | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| LCD | Lower | Uses liquid crystal pixels that are backlit, leading to less precise color representation. |
| LED | Higher | Utilizes light-emitting diodes for better color accuracy and sharper images. |
You also find differences in color gamut, which measures how many colors a display can show. Most TVs and monitors cover about 68% to 72% of the NTSC color gamut. Displays with a color gamut above 92% are considered wide color gamut (WCG) and deliver more vibrant, lifelike colors. Technologies like quantum dot QLED and OLED help led monitors reach these high percentages.
- The NTSC color gamut for typical TVs ranges from approximately 68% to 72%.
- A TV with an NTSC color gamut exceeding 92% is classified as a high color saturation/wide color gamut (WCG) TV.
- Technologies such as quantum dot QLED, OLED, or high color saturation backlighting are often used to achieve these high color gamut percentages.
- Rec.2020 > NTSC > Adobe RGB > DCI-P3 > Rec.709/sRGB
If you value a display that shows a wider range of colors, led monitors with advanced backlighting offer a clear advantage.
Suitability for Photo and Video Editing
When you edit photos or videos, you need a monitor that shows colors accurately. LED displays, especially those with IPS panels, provide better color consistency and vibrancy. You see subtle differences in shades and tones, which helps you make precise adjustments. LCD monitors with TN panels may fall short in this area, as their color reproduction is less accurate. For creative professionals, led monitors with wide color gamut support are the preferred choice.
Viewing Angles
Consistency Across the Screen
Viewing angles affect how the picture looks when you move to the side of the display. LCD monitors, especially those with TN panels, lose color accuracy and contrast at sharp angles. You might notice the picture looks washed out or colors shift when you view the monitor from the side.
LED displays with IPS technology maintain color accuracy and brightness from almost any angle. This feature makes them ideal for group settings or creative work where you need a consistent picture across the screen.
Here’s a summary of how different displays perform:
| Display Type | Viewing Angle Characteristics |
|---|---|
| LCD | Reduced color accuracy and contrast at acute angles. |
| LED (IPS) | Better viewing angles with maintained color accuracy and brightness. |
| OLED | Almost perfect viewing angles due to self-emissive nature. |
| TN (LCD) | Narrower viewing angles with color shifts and reduced contrast. |
| VA (LED) | Intermediate viewing angles between IPS and TN. |
- IPS panels provide the best viewing angles, maintaining color accuracy and brightness from almost any angle.
- TN panels have narrower viewing angles, leading to color shifts and reduced contrast when viewed from the side.
- VA panels offer a middle ground in terms of viewing angles.
If you often share your screen or move around your workspace, led monitors with IPS panels deliver a clearer image and consistent picture quality.
LCD vs LED: Energy Efficiency and Lifespan
Power Consumption
Energy Use in LCD Displays
You often look for a monitor that balances performance with low energy use. LCD monitors use a backlight, usually LED-based in modern models, to illuminate the screen. The power consumption of these displays depends on size and technology. For example, a 24-inch LCD monitor with LED backlighting typically uses between 20 and 30 watts per square meter. Larger commercial LCD displays may require 100 to 150 watts per square meter.
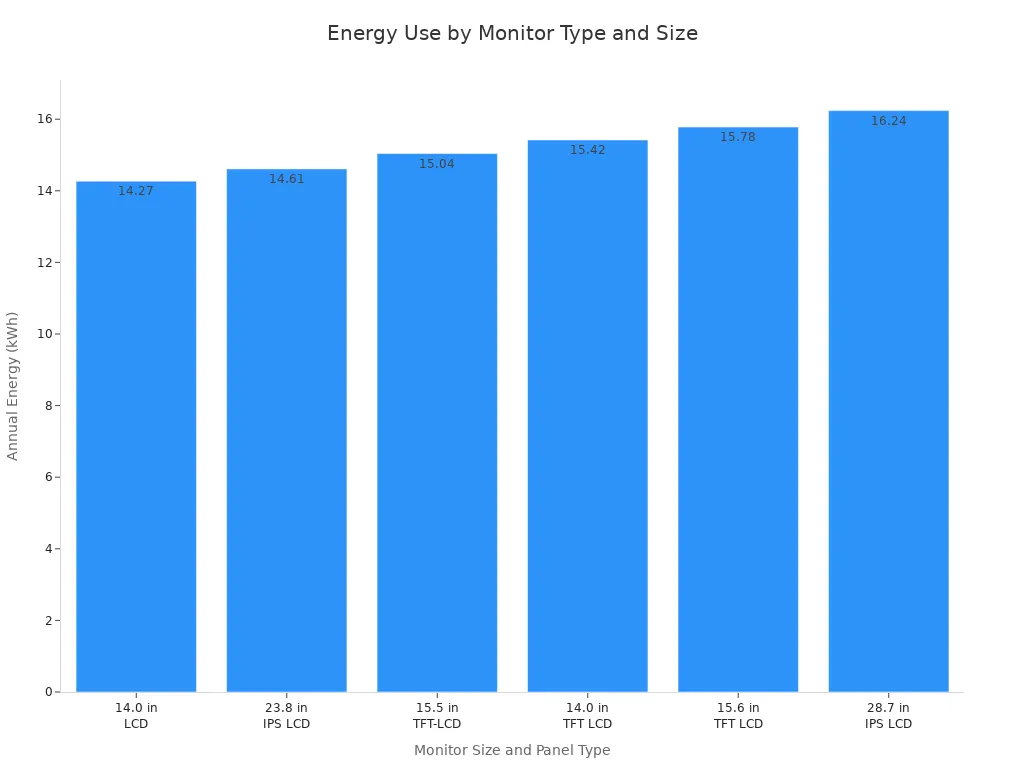
You can see how different LCD panel types and sizes compare in energy use:
| Monitor Size | Panel Type | On Mode Power (watts) | Sleep Mode Power (watts) | Total Energy Consumption (kWh/yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.0 Inches | LCD | 3.78 | 0.47 | 14.27 |
| 23.8 Inches | IPS LCD | 4.25 | 0.28 | 14.61 |
| 15.5 Inches | TFT-LCD | 4.35 | 0.19 | 15.04 |
| 28.7 Inches | IPS LCD | 16.24 | 0.18 | 16.24 |
Tip: Choosing an LCD monitor with an Energy Star rating helps you reduce electricity costs over time.
Energy Use in LED Displays
LED displays stand out for their energy efficiency, especially in larger formats. You find that high-resolution indoor LED displays use about 200 to 300 watts per square meter. Outdoor LED billboards can consume between 300 and 400 watts per square meter, but they deliver much higher brightness. For smaller LED monitors, the power draw remains competitive with LCDs, often matching or slightly exceeding them depending on brightness settings.
Here’s a quick comparison of power consumption by display type and use case:
| Display Type | Power Consumption (W/m²) | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| LED | 100 – 1,000 | LED billboard (300-400 W/m²) |
| 200 – 300 | High-resolution indoor display | |
| LCD | 20 – 30 | 24-inch LED-backlit monitor |
| 100 – 150 | Larger commercial display |
You can visualize annual energy consumption for different monitors in the chart below:
Lifespan and Durability
Burn-in and Image Retention
You want your display to last as long as possible without losing quality. LCD monitors rarely suffer from burn-in or permanent image retention. The liquid crystal technology prevents static images from causing long-term damage. LED monitors, especially those using direct-emitting LEDs, also resist burn-in. OLED displays, which use organic materials, can experience burn-in, but this issue does not affect traditional LED or LCD monitors.
Maintenance and Reliability
You benefit from the long lifespan of LED technology. Direct-emitting LED displays can last up to 100,000 hours under optimal conditions. LED backlights in LCD monitors typically last between 30,000 and 100,000 hours, depending on usage and quality. Traditional LCD displays, which rely on external light sources, generally have a shorter lifespan than LED displays.
| Display Type | Typical Lifespan (Hours) | Key Durability Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-emitting LED | Up to 100,000 | Longer absolute lifespans, lower degradation rates |
| LED Backlights | 30,000 – 100,000 | Consistent performance, minimal maintenance |
| Traditional LCD | Varies (shorter) | Lifespan depends on backlight quality and usage |
You will notice the advantages of LED technology in both durability and reliability. LED monitors require less maintenance and experience lower failure rates over time. This makes them a smart investment for anyone seeking a long-lasting, high-quality display.
LCD vs LED: Price and Value
Upfront Cost Comparison
Entry-Level Models
When you shop for your first monitor, you often notice that lcd models come with a lower price tag. Manufacturers use simpler technology in lcd displays, which keeps production costs down. This makes lcd monitors a popular choice for students, small offices, and anyone with strict budget considerations. You can expect to pay less for an entry-level lcd display than for a comparable led model.
- LCD displays have a lower initial cost compared to LED displays, making them more budget-friendly.
- LED displays are more expensive upfront but offer better performance, energy efficiency, and longer lifespans, providing greater long-term value.
Premium Models
If you want advanced features or superior image quality, you will see a bigger price gap between lcd and led monitors. Premium led displays use advanced semiconductor technology, which increases production costs. These monitors often include features like higher refresh rates, better color accuracy, and enhanced brightness. You pay more for these benefits, but you also get a display that excels in demanding environments.
- LED displays are initially more costly than LCDs due to advanced features and superior picture quality.
- The production of LED screens involves advanced semiconductor technology, which is more complex and leads to higher production costs.
Note: If you prioritize top-tier performance or plan to use your monitor for creative work or gaming, investing in a premium led model can be worthwhile.
Long-Term Value
Cost of Ownership
You should consider more than just the sticker price when comparing lcd vs led. Over time, led monitors often save you money through lower energy consumption and reduced maintenance needs. For example, annual maintenance costs for owned led screens range from $500 to $1,200. Color calibration costs for owned displays average $1.11 per square foot per month. While these costs may seem high, led technology typically requires less frequent repairs and offers a longer lifespan, which can offset the initial investment.
Resale and Upgrade Considerations
When you decide to upgrade your display, led monitors usually retain more value. The longer lifespan and higher demand for led technology make these monitors easier to resell. LCD monitors, while affordable at first, tend to depreciate faster as newer, more efficient models enter the market. If you plan to upgrade regularly, choosing an led display can help you recover more of your initial investment.
Tip: Weigh both the upfront price and the total cost of ownership to find the best value for your needs.
LCD vs LED: Eye Comfort and Health
Blue Light and Eye Strain
You spend hours each day in front of screens, so eye comfort becomes a top priority. Both lcd and led technologies emit blue light, which can contribute to digital eye strain and disrupt your sleep cycle. Blue light exposure, especially in the evening, can suppress melatonin production and make it harder for you to fall asleep.
Recent studies show that lcd screens emit higher levels of blue light compared to newer display technologies. The table below highlights the differences in blue light emission:
| Display Type | Blue Light Emission Level |
|---|---|
| LCD | High |
| OLED | Low |
- LCDs emit about twice as much blue light as OLEDs.
- Higher blue light levels from lcds can disrupt melatonin secretion.
- OLEDs are certified for lower blue light emissions.
If you use your display for long periods, you may notice symptoms like eyestrain, headaches, or blurred vision. Clinical trials have found that up to 90% of users experience visual symptoms after extended use of laptops and computers. In comparison studies, devices like iPads, which use lcd technology, led to higher pain scores and more frequent complaints of blurred vision than traditional computers.
Flicker and Comfort Features
Flicker is another factor that affects your eye comfort. Many lcd and led monitors use pulse width modulation (PWM) to control brightness. This method can cause subtle flickering, which may not be visible but can still lead to eye fatigue over time. Some modern displays include flicker-free technology, which helps reduce this effect and makes viewing more comfortable.
You can look for comfort features such as:
- Flicker-free backlighting
- Adjustable brightness and color temperature
- Built-in blue light filters or “night mode” settings
Tip: Choosing a monitor with flicker-free certification and blue light reduction features can help you work or study longer without discomfort.
Reducing Eye Fatigue
You can take several steps to minimize eye fatigue when using lcd or led displays:
- Adjust the brightness and contrast to match your environment.
- Enable blue light reduction modes, especially in the evening.
- Take regular breaks using the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
- Position your display at eye level and about an arm’s length away.
- Use ambient lighting to reduce glare and reflections.
If you follow these practices, you can reduce the risk of digital eye strain and protect your vision during long sessions at your desk.
LCD vs LED: Best Uses and Recommendations
Gaming
Response Time and Refresh Rate
When you choose a gaming monitor, you want fast response times and high refresh rates. These features help you enjoy smoother motion and sharper visuals during intense gaming sessions. The table below shows the recommended values for top-tier performance:
| Metric | Recommended Value | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Refresh Rate | 144Hz or higher | Provides smoother motion and reduces blurring in fast-paced games. |
| Response Time | 1ms or lower | Minimizes ghosting effects, ensuring sharp and clear transitions in visuals. |
You will find that both lcd and led monitors can meet these benchmarks, but led models often deliver better consistency at higher refresh rates. If you play competitive games, you should prioritize these specifications.
Input Lag and Motion Handling
You want low input lag for responsive controls. Higher refresh rates lead to lower input lag, so a 120Hz display has half the input lag of a 60Hz model. Most new high refresh rate monitors offer imperceptible input lag, which is ideal for gaming. TVs usually have higher input lag than monitors, but you can reduce this by enabling ‘Game Mode’ to bypass extra image processing.
- Higher refresh rates lead to lower input lag.
- A 120Hz display has half the input lag of a 60Hz display.
- New high refresh rate monitors generally have imperceptible input lag.
- TVs typically have higher input lag than monitors, so a TV with a native refresh rate of at least 120Hz is recommended.
- Enabling ‘Game Mode’ on TVs reduces input lag by bypassing image post-processing.
For motion handling, lcd and led displays have improved, but they still trail behind older CRT and plasma screens. Movements at 60fps appear less clear on modern displays compared to CRTs. However, for most gamers, the difference is minor, especially with high refresh rate led monitors. If you compare lcd vs led for gaming, led displays often provide a more immersive experience.
Office and Productivity
Text Clarity and Multitasking
You spend hours reading text and working with documents. Both lcd and led monitors offer sharp text, but led models with IPS panels provide better clarity and color consistency. Many professionals prefer dual monitors for multitasking. Studies show that dual monitors align with user preferences and can boost task efficiency. However, using multiple monitors may lead to nonneutral neck postures, so you should adjust your setup for comfort.
| Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
| Strong Evidence | Dual monitors align with user preferences. |
| Moderate Evidence | Multiple monitors may enhance task efficiency but can lead to nonneutral neck postures. |
Ergonomics and Eye Comfort
You should position your monitor at eye level and use adjustable stands to reduce strain. Features like flicker-free backlighting and blue light filters, common in modern led displays, help protect your eyes during long work sessions. If you work with spreadsheets or code, a larger screen or dual monitor setup can improve productivity.
Tip: Take regular breaks and adjust your monitor settings to reduce eye fatigue.
Creative Work
Color Accuracy for Designers
If you work in design or photography, you need accurate color reproduction. The table below compares lcd and led displays for creative tasks:
| Feature | LCD (CCFL) | LED |
|---|---|---|
| Color Consistency | Fairly consistent among manufacturers | Newer technology, less consistent |
| Calibration Challenges | Standard measurement devices work well | Some devices struggle with calibration |
| Backlighting Technology | CCFL backlighting | LED backlighting |
| Color Management Solutions | Established solutions available | May require advanced tools |
| Price Range for High-End | Prices have dropped recently | Higher quality available |
You will find that lcd monitors with CCFL backlighting offer consistent color, but led displays provide higher brightness and a wider color gamut. Some led monitors may require advanced calibration tools, so you should check compatibility with your workflow.
Video Editing and Media Creation
For video editing, you want a display that shows accurate colors and smooth gradients. High-end led monitors excel in brightness and color range, making them suitable for media creation. If you need established color management solutions, lcd monitors remain a reliable choice. You should select a monitor that matches your software and calibration tools for the best results.
Home Entertainment
Movie Watching Experience
You want a display that transforms your living room into a personal theater. LED monitors and TVs deliver a superior movie watching experience because they produce brighter images and deeper blacks. You notice richer contrast, especially in scenes with both shadows and highlights. Full-array LED backlighting with local dimming enhances this effect, making dark scenes more immersive. LCD screens, especially those with older CCFL backlights, struggle to achieve the same depth in black levels. You may see grayish tones instead of true black, which reduces the cinematic impact.
Color accuracy plays a key role in movie enjoyment. LED displays with advanced technologies, such as quantum dot or OLED panels, offer a wider color gamut. You see vibrant colors that closely match the director’s intent. LCD panels, particularly TN types, often show less accurate colors and narrower viewing angles. If you watch movies with friends or family, LED screens with IPS panels maintain consistent color and brightness from almost any seat in the room.
Consider the following comparison:
| Feature | LCD (CCFL/Basic LED) | LED (Full-array/OLED) |
|---|---|---|
| Black Levels | Moderate | Deep, true blacks |
| Color Vibrancy | Fair | Excellent |
| Viewing Angles | Limited | Wide |
| Brightness | Adequate | High |
Tip: For the best movie experience, choose an LED TV with local dimming and wide color gamut support.
Streaming and Smart Features
You rely on streaming platforms for entertainment. Modern LED TVs and monitors integrate smart features that make streaming easy. You access apps like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ directly from the display. LED models often include faster processors and more memory, which improves app performance and reduces lag. LCD TVs with basic smart features may load apps slower and offer fewer updates.
LED displays support higher resolutions, such as 4K and even 8K. You enjoy crisp visuals and smooth playback, especially when streaming high-definition content. Many LED TVs feature advanced upscaling technology, which enhances lower-resolution videos for a sharper look. LCD screens can struggle with upscaling, resulting in softer images.
You benefit from additional smart features on LED TVs:
- Voice control for hands-free navigation
- Screen mirroring from smartphones and tablets
- Automatic updates for new streaming apps
- Energy-saving modes for lower power consumption
Note: If you want seamless streaming and future-proof technology, LED TVs provide a smarter investment for home entertainment.
You enhance your movie nights and streaming sessions by choosing a display that matches your viewing habits. LED technology leads in image quality, smart features, and overall user experience, making it the preferred choice for most home entertainment setups.
LCD vs LED: Pros and Cons
When you explore the lcd vs led debate, you see that each technology brings unique strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these can help you make a smarter choice for your needs. The following breakdown highlights the main points you should consider.
LCD Pros and Cons
You find lcd displays in many homes and offices. Their popularity comes from a balance of performance, cost, and reliability. The debate often centers on how these displays perform in real-world scenarios.
| Advantages of LCD Displays | Disadvantages of LCD Displays |
|---|---|
| Low power consumption | Slower response speed |
| High resolution | Lower contrast ratio |
| Excellent color performance | Viewing angle dependence |
| Wide viewing angle | Poor black level performance |
| Slim and lightweight design | Sensitive to temperature |
| Long lifespan | Higher production cost |
| No harmful radiation | Backlight bleeding |
You benefit from low energy bills and a slim profile when you choose lcd. High resolution and color performance make these displays suitable for daily tasks and creative work. The debate often points out that lcd screens can struggle with deep blacks and contrast, especially in dark rooms. Viewing angles may also shift colors, depending on the panel type. Backlight bleeding and temperature sensitivity can affect performance in some environments.
Tip: If you want a display that balances cost, energy use, and color accuracy, lcd remains a solid option in the ongoing debate.
LED Pros and Cons
The led debate focuses on brightness, durability, and adaptability. You see led displays in both indoor and outdoor settings, from living rooms to digital billboards.
| Advantages of LED Displays | Disadvantages of LED Displays |
|---|---|
| No seams (ideal for large screens) | Lower resolution in some models |
| Waterproof and sunscreen features | Lower contrast in certain setups |
| High brightness and adjustable | Higher after-sales service rate |
| Requires auxiliary heat dissipation |
You gain high brightness and weather resistance with led, making them perfect for outdoor use. Seamless design allows for large, immersive screens. The debate highlights that some led models may offer lower resolution or contrast compared to premium lcds. You may also need to consider heat management and potential service needs over time.
Note: If you need a display for bright or outdoor environments, led technology often leads the debate with its adaptability and robust features.
The lcd vs led debate continues as both technologies evolve. You should weigh the pros and cons based on your priorities, whether you value energy efficiency, image quality, or durability. This approach ensures you make an informed decision in the ongoing debate.
When you compare lcd vs led, you see that LED displays deliver superior image quality, durability, and energy efficiency, making them the smarter buy for most users. LCD displays remain a practical choice if you prioritize affordability or need a solution for short-term use. Your ideal display depends on your specific needs, such as viewing environment and long-term value.
| Consideration | Choose LCD | Choose LED |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | Limited | Flexible |
| Usage Duration | Short-term | Long-term |
| Image Quality | Good | Excellent |
| Maintenance | More frequent | Minimal |
- Ask yourself: lcd vs led which is better for your space, budget, and viewing habits?
- Review your priorities before making a final decision.
FAQ
What is the main difference between LCD and LED displays?
You see the main difference in the backlighting. LCDs use fluorescent or LED backlights, while LED displays use light-emitting diodes for illumination. This change improves brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency.
Are LED displays always better than LCDs?
You get better image quality and efficiency with LED displays in most cases. However, LCDs offer lower upfront costs. If you have a tight budget or need a basic monitor, LCDs remain a practical choice.
Do LED monitors last longer than LCD monitors?
You benefit from a longer lifespan with LED monitors. Most LED displays last up to 50,000 hours or more, while traditional LCDs usually last around 30,000 hours.
Which display type is better for eye comfort?
You experience less eye strain with LED monitors that feature flicker-free technology and blue light filters. Both LCD and LED screens emit blue light, but modern LED displays often include more comfort features.
Can I use an LED TV as a computer monitor?
You can use an LED TV as a monitor if it supports the right input (HDMI or DisplayPort). You may notice higher input lag and less sharp text compared to dedicated monitors.
Are LED displays more energy efficient than LCDs?
You save more energy with LED displays. LEDs use less power to produce brighter images, which lowers your electricity bills over time.
What should I consider when choosing between LCD and LED?
You should consider your budget, usage duration, image quality needs, and maintenance preferences. LED displays suit long-term, high-performance use. LCDs fit short-term or budget-focused needs.
Tip: Always check for features like refresh rate, color accuracy, and eye comfort before making your final choice.


